ppt - Click here to
... inconsistent and disorganised medial histories. Has impaired social/work/personal functioning Symptoms may be exacerbated by stress No element of feigning symptoms to occupy sick role (Facititious Disorder) or for material gain (Malingerer) ...
... inconsistent and disorganised medial histories. Has impaired social/work/personal functioning Symptoms may be exacerbated by stress No element of feigning symptoms to occupy sick role (Facititious Disorder) or for material gain (Malingerer) ...
disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence
... – – no intent of clear distinction between “adult’/“childhood” disorders ...
... – – no intent of clear distinction between “adult’/“childhood” disorders ...
Schizophrenia and Related Disorders
... Biological THEORIES Endophenotypes biobehavioral abnormalities linked to genetic and neurobiological causes of mental illness ...
... Biological THEORIES Endophenotypes biobehavioral abnormalities linked to genetic and neurobiological causes of mental illness ...
02 Psychology of personality. Modern theories of personality
... Similar chronic relapsing condition as the somatization disorder. Patients report worse health than do those with chronic medical condition and their report of specific symptoms if they meet the severity criteria is sufficient and need not to be considered legitimate by the clinician. Treatment stra ...
... Similar chronic relapsing condition as the somatization disorder. Patients report worse health than do those with chronic medical condition and their report of specific symptoms if they meet the severity criteria is sufficient and need not to be considered legitimate by the clinician. Treatment stra ...
Eating disorders - Back to Medical School
... condition. We do not, however, accept referrals for individuals who have a current history of substance misuse or dependence and we would ask that such individuals remain abstinent for a period of 6 months before we offer any clinical input. ...
... condition. We do not, however, accept referrals for individuals who have a current history of substance misuse or dependence and we would ask that such individuals remain abstinent for a period of 6 months before we offer any clinical input. ...
Chapter 16 PowerPoint Notes
... Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Personality Disorders Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually witho ...
... Psychological and environmental factors can trigger schizophrenia if the individual is genetically predisposed (Nicols & Gottesman, 1983). Personality Disorders Personality disorders are characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. They are usually witho ...
hi low
... Conversion Disorder A. One or more symptoms or deficits affecting voluntary motor or sensory function that suggests a neurological or general medical condition B. Preceded by a conflict or stressor C. Not intentionally produced D. Cannot be fully explained by a medical condition E. Significant dist ...
... Conversion Disorder A. One or more symptoms or deficits affecting voluntary motor or sensory function that suggests a neurological or general medical condition B. Preceded by a conflict or stressor C. Not intentionally produced D. Cannot be fully explained by a medical condition E. Significant dist ...
Psychological Disorders
... • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events around the abuse. • Generalized amnesia is diagnosed when a person's amnesia encompasses his or ...
... • Selective amnesia happens when a person can recall only small parts of events that took place in a defined period of time. For example, an abuse victim may recall only some parts of the series of events around the abuse. • Generalized amnesia is diagnosed when a person's amnesia encompasses his or ...
Slide 1
... B. Negative Symptoms: behaviors that are notable because of their absence (lack of emotional expression). C. Positive Symptoms: behaviors that are notable because of their presence (hallucinations and delusions). D. What are some positive symptoms? 1) Hallucinations: false sensory experiences. 2) D ...
... B. Negative Symptoms: behaviors that are notable because of their absence (lack of emotional expression). C. Positive Symptoms: behaviors that are notable because of their presence (hallucinations and delusions). D. What are some positive symptoms? 1) Hallucinations: false sensory experiences. 2) D ...
Brief Overview of Common Psychotropic Medications - CE
... seizure disorder, less risk with the slow-release form. 2. Effexor (Venlafaxine)-some believe may be helpful in ADHD and depression. Considered activating. Often used after other antidepressants fail. Mechanism of action also involves increased norepinephrine reuptake blockade as well as serotonin r ...
... seizure disorder, less risk with the slow-release form. 2. Effexor (Venlafaxine)-some believe may be helpful in ADHD and depression. Considered activating. Often used after other antidepressants fail. Mechanism of action also involves increased norepinephrine reuptake blockade as well as serotonin r ...
Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Overview
... • A child must evidence the onset of inattentive or hyperactive symptoms before age 7. In DSM 5 before age 12. • Features must be present in two or more settings (e.g., school, home). • Symptoms in only one setting suggest an environmental or psychodynamic cause, and it is important to distinguish A ...
... • A child must evidence the onset of inattentive or hyperactive symptoms before age 7. In DSM 5 before age 12. • Features must be present in two or more settings (e.g., school, home). • Symptoms in only one setting suggest an environmental or psychodynamic cause, and it is important to distinguish A ...
Celiac Disease and Eating Disorders
... What is IBS? Irritable Bowel Syndrome • A complex digestive condition that occurs in episodes characterized by symptoms of abdominal pain, cramping, constipation or diarrhea, bloating and gassiness. • People with IBS have a sensitive digestive tract in which diet and stress can play a role. • Diet ...
... What is IBS? Irritable Bowel Syndrome • A complex digestive condition that occurs in episodes characterized by symptoms of abdominal pain, cramping, constipation or diarrhea, bloating and gassiness. • People with IBS have a sensitive digestive tract in which diet and stress can play a role. • Diet ...
Bianca_Paranoid Personality Disorder
... Schizophrenia, a mood disorder with psychotic features, or another Psychotic Disorder and is not due to the direct physiological effects of a general medical condition. ...
... Schizophrenia, a mood disorder with psychotic features, or another Psychotic Disorder and is not due to the direct physiological effects of a general medical condition. ...
Schizophrenia and assotiated disorders
... Bleuler shifted the emphasis in schizophrenia from course and outcome to the cross-sectional study of symptoms, esssentially broadening the concept of the disease and give a more generous ...
... Bleuler shifted the emphasis in schizophrenia from course and outcome to the cross-sectional study of symptoms, esssentially broadening the concept of the disease and give a more generous ...
Agoraphobia : A fear of going out to public places. Amnesia: A
... situation that presents no realistic danger. Positive symptoms: Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral excesses or peculiarities, such as hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and wild flights of ideas. Preparedness: A species-specific predisposition to be conditioned in certain ways ...
... situation that presents no realistic danger. Positive symptoms: Schizophrenic symptoms that involve behavioral excesses or peculiarities, such as hallucinations, delusions, bizarre behavior, and wild flights of ideas. Preparedness: A species-specific predisposition to be conditioned in certain ways ...
Document
... • often no memory of a traumatic experience • traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
... • often no memory of a traumatic experience • traumatic experience may not produce phobia ...
Chapter 18---Psychological Disorders new
... by sudden lost of memory following a stressful or traumatic event Typically can’t remember any events that occurred for a certain period of time surrounding the traumatic event May forget all prior experiences, personal information, own name, family and friends May last a few hours or years ...
... by sudden lost of memory following a stressful or traumatic event Typically can’t remember any events that occurred for a certain period of time surrounding the traumatic event May forget all prior experiences, personal information, own name, family and friends May last a few hours or years ...
Integrative Model of Rumination - Open Research Exeter
... Rescorla & Wagner, 1972), in which (1) habits are acquired when responses are contingent on stimulus contexts; (2) S-R habit strength is not mediated by goals; (3) Because habits are acquired slowly, they extinguish or counter-condition slowly. We propose that these principles provide a useful frame ...
... Rescorla & Wagner, 1972), in which (1) habits are acquired when responses are contingent on stimulus contexts; (2) S-R habit strength is not mediated by goals; (3) Because habits are acquired slowly, they extinguish or counter-condition slowly. We propose that these principles provide a useful frame ...
disorders - Journal of Medical Science
... characteristics showed that in patients with CD, clinical anxiety was present in 43% of patients while 73% had clinical depression15. Other similar study with a small sample size reported 98% of the patients with conversion disorder to have comorbid complaints of anxiety and somatic symptoms16. The ...
