Pomerantz chapter 7 ppt
... Feel like “not the only one” Acknowledge significance of problem Access treatment Stigma damages self-image Stereotyping by those who know the client Legal consequences ...
... Feel like “not the only one” Acknowledge significance of problem Access treatment Stigma damages self-image Stereotyping by those who know the client Legal consequences ...
Class 8: Mental Illness and Diagnosis
... 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning at the higher or lower end of the 10-point range. For example, consider an individual who hears voices that do not influence his behavior (e.g., someone with long standing Schiz ...
... 4. To determine the specific GAF rating within the selected 10-point range, consider whether the individual is functioning at the higher or lower end of the 10-point range. For example, consider an individual who hears voices that do not influence his behavior (e.g., someone with long standing Schiz ...
McKenna - Rutgers Psychology
... to quiz yourself as part of your study. In class lecture notes: Lecture notes will be provided for you on the Sakai website (resource section). These notes are not intended to be the only source of information for the exams. Please note that additional information will be presented in lecture apart ...
... to quiz yourself as part of your study. In class lecture notes: Lecture notes will be provided for you on the Sakai website (resource section). These notes are not intended to be the only source of information for the exams. Please note that additional information will be presented in lecture apart ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – treatment usually invoves cognitive-behavioral therapy and general stress management treatment (gain retained after 1 year follow-up) ...
... – treatment usually invoves cognitive-behavioral therapy and general stress management treatment (gain retained after 1 year follow-up) ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – treatment usually invoves cognitive-behavioral therapy and general stress management treatment (gain retained after 1 year follow-up) ...
... – treatment usually invoves cognitive-behavioral therapy and general stress management treatment (gain retained after 1 year follow-up) ...
Mental Disorders - North Allegheny School District
... Signs of a mental disorder usually occur frequently and over a long period of time Signs are not always easy to identify What is normal behavior in one culture may not be in another There are more than________ types of mental disorders which are recognized 1 in 10 children in the US suffer from ...
... Signs of a mental disorder usually occur frequently and over a long period of time Signs are not always easy to identify What is normal behavior in one culture may not be in another There are more than________ types of mental disorders which are recognized 1 in 10 children in the US suffer from ...
Mental Disorders
... person starves his or her body and weighs 15% or more below the healthful body weight for his/her age/gender ...
... person starves his or her body and weighs 15% or more below the healthful body weight for his/her age/gender ...
Dissociative, Personality, and Somatoform Disorders
... 50-5. Describe somatoform disorders, and explain how the symptoms differ from other physical symptoms. Somatoform disorders are psychological disorders in which the symptoms take a bodily (somatic) form without apparent physical cause. One person may have complaints ranging from dizziness to blurred ...
... 50-5. Describe somatoform disorders, and explain how the symptoms differ from other physical symptoms. Somatoform disorders are psychological disorders in which the symptoms take a bodily (somatic) form without apparent physical cause. One person may have complaints ranging from dizziness to blurred ...
Abnormal Psychology
... other sensory or motor failure without a physical cause 4) Factitious disorder lying about physical or psychological symptoms, injury or disease; person presents themselves ill, impaired or injured Causes: Illness Anxiety disorder – learned behavior, more sensitive to changes within the body, and ju ...
... other sensory or motor failure without a physical cause 4) Factitious disorder lying about physical or psychological symptoms, injury or disease; person presents themselves ill, impaired or injured Causes: Illness Anxiety disorder – learned behavior, more sensitive to changes within the body, and ju ...
PS1000: Introduction to Abnormal Psychology Mood disorders and
... order to reduce the anxiety caused by obsessive thoughts • Fears dire consequences if act is not performed • Frequency with which such acts are performed can be staggering ...
... order to reduce the anxiety caused by obsessive thoughts • Fears dire consequences if act is not performed • Frequency with which such acts are performed can be staggering ...
Sample Student Informative Speech Outline
... 5. adopting a miserly spending style toward both self and others; money is viewed as something to be hoarded for future catastrophes a) They are anxious about things which may go wrong in their lives, and as a result, hoard large amounts of money for emergency purposes. b) For them, money isn’t some ...
... 5. adopting a miserly spending style toward both self and others; money is viewed as something to be hoarded for future catastrophes a) They are anxious about things which may go wrong in their lives, and as a result, hoard large amounts of money for emergency purposes. b) For them, money isn’t some ...
Mood Disorders
... Pediatric/Adolescent Psychiatry, reports that “All of the features of ADHD can be seen in mood disorders at times, so ADHD is a diagnosis reached only after ruling out a mood disorder.” (p. 39) Papolos, D. & Papolos, J., (2006). The Bipolar Child: The Definitive and Reassuring Guide to Childhood’s M ...
... Pediatric/Adolescent Psychiatry, reports that “All of the features of ADHD can be seen in mood disorders at times, so ADHD is a diagnosis reached only after ruling out a mood disorder.” (p. 39) Papolos, D. & Papolos, J., (2006). The Bipolar Child: The Definitive and Reassuring Guide to Childhood’s M ...
College Student`s Mental Health
... • Myth #7: Depression and other illnesses, such as anxiety disorders, do not affect children or adolescents. Any problems they have are just a part of growing up. • Myth #8: If you have a mental illness, you can will it away. Being treated for a psychiatric disorder means an individual has in some w ...
... • Myth #7: Depression and other illnesses, such as anxiety disorders, do not affect children or adolescents. Any problems they have are just a part of growing up. • Myth #8: If you have a mental illness, you can will it away. Being treated for a psychiatric disorder means an individual has in some w ...
Eating and Sexual Disorders
... • Restricting type; lose weight primarily through dieting, fasting, or excessive exercising • Binge-eating/Purging type. engage regularly in binge eating followed by purging. Binge eating means consuming a large amount of food (far greater than most people eat at one time) in a discrete period of us ...
