Vocabulary Chapter 18 The Flowering Plant: Form and Function
... A specialized underground plant food storage structure Examples: onions, daffodil bulbs, garlic leaf The flattened food-producing parts of a plant Examples: lettuce, spinach root The anchoring and nutrient and water collecting part of the plant ...
... A specialized underground plant food storage structure Examples: onions, daffodil bulbs, garlic leaf The flattened food-producing parts of a plant Examples: lettuce, spinach root The anchoring and nutrient and water collecting part of the plant ...
gloxinia - Super Floral
... ORIGINS Gloxinias are native to Brazil. HISTORY The modern gloxinia is a hybrid of two Brazilian tropical species, Sinningia speciosa and S. maxima. It arose as a chance seedling raised by a Scottish gardener, John Fyfiana, in the 19th century. ...
... ORIGINS Gloxinias are native to Brazil. HISTORY The modern gloxinia is a hybrid of two Brazilian tropical species, Sinningia speciosa and S. maxima. It arose as a chance seedling raised by a Scottish gardener, John Fyfiana, in the 19th century. ...
Arctic Adaptations Poster
... Fat, fur, and feathers are three common features that keep arctic animals warm by providing insulation from cold air and wind. ...
... Fat, fur, and feathers are three common features that keep arctic animals warm by providing insulation from cold air and wind. ...
2. Lead Plant - Friess Lake School District
... prairie shrub. The leaflets have smooth margins, but are covered with white hairs on their surfaces. ...
... prairie shrub. The leaflets have smooth margins, but are covered with white hairs on their surfaces. ...
Plants Study Guide
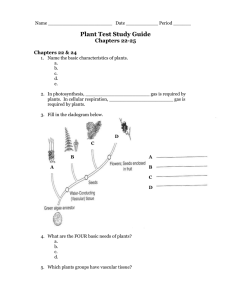
... 13. After fertilization, what happens to the ovary in the diagram? (pg. 278) It develops into a fruit. 14. Germination is when the plant is pushing out of the seed. This occurs when the seed absorbs water. 15. What is the difference between the stomata and the cuticle? stomata—small opening on the u ...
... 13. After fertilization, what happens to the ovary in the diagram? (pg. 278) It develops into a fruit. 14. Germination is when the plant is pushing out of the seed. This occurs when the seed absorbs water. 15. What is the difference between the stomata and the cuticle? stomata—small opening on the u ...
Zephyranthes Candida (White): buy nursery plants
... Difficulty level: easy to grow Planting & Care Zephyranthes are hardy bulbs that range from 5 cm to 30 cm in height; this makes them great for using in rock gardens. They have grass like foliage and bloom from spring to autumn (species dependent). When in bloom, plants carry pink, red, white, or yel ...
... Difficulty level: easy to grow Planting & Care Zephyranthes are hardy bulbs that range from 5 cm to 30 cm in height; this makes them great for using in rock gardens. They have grass like foliage and bloom from spring to autumn (species dependent). When in bloom, plants carry pink, red, white, or yel ...
Science Study Guide: Chapter 2 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants
... 8. In a flower, the stamen makes pollen. 9. Nectar helps flowers become pollinated because animals look for nectar and spread pollen. 10. Plants turn sunlight into energy for reproduction. 11. A fern grows from spores, not seeds. 12. A spore is a single tiny cell. 13. When a plant grows with seeds, ...
... 8. In a flower, the stamen makes pollen. 9. Nectar helps flowers become pollinated because animals look for nectar and spread pollen. 10. Plants turn sunlight into energy for reproduction. 11. A fern grows from spores, not seeds. 12. A spore is a single tiny cell. 13. When a plant grows with seeds, ...
NIMS GROUP OF SCHOOLS,UAE Science worksheet Grade VII L
... L-1 Nutrition in plants 1. Name the following:a. A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition b. The pores through which leaves exchange gases c. A parasitic plant with yellow ,slender and tubular stem ...
... L-1 Nutrition in plants 1. Name the following:a. A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition b. The pores through which leaves exchange gases c. A parasitic plant with yellow ,slender and tubular stem ...
Growing Beans - Communication4All
... A bean is planted in the ground. It is dry and has a tough outer shell. It only takes a few things to make changes happen. ...
... A bean is planted in the ground. It is dry and has a tough outer shell. It only takes a few things to make changes happen. ...
