CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum Theory
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
ICSE Physics - Direction Classes
... Renewable energy: biogas, solar energy, wind energy, energy from falling of water, run-of-the river schemes, energy from waste, tidal energy, etc. Issues of economic viability and ability to meet demands. Non-renewable energy - coal, oil, natural gas. Inequitable use of ...
... Renewable energy: biogas, solar energy, wind energy, energy from falling of water, run-of-the river schemes, energy from waste, tidal energy, etc. Issues of economic viability and ability to meet demands. Non-renewable energy - coal, oil, natural gas. Inequitable use of ...
Conservation of Energy Melissa Stumbaugh Andrew Raymond
... against kinetic energy and resulted again in a positive linear relationship. The slope for this graph was found to be 0.9543. Using this experimental slope, and the theoretical slope which is 1 we are able to find the percent discrepancy, which is 4.57%. If we had been taking mass into account in th ...
... against kinetic energy and resulted again in a positive linear relationship. The slope for this graph was found to be 0.9543. Using this experimental slope, and the theoretical slope which is 1 we are able to find the percent discrepancy, which is 4.57%. If we had been taking mass into account in th ...
Energy Intro
... A Newton meter is the energy needed to move a 148 weight of 1 Newton over a distance of 1 meter. A Newton meter is also called a Joule (J). Question: The gymnast on the balance beam in the picture weighs 360 Newtons. If the balance beam is 1.2 meters above the ground, what is the gymnast’s gravitati ...
... A Newton meter is the energy needed to move a 148 weight of 1 Newton over a distance of 1 meter. A Newton meter is also called a Joule (J). Question: The gymnast on the balance beam in the picture weighs 360 Newtons. If the balance beam is 1.2 meters above the ground, what is the gymnast’s gravitati ...
Physics Qualifying Examination – Part I 7-Minute Questions February 7, 2015
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
Lesson 1 Energy - Tony Ford Science
... 2. Where do we get it from? 3. What do we use it for? 4. Can it be stored? 5. What happens to it after we use it? Energy itself is hard to de1ine but we all need it. It comes from matter but it is not matter. A famous equation (E = mc2) represents the conversion of matter to energy in the ...
... 2. Where do we get it from? 3. What do we use it for? 4. Can it be stored? 5. What happens to it after we use it? Energy itself is hard to de1ine but we all need it. It comes from matter but it is not matter. A famous equation (E = mc2) represents the conversion of matter to energy in the ...
Phy107Fall06Lect08
... Water is pumped into tower when electricity cost is low Electrical energy transformed into potential energy. Work is extracted when needed to transport the water to homes. ...
... Water is pumped into tower when electricity cost is low Electrical energy transformed into potential energy. Work is extracted when needed to transport the water to homes. ...
electrical potential_ppt6mrwilson_azedit
... When released, this energy is transferred to the pile below. ...
... When released, this energy is transferred to the pile below. ...
SCH 303: THERMODYNAMICS II AND PHASE EQUILIBRIA Course
... To define systems properties such as U, H, S as path dependent or exact differentials and the consequences. To give thermodynamic determinants of spontaneous process To evaluate the entropy of systems under different conditions To define the Gibbs and Helmhotz free energies and establish their impor ...
... To define systems properties such as U, H, S as path dependent or exact differentials and the consequences. To give thermodynamic determinants of spontaneous process To evaluate the entropy of systems under different conditions To define the Gibbs and Helmhotz free energies and establish their impor ...
FREE ELECTRON THEORY - West Virginia University
... favored as they travel past the Schottky barrier due to the external magnetic field and spin filtering in the CoFe. They then fall into the quantum well and recombine with holes. Emission from the quantum well gives a good probe of spin. ...
... favored as they travel past the Schottky barrier due to the external magnetic field and spin filtering in the CoFe. They then fall into the quantum well and recombine with holes. Emission from the quantum well gives a good probe of spin. ...
forces
... Pedro has three balls of different masses. He rolls each ball down a ramp hitting an empty box at the bottom of the ramp. A. Identify which ball will push the box the farthest distance. B. Using your science vocabulary, explain why the ball you chose in part A will push the box the farthest distanc ...
... Pedro has three balls of different masses. He rolls each ball down a ramp hitting an empty box at the bottom of the ramp. A. Identify which ball will push the box the farthest distance. B. Using your science vocabulary, explain why the ball you chose in part A will push the box the farthest distanc ...
here
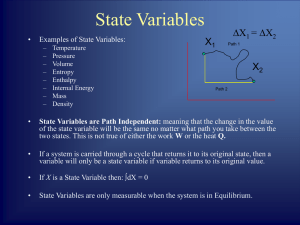
... • Every thermodynamic system in an equilibrium state possesses a state variable called the internal energy U whose change in a differential process is given by ...
... • Every thermodynamic system in an equilibrium state possesses a state variable called the internal energy U whose change in a differential process is given by ...
Energy Notes
... • A quantity of water is heated from 25.0ºC to 36.4ºC by absorbing 325 calories. What is the mass of the water? • What is the mass of a piece of ...
... • A quantity of water is heated from 25.0ºC to 36.4ºC by absorbing 325 calories. What is the mass of the water? • What is the mass of a piece of ...
TR-3
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
... Classical theory predicts that the total amount of energy in a light wave increases as the light intensity increases. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends on the value of the light frequency f and not on the intensity. The existence of a threshold frequency is completely inexplic ...
Energy
... An astronaut sets up a pendulum on the moon, where gravity is 1.6 m/s2. If the pendulum is 1 meter long, what will the period of the pendulum be? ...
... An astronaut sets up a pendulum on the moon, where gravity is 1.6 m/s2. If the pendulum is 1 meter long, what will the period of the pendulum be? ...
E142: Ammonia molecule
... (2) Assume that in t = 0 the molecule is found to be at the first state. What is the probability P (t) that the molecule is found at the second state after time t? Now, assume that each state of the molecule has electric dipole moment µ. When the molecule is inserted into electric field E, the geome ...
... (2) Assume that in t = 0 the molecule is found to be at the first state. What is the probability P (t) that the molecule is found at the second state after time t? Now, assume that each state of the molecule has electric dipole moment µ. When the molecule is inserted into electric field E, the geome ...
Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology 6 Major Forms
... Exhaustible means the something can run out, or is limited. Inexhaustible means the something cannot run out, or is unlimited. ...
... Exhaustible means the something can run out, or is limited. Inexhaustible means the something cannot run out, or is unlimited. ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.