MINERAL RESOURCES
... • Mostly in the USA, Canada, Australia, South Africa, and the Republics of the former Soviet Union. • Western Europe – depends mostly on minerals from ...
... • Mostly in the USA, Canada, Australia, South Africa, and the Republics of the former Soviet Union. • Western Europe – depends mostly on minerals from ...
CHAPTERS FROM GEOLOGY
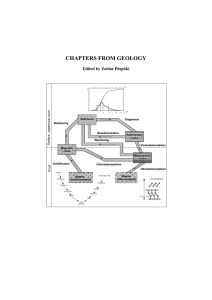
... Under superficial conditions the rock forming minerals of igneous rocks will be unstable phases and will be destroyed by the processes of weathering. The previous silicate structures will be altered into different ones becoming stable under superficial conditions. Sedimentary rocks (except some spec ...
... Under superficial conditions the rock forming minerals of igneous rocks will be unstable phases and will be destroyed by the processes of weathering. The previous silicate structures will be altered into different ones becoming stable under superficial conditions. Sedimentary rocks (except some spec ...
Movement of the Earth ’ s Crust
... almost horizontal, whereas regular reverse faults and normal faults are almost vertical. ...
... almost horizontal, whereas regular reverse faults and normal faults are almost vertical. ...
Study Guide
... 7. Our best theory as to why the plates move is the convection currents in the magma under the Earth’s crust. Explain this theory. How does it work? ...
... 7. Our best theory as to why the plates move is the convection currents in the magma under the Earth’s crust. Explain this theory. How does it work? ...
Lecture Notes
... made up from the recycled material-debris from one or more previous stars that long ago ended up their life in supernovae explosions. THE COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH The planets that are made of very rare material. According to Condensation Theory they are accreted from the Solar Nebula (FIG. 1.3). The ...
... made up from the recycled material-debris from one or more previous stars that long ago ended up their life in supernovae explosions. THE COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH The planets that are made of very rare material. According to Condensation Theory they are accreted from the Solar Nebula (FIG. 1.3). The ...
Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory?
... Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory? - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards ...
... Q. What is the concept of plate tectonics theory? - It is a scientific theory which describes the large scale motion of Earth’s lithosphere. The theory builds on the older concepts of continental drift developed by Alfred Wegner and seafloor spreading. Where the plates are relatively moving towards ...
rock - LPS
... that ascend toward the surface, where they may lead to igneous activity. • The ______________________l distribution of heat within Earth causes the thermal ____________________ in the mantle that ultimately drives plate motion. ...
... that ascend toward the surface, where they may lead to igneous activity. • The ______________________l distribution of heat within Earth causes the thermal ____________________ in the mantle that ultimately drives plate motion. ...
6.E.2.3- Questions and Answers -Worksheet
... Although weathered rock is the basic component of soil, the composition and texture of soil and its fertility and resistance to erosion are greatly influenced by plant roots and debris, bacteria, fungi, worms, insects, rodents, and other organisms. The upper-most layer of the continental crust is co ...
... Although weathered rock is the basic component of soil, the composition and texture of soil and its fertility and resistance to erosion are greatly influenced by plant roots and debris, bacteria, fungi, worms, insects, rodents, and other organisms. The upper-most layer of the continental crust is co ...
Exploration Focus: Hungary
... In Hungary, Falcon-TXM Oil and Gas Ltd. has been pioneering the exploration of unconventional resources in its Makó trough licence (Figure 3). After completing a 1100-km2 3D seismic campaign and a drilling program with 7 deep (>3500 m) wells, an active petroleum system with pervasive hydrocarbon sat ...
... In Hungary, Falcon-TXM Oil and Gas Ltd. has been pioneering the exploration of unconventional resources in its Makó trough licence (Figure 3). After completing a 1100-km2 3D seismic campaign and a drilling program with 7 deep (>3500 m) wells, an active petroleum system with pervasive hydrocarbon sat ...
Chapter 11
... Radioactivity and radiometric dating Radiometric dating • Half-life – the time for one-half of the radioactive nuclei to decay • Requires a closed system • Cross-checks are used for accuracy • Complex procedure • Yields numerical dates ...
... Radioactivity and radiometric dating Radiometric dating • Half-life – the time for one-half of the radioactive nuclei to decay • Requires a closed system • Cross-checks are used for accuracy • Complex procedure • Yields numerical dates ...
Forces in Earth`s Crust
... Key Concept: Over millions of years, the forces of plate movement can change a flat plain into landforms such as anticlines and synclines, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and plateaus. • Stresses in Earth’s crust cause the surface to change. Different stresses cause different changes. • Com ...
... Key Concept: Over millions of years, the forces of plate movement can change a flat plain into landforms such as anticlines and synclines, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and plateaus. • Stresses in Earth’s crust cause the surface to change. Different stresses cause different changes. • Com ...
Chapter 6 – Igneous rock
... quickly at the surface (lava) can become rhyolite or, if cooled slowly underground, granite. Mafic lavas can form basalt if cooled quickly but gabbro if a mafic magma is cooled slowly underground. • Glassy (non-crystalline) igneous rocks can include obsidian, pumice (many open pores), scoria (air-fi ...
... quickly at the surface (lava) can become rhyolite or, if cooled slowly underground, granite. Mafic lavas can form basalt if cooled quickly but gabbro if a mafic magma is cooled slowly underground. • Glassy (non-crystalline) igneous rocks can include obsidian, pumice (many open pores), scoria (air-fi ...
Chapter 15 Outline
... 6. The rock cycle is the interaction of physical and chemical processes that change rock from one type to another. It is the slowest of the earth’s cyclic processes. Environmental Effects of Using Mineral Resources A. The extraction, processing, and use of mineral sources has a large environmental i ...