Plants
... It’s a desert plant. It needs very little water, especially in the winter. It likes a lot of sunlight. It has no leaves, but a thick stem with spines. ...
... It’s a desert plant. It needs very little water, especially in the winter. It likes a lot of sunlight. It has no leaves, but a thick stem with spines. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Seeds and Plants
... They are formed in the center part of the flower or fruit They are in different shapes, sizes and colors Flowers make seeds Contains food for the new plant ...
... They are formed in the center part of the flower or fruit They are in different shapes, sizes and colors Flowers make seeds Contains food for the new plant ...
3point1inclassnotes
... Succession: natural changes in an environment that occur over time Refers to natural growth of plants/trees/etc 2 types Primary Secondary ...
... Succession: natural changes in an environment that occur over time Refers to natural growth of plants/trees/etc 2 types Primary Secondary ...
Buffelgrass Identification and Treatment Handout - Arizona
... There are two main ways to remove buffelgrass effectively; if the plant is green, herbicides can be used to kill the plant. Herbicide only works on actively growing plants, thus it has to be green when you spray it. If less than 50% of the plant is green manual removal is the best method. With any r ...
... There are two main ways to remove buffelgrass effectively; if the plant is green, herbicides can be used to kill the plant. Herbicide only works on actively growing plants, thus it has to be green when you spray it. If less than 50% of the plant is green manual removal is the best method. With any r ...
Seedless Plants, Chapter 27
... – produces gametes by mitosis – gametes fuse (fertilization) to form zygote (first stage of sporophyte generation) ...
... – produces gametes by mitosis – gametes fuse (fertilization) to form zygote (first stage of sporophyte generation) ...
Slides
... A person walking 3km/h would need about 27 hours to visually score traits assuming no stopping. Halting at each plot for 30 seconds would require an additional 167 hours (about 7days). ...
... A person walking 3km/h would need about 27 hours to visually score traits assuming no stopping. Halting at each plot for 30 seconds would require an additional 167 hours (about 7days). ...
Study Guide: Plants
... 20. Which part of the plant produces the pollen? ___________________ Which part receives the pollen? __________________ Which part serves to attract herbivores? ____________ Why? ___________________________________________________ 21. Review the equations for photosynthesis & cellular respiration. Y ...
... 20. Which part of the plant produces the pollen? ___________________ Which part receives the pollen? __________________ Which part serves to attract herbivores? ____________ Why? ___________________________________________________ 21. Review the equations for photosynthesis & cellular respiration. Y ...
Native Plants of Groton Informational Poster
... [1] Stritch, Larry. "Plant of the Week." American Witchhazel. USDA, n.d. Web. 14 Nov. 2016..
[2] "Mountain-Laurel." Mountain-Laurel on the Tree Guide at Arborday.org. Arbor Day Foundation, n.d. Web.
05 Dec. 2016.
... [1] Stritch, Larry. "Plant of the Week." American Witchhazel. USDA, n.d. Web. 14 Nov. 2016.
gardenia care sheet - Garden Centers of Colorado
... GARDENIA CARE SHEET The Gardenia, or Cape Jasmine, can be a delight as an indoor foliage plant, although it may be temperamental. In the spring the large, waxy white flowers fill the air with a delightful fragrance. Even without flowers, it is an attractive green plant. TEMPERATURE: Average warmth. ...
... GARDENIA CARE SHEET The Gardenia, or Cape Jasmine, can be a delight as an indoor foliage plant, although it may be temperamental. In the spring the large, waxy white flowers fill the air with a delightful fragrance. Even without flowers, it is an attractive green plant. TEMPERATURE: Average warmth. ...
Opuntia Microdasys, Bunny Ear Cactus - Plant
... Bloom time: Rarely flowers Height: 1.00 to 2.50 feet Difficulty level: easy to grow Planting & Care The vining varieties require a support structure as some can get 15 feet tall. All plants prefer sun to light shade sites with well-draining and moderately fertile soil. Install the plant in the groun ...
... Bloom time: Rarely flowers Height: 1.00 to 2.50 feet Difficulty level: easy to grow Planting & Care The vining varieties require a support structure as some can get 15 feet tall. All plants prefer sun to light shade sites with well-draining and moderately fertile soil. Install the plant in the groun ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.