principles1 - UCL Department of Geography
... – transfer of molecular kinetic (motion) energy due to contact – heat energy moves from T1 to T2 where T1 > T2 ...
... – transfer of molecular kinetic (motion) energy due to contact – heat energy moves from T1 to T2 where T1 > T2 ...
CHAPTER 7.1
... 1. 1. In what way is ATP like a compressed spring? 2. List three main types of cellular work. 3. What is the source of energy for regenerating ATP from ADP? 2. 1. Compare and contrast breathing and cellular ...
... 1. 1. In what way is ATP like a compressed spring? 2. List three main types of cellular work. 3. What is the source of energy for regenerating ATP from ADP? 2. 1. Compare and contrast breathing and cellular ...
Lecture 19
... longer any exact analytical solutions of the Schrödinger equation. Oops! Not only that, but even if you’re prepared to spend arbitrary computer time on a problem, eigenvalue equations can’t usually be solved by random functions. We need a systematic way to search for wave functions that are almost ...
... longer any exact analytical solutions of the Schrödinger equation. Oops! Not only that, but even if you’re prepared to spend arbitrary computer time on a problem, eigenvalue equations can’t usually be solved by random functions. We need a systematic way to search for wave functions that are almost ...
ENERGY SOURCES AND TYPES
... Does not release flowing water air pollution or turns turbine carbon dioxide to generate electricity ...
... Does not release flowing water air pollution or turns turbine carbon dioxide to generate electricity ...
Using Vocabulary
... _____1. Energy in the form of motion is potential energy. ____ 2. The greater mass a moving object has; the more kinetic energy it has. _____ 3. A rock at the edge of a cliff has kinetic energy because of its position. _____ 4. When a plant falls from a window its thermal energy is transformed into ...
... _____1. Energy in the form of motion is potential energy. ____ 2. The greater mass a moving object has; the more kinetic energy it has. _____ 3. A rock at the edge of a cliff has kinetic energy because of its position. _____ 4. When a plant falls from a window its thermal energy is transformed into ...
PYP001-122-Final Exam Solution [Choice A is the correct
... Q12. A 2-kg object is dropped from a height of 15 meters above ground. What is the kinetic energy of the object when it is 10 m above the ground? A) 98 J B) 196 J C) 392 J D) 294 J E) 20 J Q13. A skydiver is falling into the air. The speed-time graph of his motion is shown in the figure below. At wh ...
... Q12. A 2-kg object is dropped from a height of 15 meters above ground. What is the kinetic energy of the object when it is 10 m above the ground? A) 98 J B) 196 J C) 392 J D) 294 J E) 20 J Q13. A skydiver is falling into the air. The speed-time graph of his motion is shown in the figure below. At wh ...
Higher Level Multi A 1. Natalie measures the mass and speed of a
... A resistor is connected in series with an alternating current supply of negligible internal resistance. The peak value of the supply voltage is Vo and the peak value of the current in the resistor is I0. The average power dissipation in the resistor is A. ...
... A resistor is connected in series with an alternating current supply of negligible internal resistance. The peak value of the supply voltage is Vo and the peak value of the current in the resistor is I0. The average power dissipation in the resistor is A. ...
Heat - Geography1000
... Basic Heating & Cooling Processes in the Atmosphere • Radiation or Emission • The process by which electromagnetic energy is emitted from an object • The hotter the object the more radiation it emits • Absorption • The assimilation of electromagnetic waves by striking an object. • Different objects ...
... Basic Heating & Cooling Processes in the Atmosphere • Radiation or Emission • The process by which electromagnetic energy is emitted from an object • The hotter the object the more radiation it emits • Absorption • The assimilation of electromagnetic waves by striking an object. • Different objects ...
The Phase-Resolved Spectra of the Crab Pulsar
... Global currents flow through the null charge surface results in large regions of charge depletion, which form the gaps in the magnetosphere. The gap extends from the null charge surface to the light cylinder. Parallel electric field is induced in the gap, which can accelerate the electrons to extrem ...
... Global currents flow through the null charge surface results in large regions of charge depletion, which form the gaps in the magnetosphere. The gap extends from the null charge surface to the light cylinder. Parallel electric field is induced in the gap, which can accelerate the electrons to extrem ...
Types of Energy - Iowa Park High School
... k = spring constant x = displacement of object (how far it is stretched) ...
... k = spring constant x = displacement of object (how far it is stretched) ...
Energy - Effingham County Schools
... move faster you need to apply a force to it. Applying a force means you have to do work. The higher the speed of the cart, the more energy it has because you have to do work to increase the speed. • Kinetic energy increases with mass. If you give the same cart more mass, you have to push it with mor ...
... move faster you need to apply a force to it. Applying a force means you have to do work. The higher the speed of the cart, the more energy it has because you have to do work to increase the speed. • Kinetic energy increases with mass. If you give the same cart more mass, you have to push it with mor ...
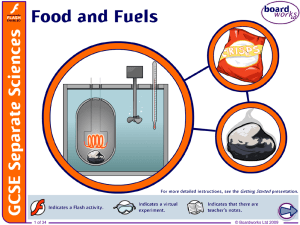
Food and Fuels
... Comparing the actual amounts of energy in food with the values found in calorimetry experiments, the experimental values are often a lot lower than the actual values. Why is this? Calorimetry experiments are not very accurate. A lot of the energy released by the burning food is not transferred into ...
... Comparing the actual amounts of energy in food with the values found in calorimetry experiments, the experimental values are often a lot lower than the actual values. Why is this? Calorimetry experiments are not very accurate. A lot of the energy released by the burning food is not transferred into ...
First law
... The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that the two regions become able to exchange mat ...
... The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that the two regions become able to exchange mat ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.