Rock Cycle Game-1
... (Slightly modified from an exercise by Andrew Manning of the University of Utah with some ideas from "Rock Roulette" by Stan Schmidt and Courtney Palmer). Introduction The rock cycle describes the recycling of Earth materials through time. There are almost endless possibilities for how rocks may mov ...
... (Slightly modified from an exercise by Andrew Manning of the University of Utah with some ideas from "Rock Roulette" by Stan Schmidt and Courtney Palmer). Introduction The rock cycle describes the recycling of Earth materials through time. There are almost endless possibilities for how rocks may mov ...
Downloadable self-guided walking route for Bloody
... Iapetus. The cliffs below the Bloody Bridge car park are made of a fine grained sedimentary rock called “siltstone”. These rocks were deposited on the floor of the Iapetus Ocean. When the forces of plate tectonics closed the ocean, the ocean floor rocks were heated and folded. The two halves of Irel ...
... Iapetus. The cliffs below the Bloody Bridge car park are made of a fine grained sedimentary rock called “siltstone”. These rocks were deposited on the floor of the Iapetus Ocean. When the forces of plate tectonics closed the ocean, the ocean floor rocks were heated and folded. The two halves of Irel ...
isostasy - UMSL.edu
... Continental Crust is thicker and has a lower density than Oceanic Crust. Therefore, it floats higher and has a deeper "root" than Oceanic Crust. This phenomenon can be compared with the behavior of floating wood blocks, all with the same density (see figure). The thicker blocks stand higher but have ...
... Continental Crust is thicker and has a lower density than Oceanic Crust. Therefore, it floats higher and has a deeper "root" than Oceanic Crust. This phenomenon can be compared with the behavior of floating wood blocks, all with the same density (see figure). The thicker blocks stand higher but have ...
Earth`s Many Layers
... Formation of Crust • Continental crust began to form ~ 4 Ga ♣ By partial melting ♣ Has grown gradually since then • Oceanic crust (oldest ~ 200 Ma): ♣ Continuously formed (mid-ocean ridge) ♣ Then destroyed (sinks into mantle) ...
... Formation of Crust • Continental crust began to form ~ 4 Ga ♣ By partial melting ♣ Has grown gradually since then • Oceanic crust (oldest ~ 200 Ma): ♣ Continuously formed (mid-ocean ridge) ♣ Then destroyed (sinks into mantle) ...
ness of clousta to the brigs
... Tuff, 3 km to the WSW of the GCR site) have the composition, bedforms and geometry of phreatomagmatic deposits. The high content of detrital quartz and feldspar and the larger blocks of sandstone and conglomerate reflect the explosive excavation of a vent crater in the underlying alluvium. Indicator ...
... Tuff, 3 km to the WSW of the GCR site) have the composition, bedforms and geometry of phreatomagmatic deposits. The high content of detrital quartz and feldspar and the larger blocks of sandstone and conglomerate reflect the explosive excavation of a vent crater in the underlying alluvium. Indicator ...
Properties of Minerals
... crystal structure and a definite chemical composition. For a substance to be considered a mineral, it must have all five of these characteristics. Geologists have identified more than 3,000 different minerals. Of these, only about 100 are common. About 20 minerals make up most of the rocks of Earth’ ...
... crystal structure and a definite chemical composition. For a substance to be considered a mineral, it must have all five of these characteristics. Geologists have identified more than 3,000 different minerals. Of these, only about 100 are common. About 20 minerals make up most of the rocks of Earth’ ...
Name Period
... a. 25 million years ago. b. 2.5 billion years ago. c. 250 million years ago. d. 2.5 million years ago. 6. Wegener speculated that over millions of years these small continents __________________________. a. moved closer together. b. did not move. c. drifted to their present locations. 7. Why was Weg ...
... a. 25 million years ago. b. 2.5 billion years ago. c. 250 million years ago. d. 2.5 million years ago. 6. Wegener speculated that over millions of years these small continents __________________________. a. moved closer together. b. did not move. c. drifted to their present locations. 7. Why was Weg ...
significance of plate tectonics - Singh Ranendra................Its
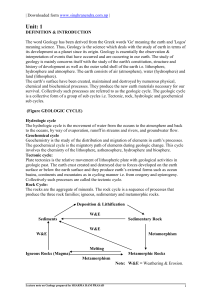
... Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is the movement of water from the oceans to the atmosphere and back to the oceans, by way of evaporation, runoff in streams and rivers, and groundwater flow. Geochemical cycle Geochemistry is the study of the distribution and migration of elements in earth‘s pro ...
... Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is the movement of water from the oceans to the atmosphere and back to the oceans, by way of evaporation, runoff in streams and rivers, and groundwater flow. Geochemical cycle Geochemistry is the study of the distribution and migration of elements in earth‘s pro ...
Geology of Tarnagulla area
... pressures had distorted them over time (more about that later). In many places, interspersed with the sediments were volcanic lava flows. As you can imagine, much more sedimentation and geological change had taken place by the time our story begins than has occurred ever since. At times the continen ...
... pressures had distorted them over time (more about that later). In many places, interspersed with the sediments were volcanic lava flows. As you can imagine, much more sedimentation and geological change had taken place by the time our story begins than has occurred ever since. At times the continen ...
C:\Users\jmhemzac\Desktop\2017 spring\121 final rev S17f.wpd
... Be able to discuss (in general terms) why volcanoes exist only in certain places Be able to describe the characteristics of a mineral, according to its definition: natural, inorganic, crystalline, solid; definite chemical composition –> How is this different from a rock? According to geologic eviden ...
... Be able to discuss (in general terms) why volcanoes exist only in certain places Be able to describe the characteristics of a mineral, according to its definition: natural, inorganic, crystalline, solid; definite chemical composition –> How is this different from a rock? According to geologic eviden ...
Presentation
... and on its surface recycle the earth’s rocks, form deposits of mineral resources, and cause volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. 2. The available supply of a mineral resource depends on how much of it is in the earth’s crust, how fast we use it, mining technology, market prices, and the ha ...
... and on its surface recycle the earth’s rocks, form deposits of mineral resources, and cause volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. 2. The available supply of a mineral resource depends on how much of it is in the earth’s crust, how fast we use it, mining technology, market prices, and the ha ...
Earth`s structure - Deakin University Blogs
... that occur when warm material from deep within Earth rises towards the surface, cools, and then, upon losing heat, descends back into the interior. Hot material rises because it is less dense (amount of material per volume) than the colder material. The cycle then begins again with hot material risi ...
... that occur when warm material from deep within Earth rises towards the surface, cools, and then, upon losing heat, descends back into the interior. Hot material rises because it is less dense (amount of material per volume) than the colder material. The cycle then begins again with hot material risi ...
Slides and text from Gold Medal Lecture
... interpreted times of erosion as times of uplift and mountain building. My balanced (retro-deformable) structure sections are based on the concept that whatever occurs on one side of a fault must have a compatible counterpart on the other side. Thus, what is discernible along the hanging wall of the ...
... interpreted times of erosion as times of uplift and mountain building. My balanced (retro-deformable) structure sections are based on the concept that whatever occurs on one side of a fault must have a compatible counterpart on the other side. Thus, what is discernible along the hanging wall of the ...
Reading Study Guide B - Swartz Creek Schools
... The sketch below shows that a normal fault has occurred. A diamond is buried in the rock. Draw arrows showing which way the diamond moved when the earthquake occurred. ...
... The sketch below shows that a normal fault has occurred. A diamond is buried in the rock. Draw arrows showing which way the diamond moved when the earthquake occurred. ...
Part B KEY
... Mountain building is a result of the crust being folded, and this will cause the lithosphere to sink further into the asthenosphere. However, the opposite occurs during erosion as sediment is carried off the mountain the crust will rebound and float higher. During the ice ages the massive ice sheets ...
... Mountain building is a result of the crust being folded, and this will cause the lithosphere to sink further into the asthenosphere. However, the opposite occurs during erosion as sediment is carried off the mountain the crust will rebound and float higher. During the ice ages the massive ice sheets ...
Types of rocks
... - is formed from sediment (loose material – rock, minerals, plant and animal remains - that is layered and compacted together by the pressure of the material above it) - stratification is the visible evidence of the layers - cementation - some of the minerals that dissolve with the addition of water ...
... - is formed from sediment (loose material – rock, minerals, plant and animal remains - that is layered and compacted together by the pressure of the material above it) - stratification is the visible evidence of the layers - cementation - some of the minerals that dissolve with the addition of water ...
