Chapter 27 SEVERE PSYCHIATRIC ILLNESS IN THE MILITARY
... but lasts for a lifetime) may be possible only after clinical observation. Often the clinician will need to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disord ...
... but lasts for a lifetime) may be possible only after clinical observation. Often the clinician will need to wait to see if the symptoms persist over time; it is estimated that 25% of these cases will resolve.3 Unfortunately for many patients, both brief psychotic disorder and schizophreniform disord ...
Presentation
... make-believe play or social imitative play) • Symptoms may not be (or have been) fully apparent “until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life” ...
... make-believe play or social imitative play) • Symptoms may not be (or have been) fully apparent “until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by learned strategies in later life” ...
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
... Should OCD be classified as an anxiety disorder? Do subtypes exist, each with different causes (for example, early onset OCD, OCD with co-morbid tics, compulsive hoarding)? Are hypochondriasis, body dysmorphic disorder, and other “spectrum” disorders variants or completely separate disorders? ...
... Should OCD be classified as an anxiety disorder? Do subtypes exist, each with different causes (for example, early onset OCD, OCD with co-morbid tics, compulsive hoarding)? Are hypochondriasis, body dysmorphic disorder, and other “spectrum” disorders variants or completely separate disorders? ...
Mood Disorders/ Reflection Paper - Jay
... experiences changes in their mood such as abnormally elevated irritation and energy levels. People with mania tend to an inflated self-esteem, fights of ideas, and they can be much more talkative. The word Mania derived from the Greek "μανία" meaning “mad, frenzy”. Bipolar disorder also known as man ...
... experiences changes in their mood such as abnormally elevated irritation and energy levels. People with mania tend to an inflated self-esteem, fights of ideas, and they can be much more talkative. The word Mania derived from the Greek "μανία" meaning “mad, frenzy”. Bipolar disorder also known as man ...
Please keep track of any disorders discussed that you would like to
... • A. Five or more of the following within 2-week period (change from previous functioning) (cannot be due to GMC or a symptom of a psychotic disorder [e.g., Catatonic Schizophrenia]) – Must Include one of: depressed mood and/or loss of interest or pleasure – Depressed mood most of the day, nearly ev ...
... • A. Five or more of the following within 2-week period (change from previous functioning) (cannot be due to GMC or a symptom of a psychotic disorder [e.g., Catatonic Schizophrenia]) – Must Include one of: depressed mood and/or loss of interest or pleasure – Depressed mood most of the day, nearly ev ...
somatoform disorders
... Somatoform Disorders •To be definitely diagnosed with somatoform disorder ...
... Somatoform Disorders •To be definitely diagnosed with somatoform disorder ...
Hypomania: A brief review of conceptual and diagnostic
... with hypomanic episodes will lead to a diagnosis of bipolar II, whilst depression with mania leads to a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder. Both disorders have different prognoses, and require different treatment1. Thus clear diagnostic criteria are needed, but are often indistinct. This occurs in rese ...
... with hypomanic episodes will lead to a diagnosis of bipolar II, whilst depression with mania leads to a diagnosis of bipolar I disorder. Both disorders have different prognoses, and require different treatment1. Thus clear diagnostic criteria are needed, but are often indistinct. This occurs in rese ...
Anxiety Disorders - Home
... – Develop anxiety, worry, or fear about another attack – Many develop agoraphobia • Prevalence of panic disorder – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are f ...
... – Develop anxiety, worry, or fear about another attack – Many develop agoraphobia • Prevalence of panic disorder – Affects about 2.7% (in a year) & 4.7% (in a lifetime) of the general population – Onset is often acute, median between 20 and 24 years of age – 75% of individuals with agoraphobia are f ...
Depression
... Complicates nursing/medical care: higher use of health care system Increase costs Diminishes quality of life for the family Increase mortality ...
... Complicates nursing/medical care: higher use of health care system Increase costs Diminishes quality of life for the family Increase mortality ...
Psychological Disorders
... People with the negative symptoms of schizophrenia will often neglect themselves and their appearance and alcohol and substance abuse is quite common. Chronic (process) schizophrenia: characterized by long periods of symptom development and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, such as flat affect. Do ...
... People with the negative symptoms of schizophrenia will often neglect themselves and their appearance and alcohol and substance abuse is quite common. Chronic (process) schizophrenia: characterized by long periods of symptom development and negative symptoms of schizophrenia, such as flat affect. Do ...
RECOGNISING BIPOLAR DISORDERS IN PRIMARY CARE
... mania or hypomania. This side of Bipolarity may only be apparent in retrospect, or via a third party, because individuals would be unlikely to see their GP if they felt energised, euphoric and not needing sleep. However, irritability (common in depression, hypomania, mania and mixed states) and pers ...
... mania or hypomania. This side of Bipolarity may only be apparent in retrospect, or via a third party, because individuals would be unlikely to see their GP if they felt energised, euphoric and not needing sleep. However, irritability (common in depression, hypomania, mania and mixed states) and pers ...
Bipolar Disorder - Psychiatric Services, PC
... People with bipolar disorder can lead healthy and productive lives when the illness is effectively treated (see below—"How Is Bipolar Disorder Treated?"). Without treatment, however, the natural course of bipolar disorder tends to worsen. Over time a person may suffer more frequent (more rapid-cycli ...
... People with bipolar disorder can lead healthy and productive lives when the illness is effectively treated (see below—"How Is Bipolar Disorder Treated?"). Without treatment, however, the natural course of bipolar disorder tends to worsen. Over time a person may suffer more frequent (more rapid-cycli ...
The improvement of living. How do people cope with modern
... communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism involves many parts of the brain; how this occurs is not well understood. The two other autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are Asperger syndrome, which lacks delays in cognitive dev ...
