Stealing What teachers need to know about students that steal.
... violated, as manifested by the presence of three (or more) of the following criteria in the past 12 months, with at least one criterion present in the past 6 months.” ...
... violated, as manifested by the presence of three (or more) of the following criteria in the past 12 months, with at least one criterion present in the past 6 months.” ...
abnormal anxiety and mood disorders
... • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
... • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
Mental Disorders and Suicide
... ◦ Group therapy involves meeting with other people who suffer from similar disorders. A mental-health professional leads the group. Group members support each other and work together to develop coping skills. ◦ Family therapy focuses on family problems, such as a divorce, and how they affect the fam ...
... ◦ Group therapy involves meeting with other people who suffer from similar disorders. A mental-health professional leads the group. Group members support each other and work together to develop coping skills. ◦ Family therapy focuses on family problems, such as a divorce, and how they affect the fam ...
Conversion Disorder in the Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology 2
... non-pathological "normal" psychological process. In these models, the term dissociation is used descriptively rather than mechanistically, and traumatic experiences are no longer incorporated as a necessary causal factor in the development of dissociative symptoms. Brown (2004), for example, emphasi ...
... non-pathological "normal" psychological process. In these models, the term dissociation is used descriptively rather than mechanistically, and traumatic experiences are no longer incorporated as a necessary causal factor in the development of dissociative symptoms. Brown (2004), for example, emphasi ...
Lecture PowerPoint
... a mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania Sometimes (formerly) called manic-depressive disorder ...
... a mood disorder in which the person alternates between the hopelessness and lethargy of depression and the overexcited state of mania Sometimes (formerly) called manic-depressive disorder ...
Defining Psychological Disorders
... – n ongoing dysfunctional pattern of thought, emotion, and behavior that causes significant distress, and that is considered deviant in that person’s culture comorbidity – occurs when people who suffer from one disorder also suffer at the same time from other disorders – Because many psychological d ...
... – n ongoing dysfunctional pattern of thought, emotion, and behavior that causes significant distress, and that is considered deviant in that person’s culture comorbidity – occurs when people who suffer from one disorder also suffer at the same time from other disorders – Because many psychological d ...
the diagnosis and management of depression in primary - Pri-Med
... than not, as indicated by either subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years ▫ B. Presence while depressed of 2> : poor appetite or overeating; insomnia or hypersomnia; low energy or fatigue; low self esteem; poor concentration or difficulty making decisions; hopelessness ...
... than not, as indicated by either subjective account or observation by others, for at least 2 years ▫ B. Presence while depressed of 2> : poor appetite or overeating; insomnia or hypersomnia; low energy or fatigue; low self esteem; poor concentration or difficulty making decisions; hopelessness ...
Do You Send a Get Well Card to the Psychiatric Ward?
... 31)A priest happened to be going down the same road, and when he saw the man, he passed by on the other side. 32)So too, a Levite, when he came to the place and saw him, passed by on the other side. 33)But a Samaritan, as he traveled, came where the man was; and when he saw him, he took pity on him. ...
... 31)A priest happened to be going down the same road, and when he saw the man, he passed by on the other side. 32)So too, a Levite, when he came to the place and saw him, passed by on the other side. 33)But a Samaritan, as he traveled, came where the man was; and when he saw him, he took pity on him. ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders - Jay
... Dissociative Disorders These disorders can happen to people who have suffered from severe trauma. Not just any trauma but, psychological trauma that can sometimes cause a person to experience a long lasting disturbance of memory, which is the heart of dissociative disorders. It is called dissociativ ...
... Dissociative Disorders These disorders can happen to people who have suffered from severe trauma. Not just any trauma but, psychological trauma that can sometimes cause a person to experience a long lasting disturbance of memory, which is the heart of dissociative disorders. It is called dissociativ ...
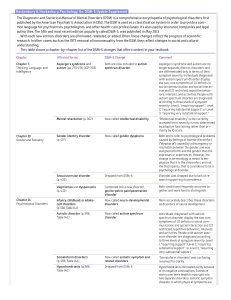
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is
... Hockenbury & hockenbury Psychology, 6e: dsm-5 update supplement ...
... Hockenbury & hockenbury Psychology, 6e: dsm-5 update supplement ...
Eating Disorders - Bradley Hospital
... • Low self-esteem • Believing he or she is fat regardless of how thin he or she becomes • The need to feel control over his or her life • Dramatic weight fluctuations E VA L U AT I O N A N D D I A G N O S I S ...
... • Low self-esteem • Believing he or she is fat regardless of how thin he or she becomes • The need to feel control over his or her life • Dramatic weight fluctuations E VA L U AT I O N A N D D I A G N O S I S ...
Slide 1
... Identity disturbance: markedly and persistently unstable selfimage or sense of self Impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially self-damaging Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures or threats, or self-mutilating behavior Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood Chronic feel ...
... Identity disturbance: markedly and persistently unstable selfimage or sense of self Impulsivity in at least two areas that are potentially self-damaging Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures or threats, or self-mutilating behavior Affective instability due to a marked reactivity of mood Chronic feel ...