Rock Cycle Roundabout - California Academy of Sciences
... Metamorphic rocks can be weathered and compacted into sedimentary rocks, or they can be subjected to heat and/or pressure causing them to melt and eventually erupt as igneous rocks. Alternatively, metamorphic rocks may be transformed again into different metamorphic rocks. The simplest way to unders ...
... Metamorphic rocks can be weathered and compacted into sedimentary rocks, or they can be subjected to heat and/or pressure causing them to melt and eventually erupt as igneous rocks. Alternatively, metamorphic rocks may be transformed again into different metamorphic rocks. The simplest way to unders ...
Earth and Atmosphere
... – Slate is formed when pressure squeezes mudstone into plate like grey sheets. It is used in roofing. – Schist and mica are formed when mudstone is subjected to very high temperatures as well as pressure. Again they contain layers which is typical of many (not all) metamorphic rocks. © Boardworks Lt ...
... – Slate is formed when pressure squeezes mudstone into plate like grey sheets. It is used in roofing. – Schist and mica are formed when mudstone is subjected to very high temperatures as well as pressure. Again they contain layers which is typical of many (not all) metamorphic rocks. © Boardworks Lt ...
CHapter 14 APES Test
... ____ 72. Scarcity of minerals does not raise the price of material goods much because a. investment capital is usually abundantly available. b. all resource supplies are theoretically infinite. c. the mining industry is fiercely competitive and poorly regulated. d. raw materials typically account f ...
... ____ 72. Scarcity of minerals does not raise the price of material goods much because a. investment capital is usually abundantly available. b. all resource supplies are theoretically infinite. c. the mining industry is fiercely competitive and poorly regulated. d. raw materials typically account f ...
Full-Text - Journal of Tethys
... The rocks studied have porphyritic texture and phenocrysts with plagioclase, sanidine, amphibole, biotite and quartz. Based on geochemical data and multi elements pattern, these rocks are medium to high K calc-alkaline suite and show LILE and LREE enriched normalized multi-element patterns, and Nb a ...
... The rocks studied have porphyritic texture and phenocrysts with plagioclase, sanidine, amphibole, biotite and quartz. Based on geochemical data and multi elements pattern, these rocks are medium to high K calc-alkaline suite and show LILE and LREE enriched normalized multi-element patterns, and Nb a ...
Jigsaw Puzzle Earth
... sea-floor spreading. Paleomagnetism refers to the magnetic properties that rocks acquire during their formation and that become permanent after they harden. Scientists found that as magma cools and solidifies, the rock that is formed contains minerals rich in iron. These minerals align with the Eart ...
... sea-floor spreading. Paleomagnetism refers to the magnetic properties that rocks acquire during their formation and that become permanent after they harden. Scientists found that as magma cools and solidifies, the rock that is formed contains minerals rich in iron. These minerals align with the Eart ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Weathering, erosion & transportation Rocks exposed at Earth’s surface are constantly changed by water, air, temperature variations and other factors • weathering is the group of destructive processes that change physical and chemical character of rocks at or near Earth’s surface • erosion is physic ...
... Weathering, erosion & transportation Rocks exposed at Earth’s surface are constantly changed by water, air, temperature variations and other factors • weathering is the group of destructive processes that change physical and chemical character of rocks at or near Earth’s surface • erosion is physic ...
Chapter 1 Introduction – Review of Rocks and
... Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks represent the three major types or groups of rock on planet Earth. Igneous rocks make up the vast majority of our planet while sedimentary and metamorphic rocks making up a lesser volume. Classifying a rock into one of these three groups ...
... Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks represent the three major types or groups of rock on planet Earth. Igneous rocks make up the vast majority of our planet while sedimentary and metamorphic rocks making up a lesser volume. Classifying a rock into one of these three groups ...
Oceanic crust
... • The continents include a wide range of rock types, including granitic igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and the metamorphic rocks formed by the alterations of both. They contain a lot of quartz, a mineral absent in oceanic crust. • This core foundation is often referred to as a shield or basement ...
... • The continents include a wide range of rock types, including granitic igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and the metamorphic rocks formed by the alterations of both. They contain a lot of quartz, a mineral absent in oceanic crust. • This core foundation is often referred to as a shield or basement ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.