Morning Glory Coastal - Information Sheet
... are easily dispersed by water and garden refuse. It forms dense tangles that smother other more desirable plants and is costly to remove. WHAT IS YOUR LEGAL RESPONSIBILITY? Due to its highly invasive nature, Ipomoea cairica is listed as a Class 4 Noxious Weed under the Noxious Weeds Act 1993. This m ...
... are easily dispersed by water and garden refuse. It forms dense tangles that smother other more desirable plants and is costly to remove. WHAT IS YOUR LEGAL RESPONSIBILITY? Due to its highly invasive nature, Ipomoea cairica is listed as a Class 4 Noxious Weed under the Noxious Weeds Act 1993. This m ...
40. Hepatica - Friess Lake School District
... The one-inch flowers are usually white (but can range from pale pink to lavender) with a yellow center. The flowers do not actually have petals. What look like petals are really delicate, colored sepals (parts that cover the flower buds). The flowers sprout directly from the fibrous root and appear ...
... The one-inch flowers are usually white (but can range from pale pink to lavender) with a yellow center. The flowers do not actually have petals. What look like petals are really delicate, colored sepals (parts that cover the flower buds). The flowers sprout directly from the fibrous root and appear ...
Desert Biogeography Labkey
... aridity to warm dry subsiding airflow associated with subtropical high pressure. In addition, these deserts have westerly airflow that has steered maritime air masses over mountains or cold ocean currents before arriving depleted of moisture. The Sonoran Desert contains many plant species which have ...
... aridity to warm dry subsiding airflow associated with subtropical high pressure. In addition, these deserts have westerly airflow that has steered maritime air masses over mountains or cold ocean currents before arriving depleted of moisture. The Sonoran Desert contains many plant species which have ...
Fiveleaf Akebia
... vine, it tends to be leggy near the base and should be underplanted with low-growing facer plants. It should be planted near a fence, trellis or other landscape structure where it can be trained to grow upwards on it, or allowed to trail off a retaining wall or slope. It grows at a fast rate, and un ...
... vine, it tends to be leggy near the base and should be underplanted with low-growing facer plants. It should be planted near a fence, trellis or other landscape structure where it can be trained to grow upwards on it, or allowed to trail off a retaining wall or slope. It grows at a fast rate, and un ...
File - Mrs. Roberts` Science Resource Page
... Though small in stature, mosses are very important members of our ecosystem. They lay the foundations for other plant growth, prevent erosion, and contribute to the lush green appearance of many forested areas. ...
... Though small in stature, mosses are very important members of our ecosystem. They lay the foundations for other plant growth, prevent erosion, and contribute to the lush green appearance of many forested areas. ...
plants - Images
... • Some plants reproduce asexually by a process called vegetative propagation ...
... • Some plants reproduce asexually by a process called vegetative propagation ...
Mark Scheme - Holly Hall Academy
... Task: You need to design your own plant (flora) that has adapted to live in a rainforest environment. Your plant does not have to be like any existing plant as long as you can explain how it can survive in the rainforest. To start, you should think about the following: a) what the climate of the rai ...
... Task: You need to design your own plant (flora) that has adapted to live in a rainforest environment. Your plant does not have to be like any existing plant as long as you can explain how it can survive in the rainforest. To start, you should think about the following: a) what the climate of the rai ...
HM6 Science Unit A Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Outline - Spring
... 2) Ginkgo trees are large trees, normally reaching a height of 66–115 ft.; some specimens in China are over 160 ft. 3) The deeply fissured, brown bark may appear cork-like in older trees. 4) Its greenish-yellow leaves are fan-shaped and composed of two or more distinct lobes; the Latin species name ...
... 2) Ginkgo trees are large trees, normally reaching a height of 66–115 ft.; some specimens in China are over 160 ft. 3) The deeply fissured, brown bark may appear cork-like in older trees. 4) Its greenish-yellow leaves are fan-shaped and composed of two or more distinct lobes; the Latin species name ...
Name: Period: Date: Lesson 1-6 Study Guide Lesson 1: What are
... For example, when writing the scientific name it needs to be underlined: Homo sapiens For example, when typing the scientific name it needs to be italicized : Homo sapiens ...
... For example, when writing the scientific name it needs to be underlined: Homo sapiens For example, when typing the scientific name it needs to be italicized : Homo sapiens ...
Biology 101: Spring 2007
... Where are the male gametophytes produced? b. Where are the sperm produced? c. How does the pollen grain travel to the female gametophyte (usually?) d. Once the pollen grain reaches the female gametophyte, what must happen in order for the sperm to reach the egg? How long does this take? ...
... Where are the male gametophytes produced? b. Where are the sperm produced? c. How does the pollen grain travel to the female gametophyte (usually?) d. Once the pollen grain reaches the female gametophyte, what must happen in order for the sperm to reach the egg? How long does this take? ...
PLANTS
... and nourish the embryo. Seeds can remain dormant for years before germination. Seeds are dispersed (transported) by animals eating them or carrying them to other locations. ...
... and nourish the embryo. Seeds can remain dormant for years before germination. Seeds are dispersed (transported) by animals eating them or carrying them to other locations. ...
Seeds and Plants - Whitman College
... A seed is the part of the plant that produces the next plant. Think of it like a baby or a pre-baby—an embryo; it grows from a small creature into an adult than can then produce more seeds aka babies/embryos. ...
... A seed is the part of the plant that produces the next plant. Think of it like a baby or a pre-baby—an embryo; it grows from a small creature into an adult than can then produce more seeds aka babies/embryos. ...
