Slide 1
... • Vba is generally referred to as a voltage difference; (units of Vba are volts, V) • Generally defined in terms of derivatives, for infinitesimal variations in charge and energy: dw v dq change in energy Joules ...
... • Vba is generally referred to as a voltage difference; (units of Vba are volts, V) • Generally defined in terms of derivatives, for infinitesimal variations in charge and energy: dw v dq change in energy Joules ...
PHYS 272 Fall 2010 Practice Exam 1
... There are two parts to the Exam 1, part 1 is a machine-graded test (multiple choice problems) and part 2 is a separate test that you turn in to be graded by hand. A formula sheet is provided (see end page). Machine Answer Sheet: Using a pencil, fill in Last Name, First Name, & Middle Initial, plus y ...
... There are two parts to the Exam 1, part 1 is a machine-graded test (multiple choice problems) and part 2 is a separate test that you turn in to be graded by hand. A formula sheet is provided (see end page). Machine Answer Sheet: Using a pencil, fill in Last Name, First Name, & Middle Initial, plus y ...
e - Mr. Schroeder
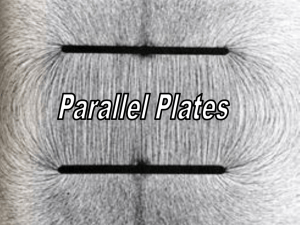
... • Connecting two parallel plates to a battery produces uniform electric field ...
... • Connecting two parallel plates to a battery produces uniform electric field ...
Electrostatic Simulation Questions
... 6. The equation for the force of attraction for gravity looks similar to coulomb’s law: Force= k*m 1*m2 / r2. the only difference is the constant k (smaller for gravity) and the use of masses (m 1,m2) instead of charges. Why are both laws called an Inverse Square Law? Which force can only attract ot ...
... 6. The equation for the force of attraction for gravity looks similar to coulomb’s law: Force= k*m 1*m2 / r2. the only difference is the constant k (smaller for gravity) and the use of masses (m 1,m2) instead of charges. Why are both laws called an Inverse Square Law? Which force can only attract ot ...
Chap. 16 Conceptual Modules Giancoli
... feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
... feels an electrical force of 12 N. If this charge is removed and a 6 C charge is placed at that point instead, what force will it feel? ...
Physics Lecture #22
... a) What is the magnitude of the electric field? b) A proton is placed in that same electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric force on that proton? ...
... a) What is the magnitude of the electric field? b) A proton is placed in that same electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric force on that proton? ...
Ch 21 PPT
... • Electric field (E): a vector quantity that relates the force exerted on a test charge to the size of the test charge ...
... • Electric field (E): a vector quantity that relates the force exerted on a test charge to the size of the test charge ...
The Electric Field
... defined as the net force on a positive test charge q0, divided by q0. Writing this down algebraically: ...
... defined as the net force on a positive test charge q0, divided by q0. Writing this down algebraically: ...
PHY481: Electrostatics Introductory E&M review (2) Course web site: www.pa.msu.edu/courses/phy481
... Same electric field as charge Q at the origin Carl Bromberg - Prof. of Physics ...
... Same electric field as charge Q at the origin Carl Bromberg - Prof. of Physics ...
Chapter 23
... The term point charge refers to a particle of zero size that carries an electric charge The electrical force between two stationary point-charged particles is given by Coulomb’s Law The force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation r between the particles and directed along the lin ...
... The term point charge refers to a particle of zero size that carries an electric charge The electrical force between two stationary point-charged particles is given by Coulomb’s Law The force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation r between the particles and directed along the lin ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.