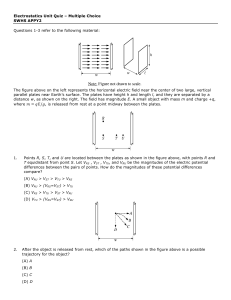
Topic IX – Charge Behavior and Interactions - Science - Miami
... Discuss the patterns and distribution of particles within the atom, including the forces that shape this distribution Compare the magnitude and range of the four fundamental forces Describe the fundamental rule at the base of all electrical phenomena. Understand the properties of electric ch ...
... Discuss the patterns and distribution of particles within the atom, including the forces that shape this distribution Compare the magnitude and range of the four fundamental forces Describe the fundamental rule at the base of all electrical phenomena. Understand the properties of electric ch ...
Electric potential - Mona Shores Blogs
... • Every point in space has an electric potential, no matter what charge. • The potential depends on the size of the charge and how far the charge is from the reference point. – Electric potential is a scalar quantity, so direction does not matter. • But the sign does. ...
... • Every point in space has an electric potential, no matter what charge. • The potential depends on the size of the charge and how far the charge is from the reference point. – Electric potential is a scalar quantity, so direction does not matter. • But the sign does. ...
PHY481: Electrostatics Introductory E&M review (2) Lecture 2
... For symmetric charge distributions, pick enclosing surfaces, so that E and dA are are parallel to each other. – For a point charge at the origin, use a spherical surface, radius R, centered on the charge (makes direction of normal = radial) ...
... For symmetric charge distributions, pick enclosing surfaces, so that E and dA are are parallel to each other. – For a point charge at the origin, use a spherical surface, radius R, centered on the charge (makes direction of normal = radial) ...
electric fields
... SIGN CONVENTION: If the charges are the same, than the electric potential is positive, which makes intuitive sense. If the charges are opposite however, we get a NEGATIVE potential energy. What does this mean? How can you have negative potential? It is really a matter of “relativity”. It is only neg ...
... SIGN CONVENTION: If the charges are the same, than the electric potential is positive, which makes intuitive sense. If the charges are opposite however, we get a NEGATIVE potential energy. What does this mean? How can you have negative potential? It is really a matter of “relativity”. It is only neg ...
Electric Field
... l Let’s define now the electric flux through a surface (for the moment not necessarily a closed surface) ◆ Φ = ETA = EA cosθ ◆ where θ is the angle between the normal to a surface at a particular point and the electric field ...
... l Let’s define now the electric flux through a surface (for the moment not necessarily a closed surface) ◆ Φ = ETA = EA cosθ ◆ where θ is the angle between the normal to a surface at a particular point and the electric field ...
PHYS_2326_012009
... • Relation between field lines and electric field vectors: a. The direction of the tangent to a field line is the direction of the electric field E at that point b. The number of field lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of E: the more field lines the stronger E • Electric field lin ...
... • Relation between field lines and electric field vectors: a. The direction of the tangent to a field line is the direction of the electric field E at that point b. The number of field lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of E: the more field lines the stronger E • Electric field lin ...
Electricity (1)
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.