... communication, and by restricted and repetitive behavior. These signs all begin before a child is three years old. Autism involves many parts of the brain; how this occurs is not well understood. The two other autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are Asperger syndrome, which lacks delays in cognitive dev ...
Abnormal Psych - mood disorders
... • many symptoms do not obviously point to depression • stigma associated with diagnosis of depression ...
... • many symptoms do not obviously point to depression • stigma associated with diagnosis of depression ...
Abnormal Psychology - People Server at UNCW
... – Individual experiences depressed characteristics for at least two weeks – Symptoms are: Cognitive Emotional somatic ...
... – Individual experiences depressed characteristics for at least two weeks – Symptoms are: Cognitive Emotional somatic ...
Mental Illness & Crime Key Issues & Debates (part 2) Dr
... be a neuro-developmental disorder caused by complex interaction of both genetic & environmental factors. ...
... be a neuro-developmental disorder caused by complex interaction of both genetic & environmental factors. ...
Major Depressive Episode
... Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Recurrent obsessions and/or compulsions that are severe enough to be time consuming or cause marked distress and/or significant impairment. • At some point, person has recognized that the obsessions or compulsions are excessive or ...
... Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Recurrent obsessions and/or compulsions that are severe enough to be time consuming or cause marked distress and/or significant impairment. • At some point, person has recognized that the obsessions or compulsions are excessive or ...
Mental Disorders
... and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delu ...
... and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available. The most prevalent symptoms of these diseases are usually delu ...
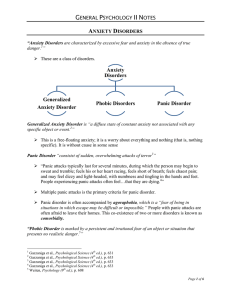
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... Major Depresssive Disorder is “a person must experience a major depressive episode, during which he or she experiences a depressed mood or a loss of interest in pleasuable activities every day for at least two weeks. In addition, the person must have other symptoms, such as appetite and weight chang ...
... Major Depresssive Disorder is “a person must experience a major depressive episode, during which he or she experiences a depressed mood or a loss of interest in pleasuable activities every day for at least two weeks. In addition, the person must have other symptoms, such as appetite and weight chang ...
Mood (affective) disorders (F30-F39)
... A persistent instability of mood involving numerous periods of depression and mild elation, none of which is sufficiently severe or prolonged to justify a diagnosis of bipolar affective disorder (F31.-) or recurrent depressive disorder (F33.-). This disorder is frequently found in the relatives of p ...
... A persistent instability of mood involving numerous periods of depression and mild elation, none of which is sufficiently severe or prolonged to justify a diagnosis of bipolar affective disorder (F31.-) or recurrent depressive disorder (F33.-). This disorder is frequently found in the relatives of p ...
Understanding Bipolar Disorder and Its Treatment
... (seeing, hearing, or sensing things that are not there). Mania: The Manic ‘Pole’ A manic episode is diagnosed if there is elevated mood accompanied by three or more of the other symptoms most of the day, nearly every day, for one week or longer. If the mood is irritable, then four additional symptom ...
... (seeing, hearing, or sensing things that are not there). Mania: The Manic ‘Pole’ A manic episode is diagnosed if there is elevated mood accompanied by three or more of the other symptoms most of the day, nearly every day, for one week or longer. If the mood is irritable, then four additional symptom ...
Kinds of Anxiety Issues I Work With Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
... humiliation (social phobia). Feeling socially clumsy, having trouble with small talk in social situations, and letting fear of embarrassment or humiliation cause avoidance of triggering situations. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder - Can manifest from mild to severe including obsessive thoughts and repe ...
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as bipolar affective disorder and manic-depressive illness, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of elevated mood and periods of depression. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania depending on the severity or whether there is psychosis. During mania an individual feels or acts abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable. They often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced. During periods of depression there may be crying, poor eye contact with others, and a negative outlook on life. The risk of suicide among those with the disorder is high at greater than 6% over 20 years, while self harm occurs in 30–40%. Other mental health issues such as anxiety disorder and substance use disorder are commonly associated.The cause is not clearly understood, but both genetic and environmental factors play a role. Many genes of small effect contribute to risk. Environmental factors include long term stress and a history of childhood abuse. It is divided into bipolar I disorder if there is at least one manic episode and bipolar II disorder if there are at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. In those with less severe symptoms of a prolonged duration the condition cyclothymic disorder may be present. If due to drugs or medical problems it is classified separately. Other conditions that may present in a similar manner include substance use disorder, personality disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and schizophrenia as well as a number of medical conditions.Treatment commonly includes psychotherapy and medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Examples of mood stabilizers that are commonly used include lithium and anticonvulsants. Treatment in hospital against a person's wishes may be required at times as people may be a risk to themselves or others yet refuse treatment. Severe behavioural problems may be managed with short term benzodiazepines or antipsychotics. In periods of mania it is recommended that antidepressants be stopped. If antidepressants are used for periods of depression they should be used with a mood stabilizer. Electroconvulsive therapy may be helpful in those who do not respond to other treatments. If treatments are stopped it is recommended that this be done slowly. Many people have social, financial, or work-related problems due to the disorder. These difficulties occur a quarter to a third of the time on average. The risk of death from natural causes such as heart disease is twice that of the general population. This is due to poor lifestyle choices and the side effects from medications.About 3% of people in the United States have bipolar disorder at some point in their life. Lower rates of around 1% are found in other countries. The most common age at which symptoms begin is 25. Rates appear to be similar in males as females. The economic costs of the disorder has been estimated at $45 billion for the United States in 1991. A large proportion of this was related to a higher number of missed work days, estimated at 50 per year. People with bipolar disorder often face problems with social stigma.