Electric field strength
... Edexcel Topic 4.4 – Electric and magnetic fields 83. Explain what is meant by an electric field and recognise and use the expression electric field strength E = F / Q. 84. Draw and interpret diagrams using lines of force to describe radial and uniform electric fields qualitatively. 85. Derive and us ...
... Edexcel Topic 4.4 – Electric and magnetic fields 83. Explain what is meant by an electric field and recognise and use the expression electric field strength E = F / Q. 84. Draw and interpret diagrams using lines of force to describe radial and uniform electric fields qualitatively. 85. Derive and us ...
CJ Electrostatics Assignment 1 Solutions
... We wish to deduce the direction of the electric field at the point P, which is directly above the midpoint of the rod. We first imagine dividing the rod up into a large number of small length elements. Since the charge per unit length is the same along the rod, each element will contain an equal amo ...
... We wish to deduce the direction of the electric field at the point P, which is directly above the midpoint of the rod. We first imagine dividing the rod up into a large number of small length elements. Since the charge per unit length is the same along the rod, each element will contain an equal amo ...
Questions 51-52 - ISMScience.org
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
chap5_electricityandmagnetism
... • He referred to a rubber rod, which had been rubbed across a piece of fur as having a negative charge. • A glass rod rubbed with a piece of silk as having a positive charge. • An object whose positive and negative charges exactly balance out is said to be electrically neutral. ...
... • He referred to a rubber rod, which had been rubbed across a piece of fur as having a negative charge. • A glass rod rubbed with a piece of silk as having a positive charge. • An object whose positive and negative charges exactly balance out is said to be electrically neutral. ...
Physics - Electric Fields
... Of course this is also true for gravity. Objects with gravity are surrounded by a gravity field. The thing is that gravity fields aren’t very useful (because gravity is pretty simple), but electric fields are. The electric field E is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. The direct ...
... Of course this is also true for gravity. Objects with gravity are surrounded by a gravity field. The thing is that gravity fields aren’t very useful (because gravity is pretty simple), but electric fields are. The electric field E is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. The direct ...
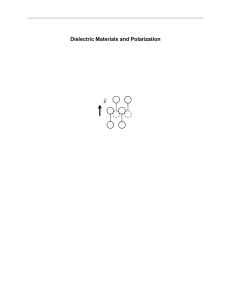
Dielectric Materials and Polarization Chapter 6
... Many more solids are insulators. In an insulator, all of the electrons are bound in atomic ore molecular orbitals and are not free to move about the material. In the case of a metal, an applied electric field will induce a current composed of the freely mobile electrons. In an insulator, or dielectr ...
... Many more solids are insulators. In an insulator, all of the electrons are bound in atomic ore molecular orbitals and are not free to move about the material. In the case of a metal, an applied electric field will induce a current composed of the freely mobile electrons. In an insulator, or dielectr ...
a) In the model with the smaller number of electric field lines. b) In
... centered on the point charge, a bigger sphere would have more area and hence, more actual flux, but, the number of field lines through it (in the model) would be the same as for a smaller sphere. a) Larry is right. b) Larry is wrong. ...
... centered on the point charge, a bigger sphere would have more area and hence, more actual flux, but, the number of field lines through it (in the model) would be the same as for a smaller sphere. a) Larry is right. b) Larry is wrong. ...
24.2 gauss`s law
... product E dA because E and dA are parallel. 3. The dot product in Equation 24.6 is zero because E and d A are perpendicular. 4. The field can be argued to be zero over the surface. ...
... product E dA because E and dA are parallel. 3. The dot product in Equation 24.6 is zero because E and d A are perpendicular. 4. The field can be argued to be zero over the surface. ...
ISP209 Mystery of the Physical World
... • A photon is a small bundle of energy. We see photons in the range of 1.8 eV (red) to 3.1 eV (violet) [1 eV = 1.6E-19 J] ISP209s7 Lecture 13 ...
... • A photon is a small bundle of energy. We see photons in the range of 1.8 eV (red) to 3.1 eV (violet) [1 eV = 1.6E-19 J] ISP209s7 Lecture 13 ...
Electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.