... • Restricting type; lose weight primarily through dieting, fasting, or excessive exercising • Binge-eating/Purging type. engage regularly in binge eating followed by purging. Binge eating means consuming a large amount of food (far greater than most people eat at one time) in a discrete period of us ...
Drug Intoxication and Withdrawal
... impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning • Symptoms not due to GMC or other mental disorder. ...
... impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning • Symptoms not due to GMC or other mental disorder. ...
November 8, 2012
... o Schizophrenia is not Dissociative Identity Disorder (Multiple Personality Disorder) o Individuals with schizophrenics do not tend to be violent towards themselves or others 10% have violence; more often than not it’s towards them. o Not all cases are chronic 1/3 are chronic, 1/3 are variable c ...
... o Schizophrenia is not Dissociative Identity Disorder (Multiple Personality Disorder) o Individuals with schizophrenics do not tend to be violent towards themselves or others 10% have violence; more often than not it’s towards them. o Not all cases are chronic 1/3 are chronic, 1/3 are variable c ...
(2) loss of interest or pleasure. Major depressive disorder
... MOOD DISORDERS Diagnostic issues – Types of symptoms • Mood and Emotion ...
... MOOD DISORDERS Diagnostic issues – Types of symptoms • Mood and Emotion ...
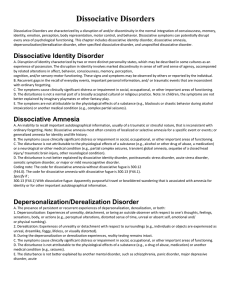
Dissociative Disorders
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
... A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states, which may be described in some cultures as an experience of possession. The disruption in identity involves marked discontinuity in sense of self and sense of agency, accompanied by related alterations in affect, beh ...
The prevalence of the psychiatric disorders in the Endocrinological
... The lowered mood varies little from day to day, and is often unresponsive to circumstances, yet may show a characteristic diurnal variation as the day goes on. In some cases, anxiety, distress and motor agitation may be more prominent at times than the depression and the mood change may also be mask ...
... The lowered mood varies little from day to day, and is often unresponsive to circumstances, yet may show a characteristic diurnal variation as the day goes on. In some cases, anxiety, distress and motor agitation may be more prominent at times than the depression and the mood change may also be mask ...
Psychological Disorders
... A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed o ...
... A mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state. Medical model The concept that diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. When applied to psychological disorders, the medical model assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed o ...
abnormal PSYCHOLOGY Third Canadian Edition
... • Usually begins in adolescence and has a chronic course • Comorbid with personality disorders, anxiety disorders, and depression • Note. Inclusion in DSM-IV-TR is controversial because unlike other dissociative disorders it does not involves disturbance of memory ...
... • Usually begins in adolescence and has a chronic course • Comorbid with personality disorders, anxiety disorders, and depression • Note. Inclusion in DSM-IV-TR is controversial because unlike other dissociative disorders it does not involves disturbance of memory ...
SHIP conference July 31 2012 Linda Grossman M.D. Anna Maria Wilms Floet M.D.
... No consistent research findings regarding food ...
... No consistent research findings regarding food ...
depressive disorders
... Additionally, there is ongoing evidence of deteriorating social and intellectual functioning. The diagnosis must be made before age 45 and symptoms must persist for at least 6 months. The Schizophrenic Experience ...
... Additionally, there is ongoing evidence of deteriorating social and intellectual functioning. The diagnosis must be made before age 45 and symptoms must persist for at least 6 months. The Schizophrenic Experience ...
Clinical Characteristics
... hyperactivity and hyper imagination, and a depressive phase of inhibition, slowness to conceive ideas and move, and anxiety or sadness. A mild mood disorder which is sometimes seen as more of a personality trait than an illness. Characterised by repetitive periods of mild depression followed by peri ...
... hyperactivity and hyper imagination, and a depressive phase of inhibition, slowness to conceive ideas and move, and anxiety or sadness. A mild mood disorder which is sometimes seen as more of a personality trait than an illness. Characterised by repetitive periods of mild depression followed by peri ...
Rumination syndrome

Rumination syndrome, or Merycism, is an under-diagnosed chronic motility disorder characterized by effortless regurgitation of most meals following consumption, due to the involuntary contraction of the muscles around the abdomen. There is no retching, nausea, heartburn, odour, or abdominal pain associated with the regurgitation, as there is with typical vomiting. The disorder has been historically documented as affecting only infants, young children, and people with cognitive disabilities (the prevalence is as high as 10% in institutionalized patients with various mental disabilities).Today it is being diagnosed in increasing numbers of otherwise healthy adolescents and adults, though there is a lack of awareness of the condition by doctors, patients and the general public.Rumination syndrome presents itself in a variety of ways, with especially high contrast existing between the presentation of the typical adult sufferer without a mental disability and the presentation of an infant and/or mentally impaired sufferer. Like related gastrointestinal disorders, rumination can adversely affect normal functioning and the social lives of individuals. It has been linked with depression.Little comprehensive data regarding rumination syndrome in otherwise healthy individuals exists because most sufferers are private about their illness and are often misdiagnosed due to the number of symptoms and the clinical similarities between rumination syndrome and other disorders of the stomach and esophagus, such as gastroparesis and bulimia nervosa. These symptoms include the acid-induced erosion of the esophagus and enamel, halitosis, malnutrition, severe weight loss and an unquenchable appetite. Individuals may begin regurgitating within a minute following ingestion, and the full cycle of ingestion and regurgitation can mimic the binging and purging of bulimia.Diagnosis of rumination syndrome is non-invasive and based on a history of the individual. Treatment is promising, with upwards of 85% of individuals responding positively to treatment, including infants and the mentally handicapped.