Lecture 4: Charged Particle Motion
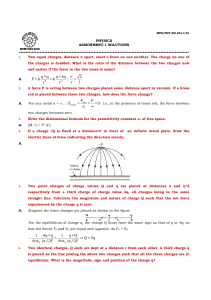
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
... + so, with current density and velocity, we can determine the charge density of an electron beam. Relativistic motion Let's back up, for non-relativistic particles, if a force acts on a particle, its velocity can change ...
Charge
... electrons that transfer (not the protons). A negatively charged object has an excess of e’s, whereas positively charged one has deficiency (by same amount) • Which object gains the electrons depends on their electron affinity: Eg. Rod has greater affinity than fur, so rod becomes –, fur + Eg. Silk h ...
... electrons that transfer (not the protons). A negatively charged object has an excess of e’s, whereas positively charged one has deficiency (by same amount) • Which object gains the electrons depends on their electron affinity: Eg. Rod has greater affinity than fur, so rod becomes –, fur + Eg. Silk h ...
electric current ppt
... • Supply energy like a pump to move charges • Provide sustained potential difference • EMF (electromotive force) is potential energy per coulomb of charge moving between battery terminals; creates electrical “pressure”; measured in volts ...
... • Supply energy like a pump to move charges • Provide sustained potential difference • EMF (electromotive force) is potential energy per coulomb of charge moving between battery terminals; creates electrical “pressure”; measured in volts ...
Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by
... Objects can be charged by rubbing ...
... Objects can be charged by rubbing ...
Potential Difference
... If 30 J of work is done when 5 C of charge passes through a component, what is the pd ...
... If 30 J of work is done when 5 C of charge passes through a component, what is the pd ...
Homework Problems I for PY2T10 Stokes’ Theorem V
... Subscripts ij refer to Cartesian components of the matrix T or position vector, r. ...
... Subscripts ij refer to Cartesian components of the matrix T or position vector, r. ...
Charge - Ms. Gamm
... 2. You write the number on the top of the assignment (#1) Reading Log 23 3. Staple all your HW in order to the back of your Cornell notes at the end ...
... 2. You write the number on the top of the assignment (#1) Reading Log 23 3. Staple all your HW in order to the back of your Cornell notes at the end ...
ppt - plutonium
... How do we describe and apply the nature of electric fields in and around conductors? How do we explain the mechanics responsible for the absence of electric field inside of a conductor? Why must all of the excess charge reside on the surface of a conductor? How do we prove that all excess ch ...
... How do we describe and apply the nature of electric fields in and around conductors? How do we explain the mechanics responsible for the absence of electric field inside of a conductor? Why must all of the excess charge reside on the surface of a conductor? How do we prove that all excess ch ...
Electrostatics 12
... History • Ben Franklin made the arbitrary choice of calling one of the demo situations positive and one negative. • He also argued that when a certain amount of charge is produced on one body, an equal amount of the opposite charge is produced on the other body… ...
... History • Ben Franklin made the arbitrary choice of calling one of the demo situations positive and one negative. • He also argued that when a certain amount of charge is produced on one body, an equal amount of the opposite charge is produced on the other body… ...
Regents Physics - Forestville Middle
... Conventional current is the direction of positive charge flowing from positive to negative terminals However… Since most current consists of electron flow, in Regents Physics we say current is the flow of negative charge from negative to positive terminals ...
... Conventional current is the direction of positive charge flowing from positive to negative terminals However… Since most current consists of electron flow, in Regents Physics we say current is the flow of negative charge from negative to positive terminals ...
Fall `12 PHY 122 Homework Solutions #2 Chapter 21 Problem 40
... A cube of side l is placed in a uniform field E0 with edges parallel to the field lines. (a) What is the net flux through the cube? (b) What is the flux through each of its six faces? Chapter 22 Problem 6 Figure 22–26 shows five closed surfaces that surround various charges in a plane, as indicated. ...
... A cube of side l is placed in a uniform field E0 with edges parallel to the field lines. (a) What is the net flux through the cube? (b) What is the flux through each of its six faces? Chapter 22 Problem 6 Figure 22–26 shows five closed surfaces that surround various charges in a plane, as indicated. ...
เนื้อหาของรายวิชา 2304104 GEN PHYS II
... เนื้อหา/ขอบเขตรายวิชา รายวิชา 2304104 GEN PHYS II 1) Electrostatic Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric ...
... เนื้อหา/ขอบเขตรายวิชา รายวิชา 2304104 GEN PHYS II 1) Electrostatic Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric ...
Lectronic Plates
... 1. Launch the PhET Sim: Capacitor Lab. For this activity, remain in the Introduction tab. 2. From the Control Panel View section, activate the Plate Charges option. 3. From the Control Panel View section, Electric Field Lines can be activated or not: your call. 4. Click the on-screen button to Disco ...
... 1. Launch the PhET Sim: Capacitor Lab. For this activity, remain in the Introduction tab. 2. From the Control Panel View section, activate the Plate Charges option. 3. From the Control Panel View section, Electric Field Lines can be activated or not: your call. 4. Click the on-screen button to Disco ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.