Slides - gserianne.com
... neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memory (STM) lasts a few seconds to a few ...
... neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memory (STM) lasts a few seconds to a few ...
doc Chapter 8
... Motor nuclei includes the caudate nucleus, the putamen and globus pallidus. Caudate nucleus-a telencephalic nucleus, one of input nuclei of basal ganglia, involved in voluntary movement Putamen-telencephalic nucleus, one of the input nuclei of the basal ganglia, involved with control of voluntary mo ...
... Motor nuclei includes the caudate nucleus, the putamen and globus pallidus. Caudate nucleus-a telencephalic nucleus, one of input nuclei of basal ganglia, involved in voluntary movement Putamen-telencephalic nucleus, one of the input nuclei of the basal ganglia, involved with control of voluntary mo ...
Neuroscience, 4e
... Figure 9.10 Somatic sensory portions of the thalamus and their cortical targets in postcentral gyrus ...
... Figure 9.10 Somatic sensory portions of the thalamus and their cortical targets in postcentral gyrus ...
cortex
... of its course. The superior temporal gyrus lies between this sulcus and the lateral fissure. The auditory cortex, areas 41 and 42, are located on the upper bank of the superior temporal gyrus where it is mostly hidden from view in the depth of the lateral fissure. The inferior temporal sulcus separa ...
... of its course. The superior temporal gyrus lies between this sulcus and the lateral fissure. The auditory cortex, areas 41 and 42, are located on the upper bank of the superior temporal gyrus where it is mostly hidden from view in the depth of the lateral fissure. The inferior temporal sulcus separa ...
1 1 THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Parcellation of the cerebral cortex
... The classical motor area occupies the precentral gyrus, areas 4 and 6, with some spillover into the postcentral gyrus. Stimulation causes a discrete, upside-down somatotopic activation of contralateral muscles through the pyramidal system. The supplementary motor area occupies the medial hemispheric ...
... The classical motor area occupies the precentral gyrus, areas 4 and 6, with some spillover into the postcentral gyrus. Stimulation causes a discrete, upside-down somatotopic activation of contralateral muscles through the pyramidal system. The supplementary motor area occupies the medial hemispheric ...
Nervous System Pt 3
... Cerebral hemispheres form superior part of brain About %80 of brain mass ...
... Cerebral hemispheres form superior part of brain About %80 of brain mass ...
Lecture 37 Notes - MIT OpenCourseWare
... (Many such columnar projections have not been mapped in surface views.) ...
... (Many such columnar projections have not been mapped in surface views.) ...
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Polymicrogyria
... composed of small irregular gyri without intervening sulci or with intervening sulci obliterated and bridged by fusion of their superficial cellular layers (particularly the molecular one). Occasionally, polymicrogyria may have many small or widened gyri separated by shallow sulci (microsulci) (1). ...
... composed of small irregular gyri without intervening sulci or with intervening sulci obliterated and bridged by fusion of their superficial cellular layers (particularly the molecular one). Occasionally, polymicrogyria may have many small or widened gyri separated by shallow sulci (microsulci) (1). ...
Somatic Sensations: General Organization
... Cellular Organization of the Cortex…cont Within the layers the neurons are also arranged in columns. Each column serves a specific sensory modality (i.e., stretch, pressure, touch). Different columns interspersed among each other. interaction of the columns occurs at different cortical leve ...
... Cellular Organization of the Cortex…cont Within the layers the neurons are also arranged in columns. Each column serves a specific sensory modality (i.e., stretch, pressure, touch). Different columns interspersed among each other. interaction of the columns occurs at different cortical leve ...
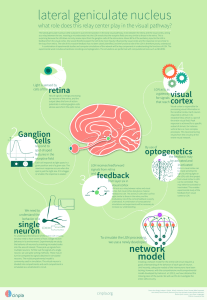
lgn - cinpla
... feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to the input from retina. The role of this massive feedback has not been clearly identified, and the functional role of the LGN is therefore poorly under ...
... feedback from the visual cortex. One would therefore expect the LGN to be more heavily influenced by visual cortex and the response not so similar to the input from retina. The role of this massive feedback has not been clearly identified, and the functional role of the LGN is therefore poorly under ...
48 0007-4888/05/14010048 © 2005 Springer Science+Business
... Kindling significantly decreased the number of GAD-positive cells in the hippocampal fields in comparison with the control: after 2 weeks their count in CA1 field decreased by 56% and after 1 month by 41%, in CA3 field it decreased by 42% after 2 weeks and by 61% after 1 month (Fig. 1). The differen ...
... Kindling significantly decreased the number of GAD-positive cells in the hippocampal fields in comparison with the control: after 2 weeks their count in CA1 field decreased by 56% and after 1 month by 41%, in CA3 field it decreased by 42% after 2 weeks and by 61% after 1 month (Fig. 1). The differen ...
Decision Making: Hitting an uncertain target | eLife
... Figure 1. Target selection and target estimation. (A) In a target selection situation there is a choice between two or more, clearly distinct, options. In this example there are two options (indicated by the two red arrows), and each option is associated with a specific probability of success (indic ...
