Children’s explanations of different forms of
... 1) Following each description, participants were asked: Why do you think Clara is like this? A list of reasons explaining why a child would have this disorder was presented. Participants rated each reason according to whether it explained why the child would have this disorder. ...
... 1) Following each description, participants were asked: Why do you think Clara is like this? A list of reasons explaining why a child would have this disorder was presented. Participants rated each reason according to whether it explained why the child would have this disorder. ...
What is a psychological disorder
... • Agoraphobia involves intense fear and anxiety of any place or situation where escape might be difficult, leading to avoidance of situations such as being alone outside of the home; traveling in a car, bus, or airplane; or being in a crowded area • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) • A condition ...
... • Agoraphobia involves intense fear and anxiety of any place or situation where escape might be difficult, leading to avoidance of situations such as being alone outside of the home; traveling in a car, bus, or airplane; or being in a crowded area • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) • A condition ...
Class 8: Mental Illness and Diagnosis
... mirroring those of psychiatric disorders – The psychiatric disorder is not diagnosed if the symptoms disappear upon treatment of the medical condition ...
... mirroring those of psychiatric disorders – The psychiatric disorder is not diagnosed if the symptoms disappear upon treatment of the medical condition ...
here
... bedroom wall before leaving the house… I had constant anxiety… I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
... bedroom wall before leaving the house… I had constant anxiety… I thought I might be nuts. Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) ...
Abnormal and treatment
... American novel” before his class reunion, which is a few months away. He expounds eloquently on his novel to anyone who will listen, talking at such rapid pace that no one can get a word in edgewise. He feels like he is wired with energy and is supremely confident about the novel, even though he has ...
... American novel” before his class reunion, which is a few months away. He expounds eloquently on his novel to anyone who will listen, talking at such rapid pace that no one can get a word in edgewise. He feels like he is wired with energy and is supremely confident about the novel, even though he has ...
Chapter 15 pt. 1: Perspectives on Psychological Disorders and Anxiety
... 3. maladaptive- harmful; causes suffering 4. unjustifiable- sometimes there’s a good reason ...
... 3. maladaptive- harmful; causes suffering 4. unjustifiable- sometimes there’s a good reason ...
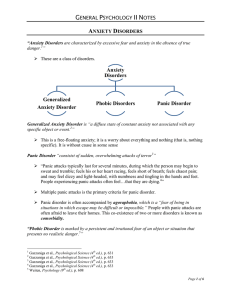
Anxiety Disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Phobic Disorders
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder is “a diffuse state of constant anxiety not associated with any specific object or event.2” This is a free-floating anxiety; it is a worry about everything and nothing (that is, nothing specific). It is without cause in some sense Panic Disorder “consistst of sudden, o ...
... Generalized Anxiety Disorder is “a diffuse state of constant anxiety not associated with any specific object or event.2” This is a free-floating anxiety; it is a worry about everything and nothing (that is, nothing specific). It is without cause in some sense Panic Disorder “consistst of sudden, o ...
(HCL-32 R1) Manual
... Over a lifetime every human being experiences significant changes in energy, activity and mood, such as lows (sadness, loss, bereavement) and highs (romantic love, personal success and achievement) of shorter (hours, days) or longer (weeks, months) duration. There is a continuum from normal lows and ...
... Over a lifetime every human being experiences significant changes in energy, activity and mood, such as lows (sadness, loss, bereavement) and highs (romantic love, personal success and achievement) of shorter (hours, days) or longer (weeks, months) duration. There is a continuum from normal lows and ...
Research-Based Direction for the Use of Amino
... are affected. Such target systems are different from those in people with other personality disorders, and from normal controls. Louis Cozolino,2 in his book The Neuroscience of Human Relations: Attachment and the Developing Social Brain, describes the complexity of neurodevelopmental dysfunction in ...
... are affected. Such target systems are different from those in people with other personality disorders, and from normal controls. Louis Cozolino,2 in his book The Neuroscience of Human Relations: Attachment and the Developing Social Brain, describes the complexity of neurodevelopmental dysfunction in ...
DSM-5 Overview
... Psychiatric Association (APA), a society of psychiatric physicians. • Who writes it? • The APA created the DSM, which contains sets of diagnostic criteria (symptoms being experienced) grouped into categories (disorders) to assist clinicians with effective diagnoses and care of people with mental hea ...
