Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
... • An inability to learn that cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, or health factors An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and teachers Inappropriate types of behavior or feelings under normal circumstances A general pervasive mood of unha ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... defense is called “splitting” – putting some people on a pedestal while devaluing others. Another defense is called “projective identification” - which involves denying one’s feelings, attributing them to someone else, and then behaving in a way that causes the other person to respond in kind. For e ...
... defense is called “splitting” – putting some people on a pedestal while devaluing others. Another defense is called “projective identification” - which involves denying one’s feelings, attributing them to someone else, and then behaving in a way that causes the other person to respond in kind. For e ...
Terms in Psychiatry - Northwest Technology Center
... •Ability to function at school, home or work is affected •Individuals are referred to as addicts ...
... •Ability to function at school, home or work is affected •Individuals are referred to as addicts ...
Genetic Disorder Research Project Introduction: There are
... profound effects on a person’s quality of life. Genetic disorders are passed from parents to offspring in the genetic code, and in some cases, a person may be a carrier for a disease and pass it to their children without knowing. Because genetic diseases are usually caused by errors or mutations in ...
... profound effects on a person’s quality of life. Genetic disorders are passed from parents to offspring in the genetic code, and in some cases, a person may be a carrier for a disease and pass it to their children without knowing. Because genetic diseases are usually caused by errors or mutations in ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Anxiety Symptoms last must longer than usual (6 Mos.) & are not tied to any specific event. Aware of unusually high anxiety, but can’t shake it off or pinpoint the cause. Usually sets in during Childhood or adolescence. ...
... Anxiety Symptoms last must longer than usual (6 Mos.) & are not tied to any specific event. Aware of unusually high anxiety, but can’t shake it off or pinpoint the cause. Usually sets in during Childhood or adolescence. ...
Pathways to psychosis: A comparison of the
... retrospect, the terms “ultra high-risk” or “clinical highrisk” or “At Risk Mental State” (ARMS) are used. The first results of these projects have indicated that ARMS individuals are indeed at imminent risk of psychosis, with transition rates ranging from 15% to 54% after 6 months to 1 year (e.g. Ha ...
... retrospect, the terms “ultra high-risk” or “clinical highrisk” or “At Risk Mental State” (ARMS) are used. The first results of these projects have indicated that ARMS individuals are indeed at imminent risk of psychosis, with transition rates ranging from 15% to 54% after 6 months to 1 year (e.g. Ha ...
- Positive Emotion and Psychopathology Lab
... Research and treatment have traditionally adopted a ‘disorder-focused’ approach by targeting one specific disorder, aiming to understanding its cause, maintenance and treatment. The aim of the present study was to contribute to the burgeoning interest in examining common, or ‘transdiagnostic,’ proces ...
... Research and treatment have traditionally adopted a ‘disorder-focused’ approach by targeting one specific disorder, aiming to understanding its cause, maintenance and treatment. The aim of the present study was to contribute to the burgeoning interest in examining common, or ‘transdiagnostic,’ proces ...
ADHD (TDAH)
... 8. Often has difficulty waiting one's turn. 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
... 8. Often has difficulty waiting one's turn. 9. Often interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games). ...
eating disorder
... after the consumption of small amounts of food. • Crossover between the subtypes over the course of the disorder is not uncommon; therefore, subtype description should be used to describe ...
... after the consumption of small amounts of food. • Crossover between the subtypes over the course of the disorder is not uncommon; therefore, subtype description should be used to describe ...
2017 Exam 1 Q`s and A`s - UCF College of Sciences
... processing, tend to be uncoordinated, and are described as daydreamers, hypoactive (term means lower than usual gross motor activity), in a fog, confused, staring into space, and forgetful. ...
... processing, tend to be uncoordinated, and are described as daydreamers, hypoactive (term means lower than usual gross motor activity), in a fog, confused, staring into space, and forgetful. ...
Dr. Carman Gill Wednesday, April 29th
... No scientific explanation - theories include psychological trauma and abuse Poor family structure (recent death in the family, divorce, relocation) poor diet (lack of nutrition or vitamin deficiencies, underlying medical conditions) neurological disability that causes poor behavior, such as migraine ...
... No scientific explanation - theories include psychological trauma and abuse Poor family structure (recent death in the family, divorce, relocation) poor diet (lack of nutrition or vitamin deficiencies, underlying medical conditions) neurological disability that causes poor behavior, such as migraine ...
Somatoform Disorders, Handout A
... • Symptoms NOT secondary to known medical condition or substance abuse • Results in significant distress or impaired functioning • Coexisting disorders: 60% depression / 50% anxiety disorder / 60% personality disorder ...
... • Symptoms NOT secondary to known medical condition or substance abuse • Results in significant distress or impaired functioning • Coexisting disorders: 60% depression / 50% anxiety disorder / 60% personality disorder ...
Psychiatry—Chronic Pain and Somatoform Disorders
... usually >6m. Despite constant reassurance the patient’s belief remains the same. Symptoms are often consistent with patient’s conception of specific illness. Characteristics 1) Onset is 20-30 4) Often a history of prior physical disease 2) Men = women 5) Causes significant distress and impairment 3) ...