... Figure 1. Target selection and target estimation. (A) In a target selection situation there is a choice between two or more, clearly distinct, options. In this example there are two options (indicated by the two red arrows), and each option is associated with a specific probability of success (indic ...
Elastic instabilities in a layered cerebral cortex: A revised axonal
... demonstrate that the intracortical buckling drives folding and not axonal tension from the underlying white matter, though the effect of growth of cells outside the cortex, i.e. new white matter, cannot be ruled out [5]. In addition, a quantitative model of buckling of an elastic plate (the top laye ...
... demonstrate that the intracortical buckling drives folding and not axonal tension from the underlying white matter, though the effect of growth of cells outside the cortex, i.e. new white matter, cannot be ruled out [5]. In addition, a quantitative model of buckling of an elastic plate (the top laye ...
The Cerebrum
... series of elevated ridges called gyri (JĪ-rī) » Increase surface area (number of cortical neurons) ...
... series of elevated ridges called gyri (JĪ-rī) » Increase surface area (number of cortical neurons) ...
ling411-11 - Rice University
... “[T]he effective unit of operation…is not the single neuron and its axon, but bundles or groups of cells and their axons with similar functional properties and anatomical connections.” Vernon Mountcastle, Perceptual Neuroscience (1998), p. 192 ...
... “[T]he effective unit of operation…is not the single neuron and its axon, but bundles or groups of cells and their axons with similar functional properties and anatomical connections.” Vernon Mountcastle, Perceptual Neuroscience (1998), p. 192 ...
Sensory Areas
... • Connect portions of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum • Send axons to cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncles The Brain Stem—The Midbrain ...
... • Connect portions of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum • Send axons to cerebellum through the middle cerebellar peduncles The Brain Stem—The Midbrain ...
Motor activity induced by disinhibition of the primary motor cortex of
... after stimulation of the infragranular layers of the motor cortex with low impedance electrodes which produce large current spreads. The rate of the spontaneous EMG activity was approximately of 0.8 + 0.2 Hz. Even though the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another ...
... after stimulation of the infragranular layers of the motor cortex with low impedance electrodes which produce large current spreads. The rate of the spontaneous EMG activity was approximately of 0.8 + 0.2 Hz. Even though the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another ...
Jennifer S. Lund
... wondering over the beauties of nature does not get one very far in exploration of how the cortex might function, so the next years passed quickly indeed as I tried to trace within the primary visual cortex the patterns of ...
... wondering over the beauties of nature does not get one very far in exploration of how the cortex might function, so the next years passed quickly indeed as I tried to trace within the primary visual cortex the patterns of ...
Central Nervous System Functional Anatomy of the Brain
... arrows indicate efferent output of reticular neurons. ...
... arrows indicate efferent output of reticular neurons. ...
4.a. the trigeminal system
... continuous with the dorsal horn. This means it is several cm long and can be involved in lesions of caudal pons and medulla. C. ...
... continuous with the dorsal horn. This means it is several cm long and can be involved in lesions of caudal pons and medulla. C. ...
THE PREFRONTAL CORTEX Connections Dorsolateral
... of information from long-term memory. The dorsolateral PFC takes this information and performs more executive functions, such as monitoring multiple behaviors and manipulating information. Foir example, simple rehearsing a phone number is a ventrolateral PFC function while saying the same number bac ...
... of information from long-term memory. The dorsolateral PFC takes this information and performs more executive functions, such as monitoring multiple behaviors and manipulating information. Foir example, simple rehearsing a phone number is a ventrolateral PFC function while saying the same number bac ...
THE SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM (p.l) 1. Introduction Like the
... Note: toes still get a fairly large amount of tissue, holdover from our primate past Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- ...
... Note: toes still get a fairly large amount of tissue, holdover from our primate past Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- ...
Cerebral cortex

The cerebral cortex is the cerebrum's (brain) outer layer of neural tissue in humans and other mammals. It is divided into two cortices, along the sagittal plane: the left and right cerebral hemispheres divided by the medial longitudinal fissure. The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perception, awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. The human cerebral cortex is 2 to 4 millimetres (0.079 to 0.157 in) thick.In large mammals, the cerebral cortex is folded, giving a much greater surface area in the confined volume of the skull. A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a gyrus (plural gyri) and a groove or fissure is termed a sulcus (plural sulci). In the human brain more than two-thirds of the cerebral cortex is buried in the sulci.The cerebral cortex is gray matter, consisting mainly of cell bodies (with astrocytes being the most abundant cell type in the cortex as well as the human brain as a whole) and capillaries. It contrasts with the underlying white matter, consisting mainly of the white myelinated sheaths of neuronal axons. The phylogenetically most recent part of the cerebral cortex, the neocortex (also called isocortex), is differentiated into six horizontal layers; the more ancient part of the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, has at most three cellular layers. Neurons in various layers connect vertically to form small microcircuits, called cortical columns. Different neocortical regions known as Brodmann areas are distinguished by variations in their cytoarchitectonics (histological structure) and functional roles in sensation, cognition and behavior.