Unit V Anatomy and Physiology
... with a plant’s growth responses to light. Abscisic Acid – inhibits growth in response to environmental cues such as lack of water. Jasmonates and Oligosaccharins – help protect plants against pathogens and predators. ...
... with a plant’s growth responses to light. Abscisic Acid – inhibits growth in response to environmental cues such as lack of water. Jasmonates and Oligosaccharins – help protect plants against pathogens and predators. ...
Fortissimo Daffodil
... ends of the stems in mid spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. Its grassy leaves remain dark green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
... ends of the stems in mid spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. Its grassy leaves remain dark green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
Fortissimo Daffodil
... ends of the stems in mid spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. Its grassy leaves remain dark green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
... ends of the stems in mid spring, which are most effective when planted in groupings. The flowers are excellent for cutting. Its grassy leaves remain dark green in color throughout the season. The fruit is not ornamentally significant. ...
Methods of Asexual Propagation: Growing Plants Without Seeds.
... An example would be impatiens and many flowers and vegetable plants ...
... An example would be impatiens and many flowers and vegetable plants ...
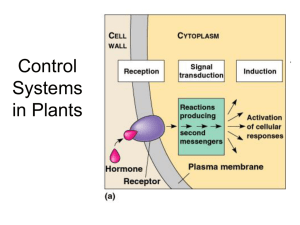
Control Systems in Plants
... growth in response to touch tendrils contacts solid and coils increased production of ethylene ...
... growth in response to touch tendrils contacts solid and coils increased production of ethylene ...
Shamrock Care Sheet
... Within 2 weeks of potting, there is a healthy show of foliage from the bulbs, and flowers within a month. The flowers will last for about 2 months. During this growing period, the plants need night temperatures in the 50’s, constantly moist soil, and a monthly feeding. At the end of the bloom period ...
... Within 2 weeks of potting, there is a healthy show of foliage from the bulbs, and flowers within a month. The flowers will last for about 2 months. During this growing period, the plants need night temperatures in the 50’s, constantly moist soil, and a monthly feeding. At the end of the bloom period ...
Parts of the plant and their functions
... of new cells •protects roots as they push through soil ...
... of new cells •protects roots as they push through soil ...
PRUNING PRETTY PLANTS FOR PERENNIAL PLEASURE By
... After pruning add a 4" pot (measurer - white arrow) of organic fertilizer around each plant. Topdress with compost to enhance the "sweet spot" (center white arrow - zone of active root growth). The "sweet spot" for ALL plants is the top 4-6" of soil (not including mulch). This soil space grows new r ...
... After pruning add a 4" pot (measurer - white arrow) of organic fertilizer around each plant. Topdress with compost to enhance the "sweet spot" (center white arrow - zone of active root growth). The "sweet spot" for ALL plants is the top 4-6" of soil (not including mulch). This soil space grows new r ...
Northeast Texas Chapter - Native Plant Society of Texas
... The flowers are pale yellow and solitary. The flowers seem to rise from the central base of the leaves. They are common in woodlands. We think that this plant is the one my mother found on the clear-cut property next to her home. In riding around the back roads of our East Texas area, we have learne ...
... The flowers are pale yellow and solitary. The flowers seem to rise from the central base of the leaves. They are common in woodlands. We think that this plant is the one my mother found on the clear-cut property next to her home. In riding around the back roads of our East Texas area, we have learne ...
Parts of the plant and their functions
... of new cells •protects roots as they push through soil ...
... of new cells •protects roots as they push through soil ...
Plant ecology

This article is about the scientific discipline, for the journal see Plant EcologyPlant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology which studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.A global overview of the Earth's major vegetation types is provided by O.W. Archibold. He recognizes 11 major vegetation types: tropical forests, tropical savannas, arid regions (deserts), Mediterranean ecosystems, temperate forest ecosystems, temperate grasslands, coniferous forests, tundra (both polar and high mountain), terrestrial wetlands, freshwater ecosystems and coastal/marine systems. This breadth of topics shows the complexity of plant ecology, since it includes plants from floating single-celled algae up to large canopy forming trees.One feature that defines plants is photosynthesis. One of the most important aspects of plant ecology is the role plants have played in creating the oxygenated atmosphere of earth, an event that occurred some 2 billion years ago. It can be dated by the deposition of banded iron formations, distinctive sedimentary rocks with large amounts of iron oxide. At the same time, plants began removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby initiating the process of controlling Earth's climate. A long term trend of the Earth has been toward increasing oxygen and decreasing carbon dioxide, and many other events in the Earths history, like the first movement of life onto land, are likely tied to this sequence of events.One of the early classic books on plant ecology was written by J.E. Weaver and F.E. Clements. It talks broadly about plant communities, and particularly the importance of forces like competition and processes like succession. Although some of the terminology is dated, this important book can still often be obtained in used book stores.Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.The study of plants and vegetation is complicated by their form. First, most plants are rooted in the soil, which makes it difficult to observe and measure nutrient uptake and species interactions. Second, plants often reproduce vegetatively, that is asexually, in a way that makes it difficult to distinguish individual plants. Indeed, the very concept of an individual is doubtful, since even a tree may be regarded as a large collection of linked meristems. Hence, plant ecology and animal ecology have different styles of approach to problems that involve processes like reproduction, dispersal and mutualism. Some plant ecologists have placed considerable emphasis upon trying to treat plant populations as if they were animal populations, focusing on population ecology. Many other ecologists believe that while it is useful to draw upon population ecology to solve certain scientific problems, plants demand that ecologists work with multiple perspectives, appropriate to the problem, the scale and the situation.