Ten thousand Poisonous Plants in the World
... the actual number that are at risk of extinction. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature took a sample of 15,674 plant species and found that 121 were extinct and 9,390 were threatened by extinction. ...
... the actual number that are at risk of extinction. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature took a sample of 15,674 plant species and found that 121 were extinct and 9,390 were threatened by extinction. ...
Creeping Jacob`s Ladder
... Creeping Jacob's Ladder will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. ...
... Creeping Jacob's Ladder will grow to be about 12 inches tall at maturity, with a spread of 18 inches. Its foliage tends to remain dense right to the ground, not requiring facer plants in front. It grows at a medium rate, and under ideal conditions can be expected to live for approximately 10 years. ...
Wedelia - ctahr - University of Hawaii
... inches. Some chemical growth regulators have shown promise in controlling the height of wedelia. Wedelia forms a dense mat and its stems root into the ground as the plant spreads horizontally. The leaves are bright green, 1–3 inches long, oval or three-lobed, toothed, and hairy. The yellow, daisy-li ...
... inches. Some chemical growth regulators have shown promise in controlling the height of wedelia. Wedelia forms a dense mat and its stems root into the ground as the plant spreads horizontally. The leaves are bright green, 1–3 inches long, oval or three-lobed, toothed, and hairy. The yellow, daisy-li ...
Parts of the plants and Functions
... presence of light are converted into sugar and oxygen • 6CO2 +6H2O + 672 kcal = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Carbon + water + light = glucose + oxygen • A kilocalorie is the energy required to heat 1000 grams of water 1 degree C • Food manufactured by the leaves moves downward through the stem to the roots where ...
... presence of light are converted into sugar and oxygen • 6CO2 +6H2O + 672 kcal = C6H12O6 + 6O2 • Carbon + water + light = glucose + oxygen • A kilocalorie is the energy required to heat 1000 grams of water 1 degree C • Food manufactured by the leaves moves downward through the stem to the roots where ...
Plant Unit Interactive Notes
... is an undeveloped baby plant, or embryo. The embryo is surrounded by food for the new plant to use that that it can begin to grow its first root, stem, and leaves. Seeds can grow into small plants, with roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, when given water and light. ...
... is an undeveloped baby plant, or embryo. The embryo is surrounded by food for the new plant to use that that it can begin to grow its first root, stem, and leaves. Seeds can grow into small plants, with roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, when given water and light. ...
section 25.notebook
... At summer’s end, the phytochrome [a pigment that plants use to detect the light] in leaves absorbs less light as days shorten and nights become longer. Auxin production drops, but the production of ethylene increases. ...
... At summer’s end, the phytochrome [a pigment that plants use to detect the light] in leaves absorbs less light as days shorten and nights become longer. Auxin production drops, but the production of ethylene increases. ...
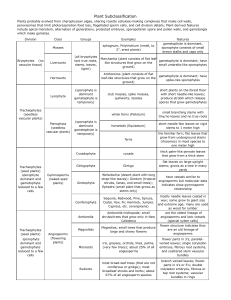
Plant Subclassification
... wax; some grow to giant size and extreme age; many are used as wood for lumber Amborella trichopoda; small are the oldest lineage of shrubs/trees that grow only in New angiosperms and lack vessels Caledonia (special xylem cells) Sequoia, Redwood, Pine, Spruce, Cedar, Yew, Fir, Hemlock, Juniper, Cypr ...
... wax; some grow to giant size and extreme age; many are used as wood for lumber Amborella trichopoda; small are the oldest lineage of shrubs/trees that grow only in New angiosperms and lack vessels Caledonia (special xylem cells) Sequoia, Redwood, Pine, Spruce, Cedar, Yew, Fir, Hemlock, Juniper, Cypr ...
Plant evolution
... diploid (sporophyte) multicellular stages. Meiosis by the sporophyte produces haploid spores that develop by mitosis into the gametophyte. Gametes produced via mitosis by the gametophyte fuse to form the zygote which produces the sporophyte by mitosis. ...
