CH 908: Mass Spectrometry Lecture 8 Tandem mass spectrometry
... Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (TOF-MS) •Separates ions based on flight time High resolution isolation requires very stable high voltage power supplies for the source, high timing accuracy and rapid response in the TIS (picoseconds) Usually limited to an isolation resolving power of 102. Usually ...
... Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (TOF-MS) •Separates ions based on flight time High resolution isolation requires very stable high voltage power supplies for the source, high timing accuracy and rapid response in the TIS (picoseconds) Usually limited to an isolation resolving power of 102. Usually ...
Photoluminescence
... LEDs. Optical absorption can take place on the already discussed impurities (optical centers), being either the activator ions or the sensitizer ions. Sensitizer ions are used when the optical absorption of the activator ions is too weak (e.g., because the optical transition is forbidden) to be usef ...
... LEDs. Optical absorption can take place on the already discussed impurities (optical centers), being either the activator ions or the sensitizer ions. Sensitizer ions are used when the optical absorption of the activator ions is too weak (e.g., because the optical transition is forbidden) to be usef ...
Chapter 13 NUCLEAR FUSION
... exclusively, of water molecules which include deuterons rather than protons and I do know that heavy water is manufactured as a byproduct of electrolysis of normal water. I also know that Fleischmann and Pons in the experiments by which they discovered cold fusion, used electrolysis to inject deuter ...
... exclusively, of water molecules which include deuterons rather than protons and I do know that heavy water is manufactured as a byproduct of electrolysis of normal water. I also know that Fleischmann and Pons in the experiments by which they discovered cold fusion, used electrolysis to inject deuter ...
[Problems] Walker, Physics, 3 Edition Chapter 30 Conceptual
... the incident direction does the scattered X-ray move? 44. •• The maximum Compton shift in wavelength occurs when a photon is scattered through 180°. What scattering angle will produce a wavelength shift of one-fourth the maximum? 45. •• IP Consider two different photons that scatter through an angle ...
... the incident direction does the scattered X-ray move? 44. •• The maximum Compton shift in wavelength occurs when a photon is scattered through 180°. What scattering angle will produce a wavelength shift of one-fourth the maximum? 45. •• IP Consider two different photons that scatter through an angle ...
work done by the electric force
... battery and then is disconnected from the battery. When this capacitor (C1) is connected to a second, uncharged capacitor (C2), the voltage on the first drops to 15 V. What is the value of C2? (Charge is ...
... battery and then is disconnected from the battery. When this capacitor (C1) is connected to a second, uncharged capacitor (C2), the voltage on the first drops to 15 V. What is the value of C2? (Charge is ...
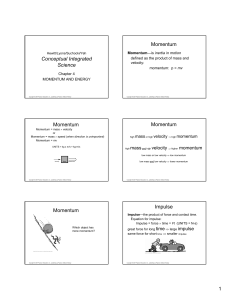
Conceptual Integrated Science Momentum Momentum Momentum
... Work is defined as the product of force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves (in the same direction as the force). Work is done only when a force succeeds in displacing the body it acts upon. ...
... Work is defined as the product of force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves (in the same direction as the force). Work is done only when a force succeeds in displacing the body it acts upon. ...
Chapter 19
... The latent heat of vaporization is relevant for evaporation as well as boiling. The heat of vaporization of water rises slightly as the temperature decreases. On a molecular level, the heat added during a change of state does not go to increasing the kinetic energy of individual molecules, but rathe ...
... The latent heat of vaporization is relevant for evaporation as well as boiling. The heat of vaporization of water rises slightly as the temperature decreases. On a molecular level, the heat added during a change of state does not go to increasing the kinetic energy of individual molecules, but rathe ...
(B): Physics in Context
... 2 (a) (ii) The diagram shows the path of electrons that are moving at a speed of 4.5 × 107 m s–1 . Calculate the accelerating potential difference between the cathode and anode in the electron gun that is required to produce electrons travelling at this speed. Assume that the electrons have zero vel ...
... 2 (a) (ii) The diagram shows the path of electrons that are moving at a speed of 4.5 × 107 m s–1 . Calculate the accelerating potential difference between the cathode and anode in the electron gun that is required to produce electrons travelling at this speed. Assume that the electrons have zero vel ...
Paper 1
... some time, the ball falls to the ground and bounces back to the same height from which it was projected. Ignore friction and assume that there is a negligible time lapse during the collision of the ball with the ground. Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT position-time graph for the motion of ...
... some time, the ball falls to the ground and bounces back to the same height from which it was projected. Ignore friction and assume that there is a negligible time lapse during the collision of the ball with the ground. Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT position-time graph for the motion of ...
Dr. Harold Aspden
... commercial scale from fusion reactors by processes replicating what they believe sustains the Sun's heat output as hydrogen is transmuted into different atomic forms. In contrast with this rather elusive objective, it having proved beyond reach even after half a century of effort, this invention is ...
... commercial scale from fusion reactors by processes replicating what they believe sustains the Sun's heat output as hydrogen is transmuted into different atomic forms. In contrast with this rather elusive objective, it having proved beyond reach even after half a century of effort, this invention is ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.


![[Problems] Walker, Physics, 3 Edition Chapter 30 Conceptual](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003654150_1-a027177e4c01d920fe185cf8e7bbe456-300x300.png)
![Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930185_1-59cc607a5cbfa43d1c480bd3c23f15ec-300x300.png)