PP Mass spectrometer and atoms
... • Example questions • Test questions • Other uses of mass spectrometry • Check list ...
... • Example questions • Test questions • Other uses of mass spectrometry • Check list ...
2 October
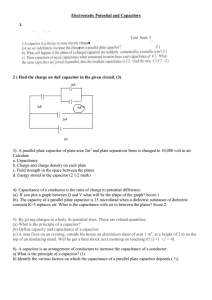
... Other materials besides conductors have capacitance, but arrangements of conductors lend themselves to straightforward calculation of C. Usually this goes as follows: Presume electric charge to be present; say, Q if there is only one conductor, or ±Q if there are two. Either: • Calculate the ele ...
... Other materials besides conductors have capacitance, but arrangements of conductors lend themselves to straightforward calculation of C. Usually this goes as follows: Presume electric charge to be present; say, Q if there is only one conductor, or ±Q if there are two. Either: • Calculate the ele ...
BASIC PHYSICS
... Extensive quantities have character of "amount", such as mass, energy, charge. The extent of extensive quantity of the system is the sum of the amount of this quantity of all subsystems. Intensive quantities describe "state" and cannot be summarized. Examples of intensive ...
... Extensive quantities have character of "amount", such as mass, energy, charge. The extent of extensive quantity of the system is the sum of the amount of this quantity of all subsystems. Intensive quantities describe "state" and cannot be summarized. Examples of intensive ...
Zahn, M., M. Hikita, K.A. Wright, C.M. Cooke, and J. Brennan, Kerr Electro-optic Field Mapping Measurements in Electron Beam Irradiated Polymethylmethacrylate, IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation EI-22, pp. 181-185, April 1987
... cm thick, using aligned polarizers with cw He-Ne Zaser light at 633 nm. Shown are the optical pattern due to mechanical birefringence before application of the electron beam, the resuZting Kerr effect pattern after 15 s of irradiation at energy 2.6 MeV and current density 220 nA/cm2, and the resulti ...
... cm thick, using aligned polarizers with cw He-Ne Zaser light at 633 nm. Shown are the optical pattern due to mechanical birefringence before application of the electron beam, the resuZting Kerr effect pattern after 15 s of irradiation at energy 2.6 MeV and current density 220 nA/cm2, and the resulti ...
SPH4UUnit SummativesJanuary 10, 2014 Electric, Gravitational
... For Coulomb’s law to be applicable, the charges of the two spheres are to be very small and they are small compared to the distance between them. If these conditions are not met, then the presence of a charged sphere forces the charge of each sphere to redistribute on the surface so that r can no lo ...
... For Coulomb’s law to be applicable, the charges of the two spheres are to be very small and they are small compared to the distance between them. If these conditions are not met, then the presence of a charged sphere forces the charge of each sphere to redistribute on the surface so that r can no lo ...
Document
... Evaluate the surface integral (electric flux). Determine the charge inside the Gaussian surface. Solve for E. Don’t forget that to completely specify a vector, your answer must contain ...
... Evaluate the surface integral (electric flux). Determine the charge inside the Gaussian surface. Solve for E. Don’t forget that to completely specify a vector, your answer must contain ...
PHYS_2326_031209
... The electron spins on its axis, giving rise to a electron current in the direction of rotation. Think of the electron as a ball with charge distributed over its surface. When the ball spins, that charge is set in motion around the electron's spin axis, resulting in a magnetic field specific to the ...
... The electron spins on its axis, giving rise to a electron current in the direction of rotation. Think of the electron as a ball with charge distributed over its surface. When the ball spins, that charge is set in motion around the electron's spin axis, resulting in a magnetic field specific to the ...
Electrostatics

Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges with no acceleration.Since classical physics, it has been known that some materials such as amber attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for amber, ήλεκτρον electron, was the source of the word 'electricity'. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law.Even though electrostatically induced forces seem to be rather weak, the electrostatic force between e.g. an electron and a proton, that together make up a hydrogen atom, is about 36 orders of magnitude stronger than the gravitational force acting between them.There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of the plastic wrap to your hand after you remove it from a package, and the attraction of paper to a charged scale, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and the operation of photocopiers. Electrostatics involves the buildup of charge on the surface of objects due to contact with other surfaces. Although charge exchange happens whenever any two surfaces contact and separate, the effects of charge exchange are usually only noticed when at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electrical flow. This is because the charges that transfer to or from the highly resistive surface are more or less trapped there for a long enough time for their effects to be observed. These charges then remain on the object until they either bleed off to ground or are quickly neutralized by a discharge: e.g., the familiar phenomenon of a static 'shock' is caused by the neutralization of charge built up in the body from contact with insulated surfaces.