... diploid (sporophyte) multicellular stages. Meiosis by the sporophyte produces haploid spores that develop by mitosis into the gametophyte. Gametes produced via mitosis by the gametophyte fuse to form the zygote which produces the sporophyte by mitosis. ...
Week 1 Topic: Plant anatomy Reading: Chapter 24, sections 1
... and build up layers of old xylem (wood) and old phloem (bark). • Roots: anchor a plant, absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil, and may store starch. Fine root hairs increase the surface area of the roots, increasing the amount of water they can absorb. Common misconceptions: • Cartoons s ...
... and build up layers of old xylem (wood) and old phloem (bark). • Roots: anchor a plant, absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil, and may store starch. Fine root hairs increase the surface area of the roots, increasing the amount of water they can absorb. Common misconceptions: • Cartoons s ...
Chapter 42a
... and build up layers of old xylem (wood) and old phloem (bark). • Roots: anchor a plant, absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil, and may store starch. Fine root hairs increase the surface area of the roots, increasing the amount of water they can absorb. Common misconceptions: • Cartoons s ...
... and build up layers of old xylem (wood) and old phloem (bark). • Roots: anchor a plant, absorb water and dissolved minerals from the soil, and may store starch. Fine root hairs increase the surface area of the roots, increasing the amount of water they can absorb. Common misconceptions: • Cartoons s ...
phaius tankervilliae (grandifolius)
... A terrestrial orchid sometimes referred to as P. grandifolius is commonly called 'Nun's Orchid' or 'Nun's Hood Orchid'. Phaius offers an interesting "new" spring flowering pot plant for the tropical foliage grower or landscaper as well as a potential new cut flower crop. A vigorous plant with thin, ...
... A terrestrial orchid sometimes referred to as P. grandifolius is commonly called 'Nun's Orchid' or 'Nun's Hood Orchid'. Phaius offers an interesting "new" spring flowering pot plant for the tropical foliage grower or landscaper as well as a potential new cut flower crop. A vigorous plant with thin, ...
Australian ecology
... Some plants, called succulents, store water in their stems or leaves; Some plants have no leaves or small seasonal leaves that only grow after it rains. The lack of leaves helps reduce water loss during photosynthesis. Leafless plants conduct photosynthesis in their green stems. Long root systems sp ...
... Some plants, called succulents, store water in their stems or leaves; Some plants have no leaves or small seasonal leaves that only grow after it rains. The lack of leaves helps reduce water loss during photosynthesis. Leafless plants conduct photosynthesis in their green stems. Long root systems sp ...
Classifying Plants coach
... to the leaves. They have other tubes that carry food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. • When the weather is very dry, plants use up the water in their tubes. After this water is gone, their stems get limp and the plants wilt. ...
... to the leaves. They have other tubes that carry food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. • When the weather is very dry, plants use up the water in their tubes. After this water is gone, their stems get limp and the plants wilt. ...
Plant Classification
... Summer annuals complete their life cycle during spring and summer Most winter annuals complete their growing season during fall and winter. ...
... Summer annuals complete their life cycle during spring and summer Most winter annuals complete their growing season during fall and winter. ...
Plant Anatomy and Physiology
... “touch”: cells on contact side grow less than those on opposite side 4. Nastic movements result from touch, shaking, or thermal stimulation: examples – closing of leaves of the “sensitive plant” and “pitcher plant” are due to ion transport out of specific cells (pulvinus and/or trichomes – act as tr ...
... “touch”: cells on contact side grow less than those on opposite side 4. Nastic movements result from touch, shaking, or thermal stimulation: examples – closing of leaves of the “sensitive plant” and “pitcher plant” are due to ion transport out of specific cells (pulvinus and/or trichomes – act as tr ...
