Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources - Baxley
... Chapter Overview Questions (cont’d) Will ...
... Chapter Overview Questions (cont’d) Will ...
Granitoids
... Common minor minerals: apatite, zircon, magnetite, ilmenite, monazite, titanite, tourmaline, allanite, fluorite and pyrite ...
... Common minor minerals: apatite, zircon, magnetite, ilmenite, monazite, titanite, tourmaline, allanite, fluorite and pyrite ...
metam
... Along faults - grinding and crushing at shallow crustal levels, stretching and recrystallization at deeper levels. Also known as cataclastic metamorphism (not in textbook). ...
... Along faults - grinding and crushing at shallow crustal levels, stretching and recrystallization at deeper levels. Also known as cataclastic metamorphism (not in textbook). ...
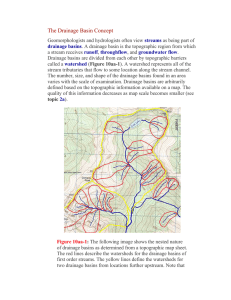
The Drainage Basin Concept
... drainage basins. A drainage basin is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and groundwater flow. Drainage basins are divided from each other by topographic barriers called a watershed (Figure 10aa-1). A watershed represents all of the stream tributaries that flow t ...
... drainage basins. A drainage basin is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and groundwater flow. Drainage basins are divided from each other by topographic barriers called a watershed (Figure 10aa-1). A watershed represents all of the stream tributaries that flow t ...
Chapter 4
... Porphyritic textures are characteristic of rocks with complex cooling histories and contain mineral grains of different sizes. Other igneous rock textures include vesicular, glassy, and pyroclastic. ...
... Porphyritic textures are characteristic of rocks with complex cooling histories and contain mineral grains of different sizes. Other igneous rock textures include vesicular, glassy, and pyroclastic. ...
Igneous Geochemistry OUTLINE
... Decompression in hotspots limited by plate thickness; due to high T, melt relatively deep up to plate’s bottom ...
... Decompression in hotspots limited by plate thickness; due to high T, melt relatively deep up to plate’s bottom ...
Deep Sea Drilling Project Initial Reports Volume 60
... more similar to normal ocean-floor spreading than in the other group. In order to test these hypotheses, the spreading history, in particular the rate and degree of symmetry, is of key importance. There are, however, definite differences between midocean spreading and back-arc spreading, apparently ...
... more similar to normal ocean-floor spreading than in the other group. In order to test these hypotheses, the spreading history, in particular the rate and degree of symmetry, is of key importance. There are, however, definite differences between midocean spreading and back-arc spreading, apparently ...
Draft Museum Guide - Valley Geology
... Look at the glacial varves display. These varves were deposited on the bottom of Lake Hitchcock. Notice pattern of light sediment (silt) and dark sediment (clay). Silt, which is larger and heavier than ...
... Look at the glacial varves display. These varves were deposited on the bottom of Lake Hitchcock. Notice pattern of light sediment (silt) and dark sediment (clay). Silt, which is larger and heavier than ...
kinds of metamorphism
... takes place as an after effect of igneous activity. Magmas have lots of water with dissolved minerals, but as the magma crystallizes the mineral laden water is driven off into the surrounding country rock where it seeps into cracks and pores precipitating the minerals. The most spectacular result of ...
... takes place as an after effect of igneous activity. Magmas have lots of water with dissolved minerals, but as the magma crystallizes the mineral laden water is driven off into the surrounding country rock where it seeps into cracks and pores precipitating the minerals. The most spectacular result of ...
Lecture D
... rocks into six chemically based-groups 1. Ultramafic - very high Mg, Fe, Ni, Cr 2. Mafic - high Fe, Mg, and Ca 3. Shales (pelitic) - high Al, K, Si 4. Carbonates- high Ca, Mg, CO2 5. Quartz - nearly pure SiO2. 6. Quartzo-feldspathic - high Si, Na, K, Al ...
... rocks into six chemically based-groups 1. Ultramafic - very high Mg, Fe, Ni, Cr 2. Mafic - high Fe, Mg, and Ca 3. Shales (pelitic) - high Al, K, Si 4. Carbonates- high Ca, Mg, CO2 5. Quartz - nearly pure SiO2. 6. Quartzo-feldspathic - high Si, Na, K, Al ...
General Session G01 Structural geology and Neotectonics
... SP -Scythian; TAI - Taurus-Anatolia-Iranian. 2. Fold-thrust mountain belts: Great Caucasus (GC); Achara-Trialeti (AT); Talysh (Tl); Baiburt-Garabagh-Kaphan (B). 3. Ophiolite suture belt: Sevan-Akera (SA). 4. Foredeeps: Azov-Kuban (AK), Stavropol high (ST), Terek-Caspian (TK), Gussar-Devichi (GD). 5. ...
... SP -Scythian; TAI - Taurus-Anatolia-Iranian. 2. Fold-thrust mountain belts: Great Caucasus (GC); Achara-Trialeti (AT); Talysh (Tl); Baiburt-Garabagh-Kaphan (B). 3. Ophiolite suture belt: Sevan-Akera (SA). 4. Foredeeps: Azov-Kuban (AK), Stavropol high (ST), Terek-Caspian (TK), Gussar-Devichi (GD). 5. ...
Dissociability of the fossil record. - E
... interest, related to the nature of the fossil record: the dissociability of the fossil record. Palaeontology has become an applied science in stratigraphy and geology through the usefulness of the fossils in the interpretation of the geological record. The most widespread geological application of p ...
