BIOMES
... Abiotic Factors Nonliving parts influence • The populations of plants of animals • That live in an area ...
... Abiotic Factors Nonliving parts influence • The populations of plants of animals • That live in an area ...
Plants - NVHSIntroBioGorney1
... called a capsid C. Viruses are cellular particles made up of RNA, lysosomes, and proteins D. Viruses are non-living particles that reproduce by combining with other virus particles ...
... called a capsid C. Viruses are cellular particles made up of RNA, lysosomes, and proteins D. Viruses are non-living particles that reproduce by combining with other virus particles ...
Section 22–1 Introduction to Plants (pages 551–555)
... 14. How were early plants similar to today’s mosses? They were simple in structure and grew close to the damp ground. ...
... 14. How were early plants similar to today’s mosses? They were simple in structure and grew close to the damp ground. ...
Plants that can take the heat!!
... about 4" tall and quickly spread to 2' or more in width. It is a a hot, dry western exposure or a rock garden. ...
... about 4" tall and quickly spread to 2' or more in width. It is a a hot, dry western exposure or a rock garden. ...
San Luis Valley Weed Management Association
... SERIOUS CONCERN THAT SHOULD THE RUSSIAN OLIVE CONTINUE TO ESTABLISH ITSELF, IT WILL ...
... SERIOUS CONCERN THAT SHOULD THE RUSSIAN OLIVE CONTINUE TO ESTABLISH ITSELF, IT WILL ...
Structures of Life Module Glossary
... Function: How a structure works or how it is used by an animal. (TG) Germination: The beginning of development of a seed after a period of dormancy or rest. (TG, SS) Growth: When an organism gets bigger and more complex. (TG) Habitat: Where an organism naturally lives. (SS, TG) Head: One of the segm ...
... Function: How a structure works or how it is used by an animal. (TG) Germination: The beginning of development of a seed after a period of dormancy or rest. (TG, SS) Growth: When an organism gets bigger and more complex. (TG) Habitat: Where an organism naturally lives. (SS, TG) Head: One of the segm ...
A Process to Use Food
... 3. Describe two ways that a seed plant can reproduce without seeds. A seed plant reproduces without seeds by producing runners, which are long stems that grow along surface of soil. Another way is by producing rhizomes, which are stems that run underground. A third way is by reproducing from thei ...
... 3. Describe two ways that a seed plant can reproduce without seeds. A seed plant reproduces without seeds by producing runners, which are long stems that grow along surface of soil. Another way is by producing rhizomes, which are stems that run underground. A third way is by reproducing from thei ...
Plants: Keeping plants healthy
... Pupils may look at the following short letters and write replies offering advice on how to look after the plants more effectively: I planted some sunflower seeds in soil and left them in the dark old cupboard under the stairs. I water them every day so why do the plants look unhealthy? Please explai ...
... Pupils may look at the following short letters and write replies offering advice on how to look after the plants more effectively: I planted some sunflower seeds in soil and left them in the dark old cupboard under the stairs. I water them every day so why do the plants look unhealthy? Please explai ...
6115/05 There are 2 separate new dietary... this package, please process accordingly.
... Heracleum lanatum has been widely used both in US and Chinese traditional herbal medicine for century ( Name in Chinese Character b g ), the dry roots are readily available in every Chinese herbal medicine shops in The U S Cow parsnip was also widely employed medicinally by a large number of native ...
... Heracleum lanatum has been widely used both in US and Chinese traditional herbal medicine for century ( Name in Chinese Character b g ), the dry roots are readily available in every Chinese herbal medicine shops in The U S Cow parsnip was also widely employed medicinally by a large number of native ...
Ch. 22 Plant Diversity ppt
... plants must obtain & deliver water to their cells Plants require oxygen for cellular respiration, & carbon dioxide for photosynthesis ...
... plants must obtain & deliver water to their cells Plants require oxygen for cellular respiration, & carbon dioxide for photosynthesis ...
Bookmark - Unit 4: Discovering Plants and Animals
... Living – something that grows, eats/consumes, and produces offspring/babies Non-living – something that is doesn’t grow, and doesn’t produce offspring Antenna – what some creatures like insects use to sense their world, some antenna are for touch, or smell, or taste Wings – parts of a creature that ...
... Living – something that grows, eats/consumes, and produces offspring/babies Non-living – something that is doesn’t grow, and doesn’t produce offspring Antenna – what some creatures like insects use to sense their world, some antenna are for touch, or smell, or taste Wings – parts of a creature that ...
Himalayan Touch-me-not - Harpswell Heritage Land Trust
... Choosing a control technique requires careful thought to the size and severity of the infestation and its proximity to water and other natural resources. The Harpswell Invasive Plant Partnership urges land owners to use mechanical (as opposed to chemical) controls whenever possible. Herbicide applic ...