Mosses and Liverworts (Non
... Phloem cells carry food that is produced in the leaves down the stems to the roots. (Hint for remembering this term: The “ph” in phloem has the sound of the letter “f.” The word “food” begins with the letter “f.” Phloem cells carry food.) Vascular plants have roots, stems, and leaves. Roots anchor t ...
... Phloem cells carry food that is produced in the leaves down the stems to the roots. (Hint for remembering this term: The “ph” in phloem has the sound of the letter “f.” The word “food” begins with the letter “f.” Phloem cells carry food.) Vascular plants have roots, stems, and leaves. Roots anchor t ...
Plant Diversity Stations Activity
... Brainstorm a list of different structural adaptations of xerophytes. Consider leaf size/shape, root size, location of stomata, possession of special tissues, and other morphological or physiological adaptations enabling them to thrive in dry conditions. Aim for 5-6 items on your list! Then, see th ...
... Brainstorm a list of different structural adaptations of xerophytes. Consider leaf size/shape, root size, location of stomata, possession of special tissues, and other morphological or physiological adaptations enabling them to thrive in dry conditions. Aim for 5-6 items on your list! Then, see th ...
Chapter Three
... It carries water and nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant. Phloem is also a vascular tissue. It carries food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food. Photosynthesis takes place inside leaves. ...
... It carries water and nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant. Phloem is also a vascular tissue. It carries food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food. Photosynthesis takes place inside leaves. ...
Invasive Weeds Guide
... Mass. Assoc. of Conservation Commissions - http://maccweb.org/resources_invasive.html How to manage invasive plants The most effective way generally is to remove the entire plant including the roots. Cutting is also effective, but may need to be repeated. Herbicides can also be used but may affect n ...
... Mass. Assoc. of Conservation Commissions - http://maccweb.org/resources_invasive.html How to manage invasive plants The most effective way generally is to remove the entire plant including the roots. Cutting is also effective, but may need to be repeated. Herbicides can also be used but may affect n ...
PowerPoint
... Synthetic growth regulators are very useful for commercial plant crops They can save money, time and can lead to a better crop There are at least three commercial uses of regulators: 1. Growth regulators are routinely sprayed on crops such as poinsettias, Easter lilies and mums to reduce size an ...
... Synthetic growth regulators are very useful for commercial plant crops They can save money, time and can lead to a better crop There are at least three commercial uses of regulators: 1. Growth regulators are routinely sprayed on crops such as poinsettias, Easter lilies and mums to reduce size an ...
Plants
... b.4.1 Compare the life cycles of different plants including germination, maturity, reproduction and death. b.4.2 Relate plant structures to their specific functions (e.g., growth, survival and reproduction). b.4.5 Describe how organisms interact with one another in various ways (e.g., many plants de ...
... b.4.1 Compare the life cycles of different plants including germination, maturity, reproduction and death. b.4.2 Relate plant structures to their specific functions (e.g., growth, survival and reproduction). b.4.5 Describe how organisms interact with one another in various ways (e.g., many plants de ...
K_U1_L2 Plant Parts
... things by looking at living and nonliving materials. Also, discuss observations of seeds in cups. Have they grown? What stage are they at now? (5 mins max.) 2. Ask children, “Who knows where our food comes from?” Discuss! 3. Ask children, “Do you know that we eat 6 different parts of plants? Does an ...
... things by looking at living and nonliving materials. Also, discuss observations of seeds in cups. Have they grown? What stage are they at now? (5 mins max.) 2. Ask children, “Who knows where our food comes from?” Discuss! 3. Ask children, “Do you know that we eat 6 different parts of plants? Does an ...
Plant physiology
.jpg?width=300)
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants. Closely related fields include plant morphology (structure of plants), plant ecology (interactions with the environment), phytochemistry (biochemistry of plants), cell biology, genetics, biophysics and molecular biology.Fundamental processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tropisms, nastic movements, photoperiodism, photomorphogenesis, circadian rhythms, environmental stress physiology, seed germination, dormancy and stomata function and transpiration, both parts of plant water relations, are studied by plant physiologists.