disorders - Journal of Medical Science
... females compared to males, with a ratio between 2:1 and 10:1. CD is also more prevalent in rural areas, in developing countries, among people of low socioeconomic classes, among undereducated people, and among those with relatively low medical knowledge4. Although CD may develop at any time between ...
... females compared to males, with a ratio between 2:1 and 10:1. CD is also more prevalent in rural areas, in developing countries, among people of low socioeconomic classes, among undereducated people, and among those with relatively low medical knowledge4. Although CD may develop at any time between ...
Mental & Behavioral Disorders - American Academy of Disability
... for legal purposes on behalf of their own patients.” “The dual role can be detrimental to the therapeutic relationship, can be a considerable source of examiner bias, and can compromise the patient’s legal claim.” ...
... for legal purposes on behalf of their own patients.” “The dual role can be detrimental to the therapeutic relationship, can be a considerable source of examiner bias, and can compromise the patient’s legal claim.” ...
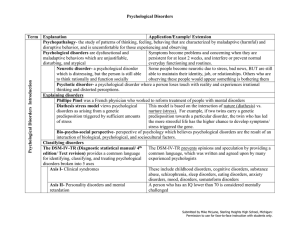
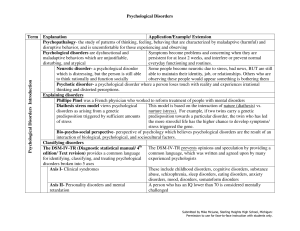
Psychological Disorders Term Explanation Application
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
... Causes of anxiety disorders Heredity- some people have a genetic predisposition that could lead to the development of an anxiety disorder Brain- people who have anxiety disorders Frontal lobes are in charge of thinking and planning, which could experience heightened activity in frontal explain why h ...
PowerPoint * Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2
... affect, perceptions, and/or memories. This disruption may be observed by others or reported by the patient • B. At least two of the alters recurrently take control of behavior • C. Inability of at least one of the alters to recall important personal information • D. Symptoms are not part of a broadl ...
... affect, perceptions, and/or memories. This disruption may be observed by others or reported by the patient • B. At least two of the alters recurrently take control of behavior • C. Inability of at least one of the alters to recall important personal information • D. Symptoms are not part of a broadl ...
chapter 15 - Cengage Learning
... 15. State the causes, according to the various theoretical models, of dissociative disorders. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 16. Define mood disorders. Give a brief description of major depressive disorder, delusions, and dysthymic disorder. (see “Mood Disorders”; see also “Depressive Disorders”) 17 ...
... 15. State the causes, according to the various theoretical models, of dissociative disorders. (see “Dissociative Disorders”) 16. Define mood disorders. Give a brief description of major depressive disorder, delusions, and dysthymic disorder. (see “Mood Disorders”; see also “Depressive Disorders”) 17 ...
A Survival Guide to the DSM-5
... problems at school. Upon assessment, child is found to meet criteria for ADHD ...
... problems at school. Upon assessment, child is found to meet criteria for ADHD ...