... 6. The rock cycle is the interaction of physical and chemical processes that change rock from one type to another. It is the slowest of the earth’s cyclic processes. Environmental Effects of Using Mineral Resources A. The extraction, processing, and use of mineral sources has a large environmental i ...
Webelos Activity Badge Geologist
... be composed, of a mix of quart (7), Feldspar (6) and mica (2). The bits of individual minerals may be large enough to recognize but impossible to test with your kit. This is where your study of rock samples and guidebooks will serve you will. Not only will you be able to recognize the major types of ...
... be composed, of a mix of quart (7), Feldspar (6) and mica (2). The bits of individual minerals may be large enough to recognize but impossible to test with your kit. This is where your study of rock samples and guidebooks will serve you will. Not only will you be able to recognize the major types of ...
Cordilleran foreland vs hinterland deformation: Thermal controls of
... mountain belt near the Rocky Mountain Trench, but there is a pronounced change in crustal thickness. The Craton crust to the east is 40-50 km thick whereas the Cordillera crust to the west is 32-34 km thick. It is concluded that thermal density reduction beneath the Cordillera balances the thinner c ...
... mountain belt near the Rocky Mountain Trench, but there is a pronounced change in crustal thickness. The Craton crust to the east is 40-50 km thick whereas the Cordillera crust to the west is 32-34 km thick. It is concluded that thermal density reduction beneath the Cordillera balances the thinner c ...
Mountain Belts and the Continental Crust
... greatest accumulation of sediment in the region. (The boundary between the two geologic regions is a line approximating the location of the modern Hudson River. ...
... greatest accumulation of sediment in the region. (The boundary between the two geologic regions is a line approximating the location of the modern Hudson River. ...
Minerals - WordPress.com
... 11. What would the correct name for each of the igneous rocks with the following characteristics? (4 pts) a. 35% dark minerals, phaneritic texture: ______________________ b. Vesicular texture, dark color: ______________________ c. 87% dark minerals, phaneritic texture: ______________________ d. Pyro ...
... 11. What would the correct name for each of the igneous rocks with the following characteristics? (4 pts) a. 35% dark minerals, phaneritic texture: ______________________ b. Vesicular texture, dark color: ______________________ c. 87% dark minerals, phaneritic texture: ______________________ d. Pyro ...
File
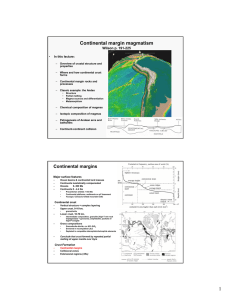
... where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, where plates are pushed together by internal forces and one plate rides up over the other. A trench generally occurs at the subduction zone. The third type of boundary is a transform fault and occurs where plates slide/ ...
... where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, where plates are pushed together by internal forces and one plate rides up over the other. A trench generally occurs at the subduction zone. The third type of boundary is a transform fault and occurs where plates slide/ ...
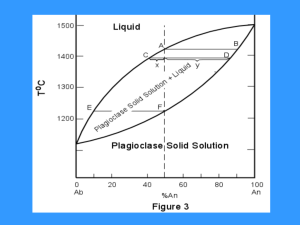
Chapter 4: Origin and Evolution of Igneous Rocks
... • Magma changes in temperature, viscosity, volatile content, and composition as it is transported toward the surface, mixes with other magmas, assimilates surrounding rock, and fractionates. • Eruption styles and volcanic structures are related to lava chemistry. • Mafic lavas generally result in ge ...
... • Magma changes in temperature, viscosity, volatile content, and composition as it is transported toward the surface, mixes with other magmas, assimilates surrounding rock, and fractionates. • Eruption styles and volcanic structures are related to lava chemistry. • Mafic lavas generally result in ge ...
Peter J. Wyllie BATHOLITHS and EXPERIMENTS in the 1970s
... in the rain, and explained to us how the tonalites had been formed by partial melting, right there - in the quarry - and then the whole mass had been intruded upwards as a tonalite pluton. He showed us migmatites with leucocratic veins termed tonalite, rocks shot through with massive tonalite dikes, ...
... in the rain, and explained to us how the tonalites had been formed by partial melting, right there - in the quarry - and then the whole mass had been intruded upwards as a tonalite pluton. He showed us migmatites with leucocratic veins termed tonalite, rocks shot through with massive tonalite dikes, ...
Chapter 9 of Earth
... a) Gently bent without much deformation b) Ascent of buoyant mantle material c) Far from plate boundaries d) Adirondack Mountains: Uplift of deep PreCambrian Igneous and Metamorphic rocks ...
... a) Gently bent without much deformation b) Ascent of buoyant mantle material c) Far from plate boundaries d) Adirondack Mountains: Uplift of deep PreCambrian Igneous and Metamorphic rocks ...
THE GEOLOGICAL MAP (1:25 000) OF THE SW PART OF
... the Isbjórnhamna Formation cannot be regarded as the crystalline basement of the remaining part of the Hecla Hoek Succession. Extent of the E i m f j e l l e t G r o u p has been here limited to the quartzite-amphibolite series of the southern tectonic block. Detailed mapping has allowed to present ...
... the Isbjórnhamna Formation cannot be regarded as the crystalline basement of the remaining part of the Hecla Hoek Succession. Extent of the E i m f j e l l e t G r o u p has been here limited to the quartzite-amphibolite series of the southern tectonic block. Detailed mapping has allowed to present ...
Basalts and Ultramafic Volcanic Rocks
... After Irvine and Baragar (1971). Can. J. Earth Sci., 8, ...
... After Irvine and Baragar (1971). Can. J. Earth Sci., 8, ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.