... Choosing a control technique requires careful thought to the size and severity of the infestation and its proximity to water and other natural resources. The Harpswell Invasive Plant Partnership urges land owners to use mechanical (as opposed to chemical) controls whenever possible. Herbicide applic ...
Classification and Systematics • Nomenclature – the first system of
... • For fossil organisms, frequently a blending of the two is used so that we can identify an unknown fossil but also group it with closely related fossils ...
... • For fossil organisms, frequently a blending of the two is used so that we can identify an unknown fossil but also group it with closely related fossils ...
Access study guide13
... Part II: True or False 31. True or False: Some seed plants are homosporous. 32. True or False: Many mosses can survive in habitats that receive very little rainfall because they can almost completely dry out without dying. 33. True or False: Though there are many species of conifers, most of them ar ...
... Part II: True or False 31. True or False: Some seed plants are homosporous. 32. True or False: Many mosses can survive in habitats that receive very little rainfall because they can almost completely dry out without dying. 33. True or False: Though there are many species of conifers, most of them ar ...
Plant Propagation - MrsLongHorticulture
... the soil where they will grow to a saleable size. • Germination flats are used if they are to be transplanted at a later time. • When reusing germination flats, be sure to sterilize the flats and soil. ...
... the soil where they will grow to a saleable size. • Germination flats are used if they are to be transplanted at a later time. • When reusing germination flats, be sure to sterilize the flats and soil. ...
planting and growing guide
... plant(s). Discard any packing material clinging to the leaves or soil. Pull away any yellow or brown leaves that may have occurred during transit. If you can not plant it into garden or larger pot within a few days, make sure it stays well watered. When ready to plant, do the job as early in the day ...
... plant(s). Discard any packing material clinging to the leaves or soil. Pull away any yellow or brown leaves that may have occurred during transit. If you can not plant it into garden or larger pot within a few days, make sure it stays well watered. When ready to plant, do the job as early in the day ...
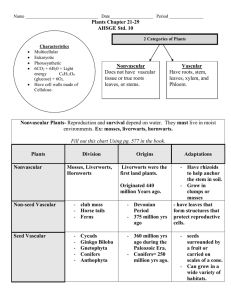
HO3 CH
... 27. Nonvascular plants transport materials within their bodies through the process of ____________________. 28. Vascular tissues are specialized cells that move ____________________, nutrients, and other materials through the plant body. 29. True roots, stems, and leaves are associated with ________ ...
... 27. Nonvascular plants transport materials within their bodies through the process of ____________________. 28. Vascular tissues are specialized cells that move ____________________, nutrients, and other materials through the plant body. 29. True roots, stems, and leaves are associated with ________ ...
student version
... Bees are fuzzy. Their bodies are like Velcro. When they fly over a flower, pollen grains attach to their bodies. When they fly on to the next flower, these pollen grains may get caught on the flower’s stigma. This is why honeybees are referred to as pollinators. FUN Facts of the week: • Bees carry a ...
... Bees are fuzzy. Their bodies are like Velcro. When they fly over a flower, pollen grains attach to their bodies. When they fly on to the next flower, these pollen grains may get caught on the flower’s stigma. This is why honeybees are referred to as pollinators. FUN Facts of the week: • Bees carry a ...
Plants
... b.4.5 Describe how organisms interact with one another in various ways (e.g., many plants depend on animals for carrying pollen or dispersing seeds). ...
... b.4.5 Describe how organisms interact with one another in various ways (e.g., many plants depend on animals for carrying pollen or dispersing seeds). ...
Big Idea 16 - Flowering Plant Reproduction and Life Cycle
... grains from the male anther of the stamen to the female stigma. • Pollen lands on a female pistil, sperm cells move down to the ovary, fertilizing the egg ...
... grains from the male anther of the stamen to the female stigma. • Pollen lands on a female pistil, sperm cells move down to the ovary, fertilizing the egg ...
Plant Notes- teacher copy
... After pollen lands, a pollen tube grows Pollen tube—extension that allows sperm to reach egg inside ovary Angiosperms have “double fertilization” meaning one sperm fertilizes egg and other sperm joins with another cell to form endosperm (nutrients). Seeds contain both endosperm and embryonic ...
... After pollen lands, a pollen tube grows Pollen tube—extension that allows sperm to reach egg inside ovary Angiosperms have “double fertilization” meaning one sperm fertilizes egg and other sperm joins with another cell to form endosperm (nutrients). Seeds contain both endosperm and embryonic ...
Definitions of Food Groups
... display; a dry bone, a dry skin, or other body part does not represent carrion, but will represent other food groups; maggots are a natural occurrence with decomposition and may be present on the carrion, but they should not be considered in grouping the specimen as carrion Crayfish: small freshwate ...
... display; a dry bone, a dry skin, or other body part does not represent carrion, but will represent other food groups; maggots are a natural occurrence with decomposition and may be present on the carrion, but they should not be considered in grouping the specimen as carrion Crayfish: small freshwate ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.