... interest, related to the nature of the fossil record: the dissociability of the fossil record. Palaeontology has become an applied science in stratigraphy and geology through the usefulness of the fossils in the interpretation of the geological record. The most widespread geological application of p ...
09_chapter 2
... Supergroup comprises of the older Nandgaon group, consisting a bimodal suite of basalts and rhyolites along with epiclastic rocks (Bandyopadhyay et al., 1995). This bimodal tholeiitic basalt-rhyolite association was earlier interpreted as of continental non-orogenic origin by Krishnamurthy et al. (1 ...
... Supergroup comprises of the older Nandgaon group, consisting a bimodal suite of basalts and rhyolites along with epiclastic rocks (Bandyopadhyay et al., 1995). This bimodal tholeiitic basalt-rhyolite association was earlier interpreted as of continental non-orogenic origin by Krishnamurthy et al. (1 ...
BR field trip - Marshall University
... collisions between the North American continent, several island arcs, and Africa. These collisions occurred during the Grenville orogeny (1.2 Ga), the Taconic orogeny (Ordovician), the Acadian orogeny (Devonian, marked by the Avalon terrane colliding with Laurentia), and the Alleghenian orogeny (Per ...
... collisions between the North American continent, several island arcs, and Africa. These collisions occurred during the Grenville orogeny (1.2 Ga), the Taconic orogeny (Ordovician), the Acadian orogeny (Devonian, marked by the Avalon terrane colliding with Laurentia), and the Alleghenian orogeny (Per ...
Earth Science Final Exam
... 77. What is evapotranspiration? 78. Draw a simple sketch of a drainage basin and divide and label each. 79. Describe the three ways a stream transport its load. 80. What is the difference between capacity and competency? 81. Describe and sketch the development of a meander bend, including how an oxb ...
... 77. What is evapotranspiration? 78. Draw a simple sketch of a drainage basin and divide and label each. 79. Describe the three ways a stream transport its load. 80. What is the difference between capacity and competency? 81. Describe and sketch the development of a meander bend, including how an oxb ...
Igneous Rocks - sir
... Partial melting and magma formation formation of granitic magmas most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma granitic magmas are more viscous than other magmas—tend to lose their mobility before reaching the surface. produce large plutonic structures ...
... Partial melting and magma formation formation of granitic magmas most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma granitic magmas are more viscous than other magmas—tend to lose their mobility before reaching the surface. produce large plutonic structures ...
Topography - Teacher Friendly Guides
... Working in conjunction with mechanical weathering, chemical weathering also helps to break down rocks. Some minerals of igneous and metamorphic rocks that are formed at high temperatures and pressures, far below the surface of the Earth, become unstable when they are exposed at the surface where the ...
... Working in conjunction with mechanical weathering, chemical weathering also helps to break down rocks. Some minerals of igneous and metamorphic rocks that are formed at high temperatures and pressures, far below the surface of the Earth, become unstable when they are exposed at the surface where the ...
New Mexico Geological Society
... Preorogenic rocks range in age from Precambrian to Late Cretaceous. The basement is composed of crystalline Precambrian rocks that deform by fracturing; these rocks are exposed in the Sangre de Cristo and Cimarron uplifts that bound the west side of the Raton Basin. The sedimentary cover is composed ...
... Preorogenic rocks range in age from Precambrian to Late Cretaceous. The basement is composed of crystalline Precambrian rocks that deform by fracturing; these rocks are exposed in the Sangre de Cristo and Cimarron uplifts that bound the west side of the Raton Basin. The sedimentary cover is composed ...
Compared to the desolate surface of the Moon, Earth must
... Temperature within Earth increases with depth: geothermal gradient ...
... Temperature within Earth increases with depth: geothermal gradient ...
Folds and Faults - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... rocks generally thicken and shorten Tension – occurs at diverging plates; rocks generally thin and lengthen Shearing – occurs at transform plate boundaries; rocks are sliced into parallel blocks ...
... rocks generally thicken and shorten Tension – occurs at diverging plates; rocks generally thin and lengthen Shearing – occurs at transform plate boundaries; rocks are sliced into parallel blocks ...
Continental Arcs
... magmas • Heat from these magmas melt the lower crust • Residual melts may rise • Exsolved volatiles also facilitate rise ...
... magmas • Heat from these magmas melt the lower crust • Residual melts may rise • Exsolved volatiles also facilitate rise ...
ROCK CYCLE
... another place it is called erosion. The rock pieces called sediments get deposited or dropped from the wind or water to make a layer. The layer can be buried under other layers of sediments. After a long time the sediments can be compacted and cemented together to make sedimentary rock. All rock can ...
... another place it is called erosion. The rock pieces called sediments get deposited or dropped from the wind or water to make a layer. The layer can be buried under other layers of sediments. After a long time the sediments can be compacted and cemented together to make sedimentary rock. All rock can ...
nur`aini_etal_2005 Makassar Strait
... parallel to the zone of rifting. Several discontinuous NNW-SSE depocentres developed with the fault zone. A change in polarity of faults can also be seen in the study area. Along strike, the faults that developed within this area seem to be discontinuous. These observations are interpreted as indica ...
... parallel to the zone of rifting. Several discontinuous NNW-SSE depocentres developed with the fault zone. A change in polarity of faults can also be seen in the study area. Along strike, the faults that developed within this area seem to be discontinuous. These observations are interpreted as indica ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.