... characteristics showed that in patients with CD, clinical anxiety was present in 43% of patients while 73% had clinical depression15. Other similar study with a small sample size reported 98% of the patients with conversion disorder to have comorbid complaints of anxiety and somatic symptoms16. The ...
Handouts Ch 9
... not be linked to a particular DSM-IV diagnostic category (DSM-IV, 844). Culture-bound syndromes are generally limited to specific societies or areas and indicate repetitive and troubling sets of experiences and observations. Consider examples of some culture-bound disorders. Try to find both central ...
... not be linked to a particular DSM-IV diagnostic category (DSM-IV, 844). Culture-bound syndromes are generally limited to specific societies or areas and indicate repetitive and troubling sets of experiences and observations. Consider examples of some culture-bound disorders. Try to find both central ...
Cotard`s syndrome. A three-case report
... while the relevant terms can’t be found in the modern diagnostic array, the question of whether the clinical state corresponds to a special nosologic being or whether it is an important indicator of seriousness or chronicity seems to remain unanswered. The syndrome appeared as case report more than ...
... while the relevant terms can’t be found in the modern diagnostic array, the question of whether the clinical state corresponds to a special nosologic being or whether it is an important indicator of seriousness or chronicity seems to remain unanswered. The syndrome appeared as case report more than ...
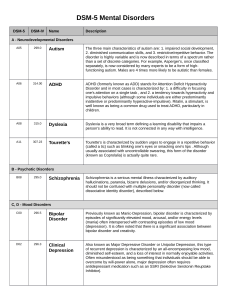
DSM V Mental Disorders
... hypochondriac. Such as person constantly worries about their health even when they have no reason to do so and often any minor symptom is perceived as being a sign of a serious illness. ...
... hypochondriac. Such as person constantly worries about their health even when they have no reason to do so and often any minor symptom is perceived as being a sign of a serious illness. ...
Psychological disorders
... • Significantly increased risk of suffering pain, death, disability or loss ...
... • Significantly increased risk of suffering pain, death, disability or loss ...
Psychological Disorders
... Involves existence of two or more personalities within a single individual Other personalities do not know of the other’s existence Two personalities control behavior Person suffering usually severely abused in ...
... Involves existence of two or more personalities within a single individual Other personalities do not know of the other’s existence Two personalities control behavior Person suffering usually severely abused in ...
Rumination syndrome

Rumination syndrome, or Merycism, is an under-diagnosed chronic motility disorder characterized by effortless regurgitation of most meals following consumption, due to the involuntary contraction of the muscles around the abdomen. There is no retching, nausea, heartburn, odour, or abdominal pain associated with the regurgitation, as there is with typical vomiting. The disorder has been historically documented as affecting only infants, young children, and people with cognitive disabilities (the prevalence is as high as 10% in institutionalized patients with various mental disabilities).Today it is being diagnosed in increasing numbers of otherwise healthy adolescents and adults, though there is a lack of awareness of the condition by doctors, patients and the general public.Rumination syndrome presents itself in a variety of ways, with especially high contrast existing between the presentation of the typical adult sufferer without a mental disability and the presentation of an infant and/or mentally impaired sufferer. Like related gastrointestinal disorders, rumination can adversely affect normal functioning and the social lives of individuals. It has been linked with depression.Little comprehensive data regarding rumination syndrome in otherwise healthy individuals exists because most sufferers are private about their illness and are often misdiagnosed due to the number of symptoms and the clinical similarities between rumination syndrome and other disorders of the stomach and esophagus, such as gastroparesis and bulimia nervosa. These symptoms include the acid-induced erosion of the esophagus and enamel, halitosis, malnutrition, severe weight loss and an unquenchable appetite. Individuals may begin regurgitating within a minute following ingestion, and the full cycle of ingestion and regurgitation can mimic the binging and purging of bulimia.Diagnosis of rumination syndrome is non-invasive and based on a history of the individual. Treatment is promising, with upwards of 85% of individuals responding positively to treatment, including infants and the mentally handicapped.