HW4 - SMU Physics
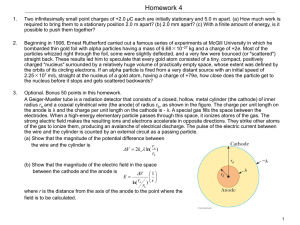
... Beginning in 1906, Ernest Rutherford carried out a famous series of experiments at McGill University in which he bombarded thin gold foil with alpha particles having a mass of 6.68×10−27 kg and a charge of +2e. Most of the particles whizzed right through the foil, some were slightly deflected, and a ...
... Beginning in 1906, Ernest Rutherford carried out a famous series of experiments at McGill University in which he bombarded thin gold foil with alpha particles having a mass of 6.68×10−27 kg and a charge of +2e. Most of the particles whizzed right through the foil, some were slightly deflected, and a ...
2.3 x 10 -8 N repulsion
... 2. Describe an insulator and give examples: Does not conduct heat and electricity very well. Cotton, air, glass, etc. 3. Describe a conductor and give examples: Allows heat and electricity to move through the substance easily. Metals, saltwater, etc. 4. Charge of an electron: -1.6 x 10-19C Charge of ...
... 2. Describe an insulator and give examples: Does not conduct heat and electricity very well. Cotton, air, glass, etc. 3. Describe a conductor and give examples: Allows heat and electricity to move through the substance easily. Metals, saltwater, etc. 4. Charge of an electron: -1.6 x 10-19C Charge of ...
Electrostatics
... History • Ben Franklin made the arbitrary choice of calling one of the demo situations positive and one negative. • He also argued that when a certain amount of charge is produced on one body, an equal amount of the opposite charge is produced on the other body… ...
... History • Ben Franklin made the arbitrary choice of calling one of the demo situations positive and one negative. • He also argued that when a certain amount of charge is produced on one body, an equal amount of the opposite charge is produced on the other body… ...
Phys 208 - Recitation E-Fields
... a. For the three arrangements of charges below, draw the electric field direction at each place where a dot is located. Try to estimate the relative magnitudes of the field vectors. (All charges have the ...
... a. For the three arrangements of charges below, draw the electric field direction at each place where a dot is located. Try to estimate the relative magnitudes of the field vectors. (All charges have the ...
Electric Field Problems - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... negative test charge. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field where the test charge is located? 2. A positive test charge of 3.75 x 1013 ec is in an electric field of 50.0 N/C [East]. What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the charge? 3. Perform the following c ...
... negative test charge. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field where the test charge is located? 2. A positive test charge of 3.75 x 1013 ec is in an electric field of 50.0 N/C [East]. What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the charge? 3. Perform the following c ...
Mrs. Chadwick`s PPT
... amount of protons as it does electrons and has no net charge If an electron is removed from an atom the atom is no longer neutral. The atom now has one more positive charge than negative charge and is said to be positively charged (called a positive ion) An atom that gains an electron is said to ...
... amount of protons as it does electrons and has no net charge If an electron is removed from an atom the atom is no longer neutral. The atom now has one more positive charge than negative charge and is said to be positively charged (called a positive ion) An atom that gains an electron is said to ...
extra example - FIU Faculty Websites
... fields at this point due to each point charge in the charge distribution. If the charges are continuously distributed along a line, over a surface, or through a volume, i.e. the charges cannot be considered as discrete point charges, it requires to integrate over the charge distribution to calculate ...
... fields at this point due to each point charge in the charge distribution. If the charges are continuously distributed along a line, over a surface, or through a volume, i.e. the charges cannot be considered as discrete point charges, it requires to integrate over the charge distribution to calculate ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.