... usually >6m. Despite constant reassurance the patient’s belief remains the same. Symptoms are often consistent with patient’s conception of specific illness. Characteristics 1) Onset is 20-30 4) Often a history of prior physical disease 2) Men = women 5) Causes significant distress and impairment 3) ...
Mental Health PP
... Would you consider plastic surgery or other drastic steps to enhance your appearance? Why or why not? ...
... Would you consider plastic surgery or other drastic steps to enhance your appearance? Why or why not? ...
ADHD - SPED*NET Wilton
... • The symptoms do not occur exclusively during the course of a pervasive developmental disorder, schizophrenia, or other psychotic disorder and are not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g., mood disorder, anxiety disorder, dissociative disorder, personality disorder). ...
... • The symptoms do not occur exclusively during the course of a pervasive developmental disorder, schizophrenia, or other psychotic disorder and are not better accounted for by another mental disorder (e.g., mood disorder, anxiety disorder, dissociative disorder, personality disorder). ...
Impulse Control Disorders - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery
... individuals experience mounting sense of tension or anxiety before fire-setting episode, which sometimes may be in form of building sexual tension and excitement (pyrolagnia). relief of tension and anxiety, or sexual pleasure, is derived when fire-setting impulse is gratified as well as during a ...
... individuals experience mounting sense of tension or anxiety before fire-setting episode, which sometimes may be in form of building sexual tension and excitement (pyrolagnia). relief of tension and anxiety, or sexual pleasure, is derived when fire-setting impulse is gratified as well as during a ...
Slide 1
... • Additionally, patients with somatization disorder may at some point ask what is wrong with them. This is an opportunity to discuss the disorder, using either somatization disorder or its other name, Briquet’s syndrome, to give it a name and to educate patients about the illness. For example, one ...
... • Additionally, patients with somatization disorder may at some point ask what is wrong with them. This is an opportunity to discuss the disorder, using either somatization disorder or its other name, Briquet’s syndrome, to give it a name and to educate patients about the illness. For example, one ...
Mood Disorders09
... May be the result of physical illness and genetics Viruses, brain chemistry & birth trauma may play a role ...
... May be the result of physical illness and genetics Viruses, brain chemistry & birth trauma may play a role ...
Somatoform and Factitious Disorders
... for which no medical basis can be found. Infers that the physical symptoms are associated with psychological factors. The production of symptoms is not under voluntary control. Specific diagnoses depend on the number and kinds of physical symptoms, as well on the cognitive process that may occ ...
... for which no medical basis can be found. Infers that the physical symptoms are associated with psychological factors. The production of symptoms is not under voluntary control. Specific diagnoses depend on the number and kinds of physical symptoms, as well on the cognitive process that may occ ...
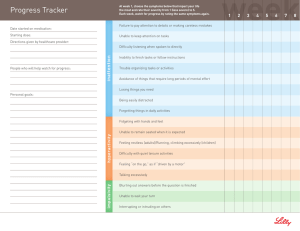
Progress Tracker
... *Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Text Revision. 4th edition. †Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition. References: 1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed, text revision. Washington, DC: Ame ...
... *Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Text Revision. 4th edition. †Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th edition. References: 1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed, text revision. Washington, DC: Ame ...
Chapter 14 Powerpoint
... thoughts • Person may feel guilty or shame of who they are and have negative thoughts on them selves • Avoid the thoughts by going somewhere else ...
... thoughts • Person may feel guilty or shame of who they are and have negative thoughts on them selves • Avoid the thoughts by going somewhere else ...
Rumination syndrome

Rumination syndrome, or Merycism, is an under-diagnosed chronic motility disorder characterized by effortless regurgitation of most meals following consumption, due to the involuntary contraction of the muscles around the abdomen. There is no retching, nausea, heartburn, odour, or abdominal pain associated with the regurgitation, as there is with typical vomiting. The disorder has been historically documented as affecting only infants, young children, and people with cognitive disabilities (the prevalence is as high as 10% in institutionalized patients with various mental disabilities).Today it is being diagnosed in increasing numbers of otherwise healthy adolescents and adults, though there is a lack of awareness of the condition by doctors, patients and the general public.Rumination syndrome presents itself in a variety of ways, with especially high contrast existing between the presentation of the typical adult sufferer without a mental disability and the presentation of an infant and/or mentally impaired sufferer. Like related gastrointestinal disorders, rumination can adversely affect normal functioning and the social lives of individuals. It has been linked with depression.Little comprehensive data regarding rumination syndrome in otherwise healthy individuals exists because most sufferers are private about their illness and are often misdiagnosed due to the number of symptoms and the clinical similarities between rumination syndrome and other disorders of the stomach and esophagus, such as gastroparesis and bulimia nervosa. These symptoms include the acid-induced erosion of the esophagus and enamel, halitosis, malnutrition, severe weight loss and an unquenchable appetite. Individuals may begin regurgitating within a minute following ingestion, and the full cycle of ingestion and regurgitation can mimic the binging and purging of bulimia.Diagnosis of rumination syndrome is non-invasive and based on a history of the individual. Treatment is promising, with upwards of 85% of individuals responding positively to treatment, including infants and the mentally handicapped.