... very close. This behavior is kept for structures W2 and W3 considered below. The optical absorption results for the W2-DQW are shown in Fig. 2. Comparing with Fig. 1 it is seen that the absorption edge is also a function of the DQW dimensions since this leads to different values for the maximum bind ...
6.9C Energy Transformations
... electrons (-). If the charges are not moving, we call it static electricity (potential energy). Examples of static electrical energy are the charge a person picks up when walking across carpet, charges in a cloud just before a lightning discharge, and the charge stored in a capacitor in an electrica ...
... electrons (-). If the charges are not moving, we call it static electricity (potential energy). Examples of static electrical energy are the charge a person picks up when walking across carpet, charges in a cloud just before a lightning discharge, and the charge stored in a capacitor in an electrica ...
Chapter 16
... potential due to q1 at some point P The work required to bring q2 from infinity to P without acceleration is q2V1 This work is equal to the potential energy of the two particle system ...
... potential due to q1 at some point P The work required to bring q2 from infinity to P without acceleration is q2V1 This work is equal to the potential energy of the two particle system ...
Design of an efficient energy harvester
... a coil can be allowed to oscillate in a magnetic field or a magnet can be used to oscillate inside a coil. In general the coil travels through a varying amount of magnetic flux so it inducing voltage according to Faraday's law. This produces a voltage which is very small (~0.1V) and varying, thus an ...
... a coil can be allowed to oscillate in a magnetic field or a magnet can be used to oscillate inside a coil. In general the coil travels through a varying amount of magnetic flux so it inducing voltage according to Faraday's law. This produces a voltage which is very small (~0.1V) and varying, thus an ...
physics
... Amongst the early scientists, heat was thought as some kind of invisible, massless fluid called ‘caloric’. Certain objects that released heat upon combustion were thought to be able to ‘store’ the fluid. However, this explanation failed to explain why friction was able to produce heat. In the 1840s, ...
... Amongst the early scientists, heat was thought as some kind of invisible, massless fluid called ‘caloric’. Certain objects that released heat upon combustion were thought to be able to ‘store’ the fluid. However, this explanation failed to explain why friction was able to produce heat. In the 1840s, ...
Mass Spectrometry 1
... Flight tube A field free region where ions drift at a velocity inversely proportional to the square root of their mass/charge. Linear Detector Measures the ion abundance in linear mode (no reflector used) and sends a signal to the digitizer. ...
... Flight tube A field free region where ions drift at a velocity inversely proportional to the square root of their mass/charge. Linear Detector Measures the ion abundance in linear mode (no reflector used) and sends a signal to the digitizer. ...
Unit 10 Exam - Sharp Honors Chemistry Multiple Choice Identify the
... temperature change better than wood. d. the mass of steel is less than wood, so it loses heat faster. e. Two of the above statements are true. ...
... temperature change better than wood. d. the mass of steel is less than wood, so it loses heat faster. e. Two of the above statements are true. ...
Topic 1: Math and Measurement Review
... b- The force that opposes the sliding of one object over another c- The force of kinetic friction is less than the force of static friction iIt is easier to keep an object moving than to start it C- What does the force of friction depend on? 1- The force pushing the surfaces together ( ) 2- The coef ...
... b- The force that opposes the sliding of one object over another c- The force of kinetic friction is less than the force of static friction iIt is easier to keep an object moving than to start it C- What does the force of friction depend on? 1- The force pushing the surfaces together ( ) 2- The coef ...
Document
... where q i exp(-i) is the molecular partition function. The second equality is satisfied because the molecules are independent of each other. The above equation applies only to molecules that are distinguishable, for instance, localized molecules. However, if the molecules are identical and free ...
... where q i exp(-i) is the molecular partition function. The second equality is satisfied because the molecules are independent of each other. The above equation applies only to molecules that are distinguishable, for instance, localized molecules. However, if the molecules are identical and free ...
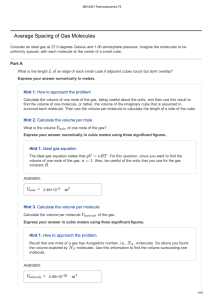
Average Spacing of Gas Molecules
... ± Gas Scaling When doing numerical calculations involving temperature, you need to pay particular attention to the temperature scale you are using. In general, you should use the Kelvin scale (for which T = 0 represents absolute zero) in such calculations. This is because the standard thermodynamic ...
... ± Gas Scaling When doing numerical calculations involving temperature, you need to pay particular attention to the temperature scale you are using. In general, you should use the Kelvin scale (for which T = 0 represents absolute zero) in such calculations. This is because the standard thermodynamic ...
Structure of Thrmodynamics
... Some non equilibrium states can be made stable by eliminating some of the allowed stated, while retaining others. This can be achieved by altering passive resistances and constraints. A state made stable by altering passive resistances and/or constraints is called a quasi-stable state. The stable st ...
... Some non equilibrium states can be made stable by eliminating some of the allowed stated, while retaining others. This can be achieved by altering passive resistances and constraints. A state made stable by altering passive resistances and/or constraints is called a quasi-stable state. The stable st ...
Chapter 5 Introduction to Order-Disorder Transitions
... A microscopic approach by crystal chemistry can provide a basis for the classification of the phase transitions [118]. If a solid undergoes a phase transition at a critical temperature Tc by absorbing thermal energy, the transformed phase possesses higher internal energy, the bonding between neighbo ...
... A microscopic approach by crystal chemistry can provide a basis for the classification of the phase transitions [118]. If a solid undergoes a phase transition at a critical temperature Tc by absorbing thermal energy, the transformed phase possesses higher internal energy, the bonding between neighbo ...
Inductance
... Use emf and current when they are caused by batteries or other sources Use induced emf and induced current when they are caused by changing magnetic fields When dealing with problems in electromagnetism, it is important to distinguish between the two situations ...
... Use emf and current when they are caused by batteries or other sources Use induced emf and induced current when they are caused by changing magnetic fields When dealing with problems in electromagnetism, it is important to distinguish between the two situations ...
Chapter 4: Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... One kilogram of water is contained in a piston-cylinder device at 100 C. The piston rests on lower stops such that the volume occupied by the water is 0.835 m3. The cylinder is fitted with an upper set of stops. When the piston rests against the upper stops, the volume enclosed by the piston-cylind ...
... One kilogram of water is contained in a piston-cylinder device at 100 C. The piston rests on lower stops such that the volume occupied by the water is 0.835 m3. The cylinder is fitted with an upper set of stops. When the piston rests against the upper stops, the volume enclosed by the piston-cylind ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.