Anxiety Disorders
... arousal as catastrophic and dangerous • This interpretation leads to further physical arousal, tending toward a vicious cycle • After their first panic attack, they become even more attuned to physical changes, increasing the likelihood of future panic attacks ...
... arousal as catastrophic and dangerous • This interpretation leads to further physical arousal, tending toward a vicious cycle • After their first panic attack, they become even more attuned to physical changes, increasing the likelihood of future panic attacks ...
Somatoform Disorders
... • Believed to originate from faulty mind-body interactions- the brain sends signals that impinge on the patients awareness falsely suggesting a serious problem in the ...
... • Believed to originate from faulty mind-body interactions- the brain sends signals that impinge on the patients awareness falsely suggesting a serious problem in the ...
Schizotypal (Personality) Disorder Delusional Disorder
... treatment of a mental or other medical disorder. Typically, the parent-child relational problem is associated with impaired functioning in behavioral, cognitive, or affective domains. Examples of behavioral problems include inadequate parental control, supervision, and involvement with the child; pa ...
... treatment of a mental or other medical disorder. Typically, the parent-child relational problem is associated with impaired functioning in behavioral, cognitive, or affective domains. Examples of behavioral problems include inadequate parental control, supervision, and involvement with the child; pa ...
Unit I
... causes of schizophrenia Schizophrenia refers to a group of very serious, usually chronic, thought disorders in which the affected person’s ability to interpret the world accurately is impaired by psychotic symptoms ...
... causes of schizophrenia Schizophrenia refers to a group of very serious, usually chronic, thought disorders in which the affected person’s ability to interpret the world accurately is impaired by psychotic symptoms ...
No Slide Title
... • Either obsessions or compulsions • At some point during course of disorder, symptoms are recognized as excessive and unreasonable • Symptoms cause marked distress • If Another Axis I Disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted to it • The disturbance is not ...
... • Either obsessions or compulsions • At some point during course of disorder, symptoms are recognized as excessive and unreasonable • Symptoms cause marked distress • If Another Axis I Disorder is present, the content of the obsessions or compulsions is not restricted to it • The disturbance is not ...
Assessing Abnormal Behaviors Chris Heimerl, MA
... - presenting problem(s) Concise history social family Medical status - diagnostic history Medication history and response Behavior, symptom baselines - data based! ...
... - presenting problem(s) Concise history social family Medical status - diagnostic history Medication history and response Behavior, symptom baselines - data based! ...
Mental Illness - WordPress.com
... Man are more likely to experience antisocial personality disorders Older people experience depression more often than younger people Mental disorders (especially depression) are more common among people who are separated, divorced, or widowed 52% of Ontarians whose parents have experienced a mental ...
... Man are more likely to experience antisocial personality disorders Older people experience depression more often than younger people Mental disorders (especially depression) are more common among people who are separated, divorced, or widowed 52% of Ontarians whose parents have experienced a mental ...
Document
... 1) They are unable to perform their life roles properly. a) An alcoholic who refuses to accept that there is a problem. b) A person who does nothing while his or her family life is falling apart. c) A parent at home with children who cannot even cope with the dirty dishes. 3. Many people in need of ...
... 1) They are unable to perform their life roles properly. a) An alcoholic who refuses to accept that there is a problem. b) A person who does nothing while his or her family life is falling apart. c) A parent at home with children who cannot even cope with the dirty dishes. 3. Many people in need of ...
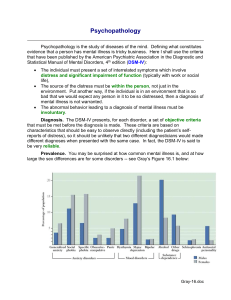
Psychopathology
... Drugs that enhance the action of serotonin alone or of norepinephrine alone can be equally effective in the same individuals, despite the fact that serotonin and norepinephrine are involved in different brain areas with different functions. Environmental Factors. Persons who have recently suffered ...
... Drugs that enhance the action of serotonin alone or of norepinephrine alone can be equally effective in the same individuals, despite the fact that serotonin and norepinephrine are involved in different brain areas with different functions. Environmental Factors. Persons who have recently suffered ...
xxxxx - Hobbs Municipal Schools
... Distinguishing Emotional Disturbance from Social Maladjustment Emotional Disturbance When one uses the term Emotional Disturbance, it refers to those psychiatric conditions that reflect a disorder in affect or emotion. That is, some type of dysfunction in emotional self-regulation must be at play in ...
... Distinguishing Emotional Disturbance from Social Maladjustment Emotional Disturbance When one uses the term Emotional Disturbance, it refers to those psychiatric conditions that reflect a disorder in affect or emotion. That is, some type of dysfunction in emotional self-regulation must be at play in ...
The Mind Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
... • The ADHD symptoms appeared later in life (e.g., at age 10 years old or older) • The symptoms of ADHD appeared abruptly in an otherwise healthy child • The ADHD symptoms were responding to stimulants and now are not • The ADHD symptoms come and go and tend to occur with mood changes ...
... • The ADHD symptoms appeared later in life (e.g., at age 10 years old or older) • The symptoms of ADHD appeared abruptly in an otherwise healthy child • The ADHD symptoms were responding to stimulants and now are not • The ADHD symptoms come and go and tend to occur with mood changes ...