... Psychiatric Association (APA), a society of psychiatric physicians. • Who writes it? • The APA created the DSM, which contains sets of diagnostic criteria (symptoms being experienced) grouped into categories (disorders) to assist clinicians with effective diagnoses and care of people with mental hea ...
Major Depressive Disorder Definition and Diagnostic Criteria Major
... the source for the depression, and these are replaced with positive thoughts. Interpersonal Therapy takes the treatment and links it to other individuals, looking at improving the personal relationships that may contribute to the depression (NAMI, ...
... the source for the depression, and these are replaced with positive thoughts. Interpersonal Therapy takes the treatment and links it to other individuals, looking at improving the personal relationships that may contribute to the depression (NAMI, ...
File
... deal with their pain. O It’s dangerous to talk about suicide with them.” People are afraid to talk to depressed people about suicide with the fear of “putting the ideas in their heads”. However, speaking openly can ease the person’s mind and reduce the risk. ...
... deal with their pain. O It’s dangerous to talk about suicide with them.” People are afraid to talk to depressed people about suicide with the fear of “putting the ideas in their heads”. However, speaking openly can ease the person’s mind and reduce the risk. ...
CH 13 study guide
... from chronic, persistent depression, and some are treatment-resistant. 12. Genotypes, in combination with environmental factors, can predispose a person to become depressed. Depression is not due to a “chemical imbalance,” although many sorts of biochemical changes may be associated with depression. ...
... from chronic, persistent depression, and some are treatment-resistant. 12. Genotypes, in combination with environmental factors, can predispose a person to become depressed. Depression is not due to a “chemical imbalance,” although many sorts of biochemical changes may be associated with depression. ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... Inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger (e.g., frequent displays of temper, constant anger, recurrent physical fights). Transient, stress-related paranoid ideation or severe dissociative symptoms. ...
... Inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger (e.g., frequent displays of temper, constant anger, recurrent physical fights). Transient, stress-related paranoid ideation or severe dissociative symptoms. ...
Psychological Disorders
... tendency to explain cause of negative uncontrollable events as one’s own stable personal qualities affecting all aspects of life Associated with health problems and premature death ...
... tendency to explain cause of negative uncontrollable events as one’s own stable personal qualities affecting all aspects of life Associated with health problems and premature death ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 38 garber edits
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
Mental Disorders
... Anxiety Disorders •A condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control. •People with anxiety disorders try to avoid situations that make them feel anxious or fearful. •The most common mental illness in the U.S. affecting 40 million ...
... Anxiety Disorders •A condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control. •People with anxiety disorders try to avoid situations that make them feel anxious or fearful. •The most common mental illness in the U.S. affecting 40 million ...
The Bipolar Child - VA Association of Visiting Teachers
... also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
... also strongly supported the hypothesis that the symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are different than those seen in adults. ...
Mental Disorders Powerpoint
... Anxiety Disorders •A condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control. •People with anxiety disorders try to avoid situations that make them feel anxious or fearful. •The most common mental illness in the U.S. affecting 40 million ...
... Anxiety Disorders •A condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control. •People with anxiety disorders try to avoid situations that make them feel anxious or fearful. •The most common mental illness in the U.S. affecting 40 million ...
Document
... Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma. Numbing of general responsiveness Persistent increased arousal (problems sleeping, irritability/anger, hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, etc.) All symptoms must last more than 1 month. ...
... Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma. Numbing of general responsiveness Persistent increased arousal (problems sleeping, irritability/anger, hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, etc.) All symptoms must last more than 1 month. ...
PSC 168 Abnormal Psychology SS1 2005 Second Midterm Form A
... 34. A psychiatrist is testifying in relation to a criminal defendant’s insanity plea. This expert witness asserts that the defendant has a several mental illness that caused the criminal action. This evidence is MOST critical to the _______ ...
... 34. A psychiatrist is testifying in relation to a criminal defendant’s insanity plea. This expert witness asserts that the defendant has a several mental illness that caused the criminal action. This evidence is MOST critical to the _______ ...
“He`s a born worrier” CBT for GAD
... living areas of the home or workplace to the extent that their intended use is no longer possible. ...
... living areas of the home or workplace to the extent that their intended use is no longer possible. ...
Lecture 6
... average age of onset 25 - 29 depression closely related to anxiety almost all depressed patients are also anxious ...
... average age of onset 25 - 29 depression closely related to anxiety almost all depressed patients are also anxious ...
Mood Disorders - School District of Cambridge
... Global – My explanation applies to many areas of my life ...
... Global – My explanation applies to many areas of my life ...