Exp 4 Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... of fall of the droplets is less than 0.1 cm s . (Droplets having this and smaller velocities have radii, on the order of 2 microns, comparable to the mean free path of air molecules, a condition which violates one of the assumptions made in deriving Stokes’Law.) Since the velocities of the droplets ...
... of fall of the droplets is less than 0.1 cm s . (Droplets having this and smaller velocities have radii, on the order of 2 microns, comparable to the mean free path of air molecules, a condition which violates one of the assumptions made in deriving Stokes’Law.) Since the velocities of the droplets ...
The Improved Electromagnetic Equations and
... carrying a steady current J. They are connected by Eqs. (12) and (14), from which we obtain Er = c 2 ρBθ /(ε r J ) . This relation tells that, when ρ = 0 , Er = 0 and vice versa. Namely, the Hall electric field together with free volume charges disappears in the wire carrying steady current. On the ...
... carrying a steady current J. They are connected by Eqs. (12) and (14), from which we obtain Er = c 2 ρBθ /(ε r J ) . This relation tells that, when ρ = 0 , Er = 0 and vice versa. Namely, the Hall electric field together with free volume charges disappears in the wire carrying steady current. On the ...
23_InstructorSolutionsWin
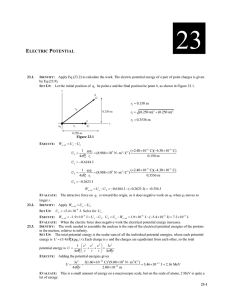
... 30.0 V V2 EVALUATE: The potential of a positive charge is positive and decreases as the distance from the point charge increases. IDENTIFY: The total potential is the scalar sum of the individual potentials, but the net electric field is the vector sum of the two fields. SET UP: The net pote ...
... 30.0 V V2 EVALUATE: The potential of a positive charge is positive and decreases as the distance from the point charge increases. IDENTIFY: The total potential is the scalar sum of the individual potentials, but the net electric field is the vector sum of the two fields. SET UP: The net pote ...
A2 Discovery of the Electron
... When the electric field was switched off the oil droplet fell and quickly reached constant speed.Explain why the oil droplet reached constant speed. ...
... When the electric field was switched off the oil droplet fell and quickly reached constant speed.Explain why the oil droplet reached constant speed. ...
C23_Current mine
... conduction electrons=charge carriers, one or more electrons from each metal atom are free to move throughout the atomic lattice. Protons do not move because they are bound inside the nuclei of atoms that are more or less locked in fixed positions. In conducting fluids—such as in a car battery—positi ...
... conduction electrons=charge carriers, one or more electrons from each metal atom are free to move throughout the atomic lattice. Protons do not move because they are bound inside the nuclei of atoms that are more or less locked in fixed positions. In conducting fluids—such as in a car battery—positi ...
Electric Field Strength
... In this section, measurement techniques for extremely low frequency (ELF, 3 Hz to 3 kHz) and ultralow frequency (ULF, below 3 Hz) electric fields are considered. Natural ELF fields are produced by thunderstorms, and natural ULF fields are produced by micropulsations in the earth’s magnetic field [7] ...
... In this section, measurement techniques for extremely low frequency (ELF, 3 Hz to 3 kHz) and ultralow frequency (ULF, below 3 Hz) electric fields are considered. Natural ELF fields are produced by thunderstorms, and natural ULF fields are produced by micropulsations in the earth’s magnetic field [7] ...
Identity Charge and the Origin of Life
... Both confer advantages, but only within a competitive environment. There are also certain benefits to size and numbers that are simply "emergent properties" of large organizations, efficiencies of scale, etc. An individual human cannot create a 747 jumbo jet, or mount an expedition to the Moon, but ...
... Both confer advantages, but only within a competitive environment. There are also certain benefits to size and numbers that are simply "emergent properties" of large organizations, efficiencies of scale, etc. An individual human cannot create a 747 jumbo jet, or mount an expedition to the Moon, but ...
Electricity and Magnetism Power Point Presentation
... lights goes out and the rest of the lights also go out – what kind of circuit is formed? ...
... lights goes out and the rest of the lights also go out – what kind of circuit is formed? ...
Nuclear ppt notes
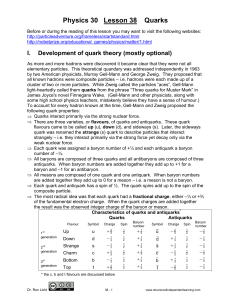
... Carbon always has 6 protons, hydrogen always has 1 proton, oxygen always has 8 protons You change the # of protons, you change the type of atom Neutrons have no chemical effect on an atom’s properties ...
... Carbon always has 6 protons, hydrogen always has 1 proton, oxygen always has 8 protons You change the # of protons, you change the type of atom Neutrons have no chemical effect on an atom’s properties ...
Washabaugh. A.P., M. Zahn, and J.R. Melcher, Electrohydrodynamic Traveling-Wave Pumping of Homogeneous Semi-Insulating Liquids, IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation, EI-24, No. 5, 807-834, October 1989
... regime, because any charge that migrates into the fluid volume remains in the vicinity of the electrodes and does not penetrate very far into the liquid volume. Thus, in this high frequency regime, the circular cylindrical geometry in MacGinitie’s experiments can be approximately considered a planar ...
... regime, because any charge that migrates into the fluid volume remains in the vicinity of the electrodes and does not penetrate very far into the liquid volume. Thus, in this high frequency regime, the circular cylindrical geometry in MacGinitie’s experiments can be approximately considered a planar ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.