B - Fort Bend ISD
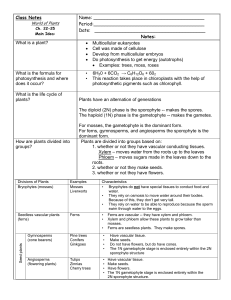
... • Known as Alternation of Generations • gametes and spores – reproductive cells • The diploid phase is know as sporophyte 2N stage the haploid phase is known as gametophyte 1N ...
... • Known as Alternation of Generations • gametes and spores – reproductive cells • The diploid phase is know as sporophyte 2N stage the haploid phase is known as gametophyte 1N ...
Structure Comp. Rev. 2008
... 1. What structure contains seeds in angiosperms? 2. What kind of veins do monocots have? 3. How are monocot flower parts arranged? 4. How many cotyledons does a bean seedling have? 5. Is an apple tree an angiosperm or a gymnosperm? 6. What structures do angiosperms use to hold their seeds for reprod ...
... 1. What structure contains seeds in angiosperms? 2. What kind of veins do monocots have? 3. How are monocot flower parts arranged? 4. How many cotyledons does a bean seedling have? 5. Is an apple tree an angiosperm or a gymnosperm? 6. What structures do angiosperms use to hold their seeds for reprod ...
Lesson 3 | Plant Reproduction - Kapuk`s E
... 3. One advantage of asexual reproduction is that just one parent organism can produce offspring ...
... 3. One advantage of asexual reproduction is that just one parent organism can produce offspring ...
Control
... 1. What are the openings on the leaves that let gases in and out? Why does a plant need these openings? 2. What controls the size of the openings on these leaves? 3. Why is the transpiration process so important to a plant? 4. Describe the process of transpiration in detail from how water enters the ...
... 1. What are the openings on the leaves that let gases in and out? Why does a plant need these openings? 2. What controls the size of the openings on these leaves? 3. Why is the transpiration process so important to a plant? 4. Describe the process of transpiration in detail from how water enters the ...
Plant Structure and Functions A26-41
... Cortex- layer just inside epidermis of roots and stems; stores food Epidermis- outermost layer of root, stem, or leaf Root cap- thin covering made up of cells; protects root tip as it grows into soil Phloem- tissue through which food from leaves moves down through plant Cambium- layer that ...
... Cortex- layer just inside epidermis of roots and stems; stores food Epidermis- outermost layer of root, stem, or leaf Root cap- thin covering made up of cells; protects root tip as it grows into soil Phloem- tissue through which food from leaves moves down through plant Cambium- layer that ...
Classifying Ornamental Plants
... Botanists call plants by their last two taxas – genus and species – This system is known as binomial nomenclature (two-word naming system) – Developed by Carolus Linnaeus – Uses Latin for three reasons: Universal ...
... Botanists call plants by their last two taxas – genus and species – This system is known as binomial nomenclature (two-word naming system) – Developed by Carolus Linnaeus – Uses Latin for three reasons: Universal ...
Euphorbia milli (Crown of thorns) Size/Shape
... Euphorbia milli (Crown of thorns) This thorny plant is native from Madagascar. Evergreen stays green all all year long and from spring to late summer produces many flowers surrounded with two showy bracts. Bracts are modified leaves around the flowers helping plants invite insects for pollination. T ...
... Euphorbia milli (Crown of thorns) This thorny plant is native from Madagascar. Evergreen stays green all all year long and from spring to late summer produces many flowers surrounded with two showy bracts. Bracts are modified leaves around the flowers helping plants invite insects for pollination. T ...
What is a Plant? - Jordan High School
... • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
... • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
Sample
... m(30 ft) and grows high in the Andes. Plants of this genus are terrestrial and have elongated stems, fully developed roots, leaves with narrow petioles, and hairs that retard water loss by providing a dense covering. A second stage in bromeliad advancement is the familiar pineapple, native to South ...
... m(30 ft) and grows high in the Andes. Plants of this genus are terrestrial and have elongated stems, fully developed roots, leaves with narrow petioles, and hairs that retard water loss by providing a dense covering. A second stage in bromeliad advancement is the familiar pineapple, native to South ...
Vascular tissue
... parallel veins on leaves – Dicots – two seed leaves; flower parts in sets of 2, 4, or 5; netted / branching veins on leaves ...
... parallel veins on leaves – Dicots – two seed leaves; flower parts in sets of 2, 4, or 5; netted / branching veins on leaves ...
Reproduction
... genetically similar copy of itself without the combination of genetic material with another individual. ...
... genetically similar copy of itself without the combination of genetic material with another individual. ...
Talinum paniculatum
... those moments were actually few. Some walks with my grandmother, a seedling gift from a great uncle, and a short conversation with an actual “birder” are the ones I remember. Those few short moments led to the life-long burning to study what God creates without the help of and despite the destructiv ...
... those moments were actually few. Some walks with my grandmother, a seedling gift from a great uncle, and a short conversation with an actual “birder” are the ones I remember. Those few short moments led to the life-long burning to study what God creates without the help of and despite the destructiv ...
Common Name: Peppervine Scientific Name: Nekemias arborea
... Peppervine is a native plant in the lower 48 states in the United States, as well as Puerto Rico. However, because of its growth behavior, it can be invasive. Wildlife Uses White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) will eat Peppervine foliage, but the plant is considered to be only a minor portion ...
... Peppervine is a native plant in the lower 48 states in the United States, as well as Puerto Rico. However, because of its growth behavior, it can be invasive. Wildlife Uses White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) will eat Peppervine foliage, but the plant is considered to be only a minor portion ...
Angelonia angustifolia
... of fertilizer or some compost in a garden bed is usually all that is needed for these plants to thrive. Due to their heat-loving nature they are one of the plants that can be planted even during the heat of mid-summer Angelonia is an erect little perennial with smooth stems and narrow leaves with to ...
... of fertilizer or some compost in a garden bed is usually all that is needed for these plants to thrive. Due to their heat-loving nature they are one of the plants that can be planted even during the heat of mid-summer Angelonia is an erect little perennial with smooth stems and narrow leaves with to ...
Internal/External Plant Strustures IN DEPTH
... 45. Root hairs-Take in the nutrients for the plant. 46. Roots-take in nutrients and water, hold the plant in the soil, and some store food made by the leaves. 47. Two types of leaves- 1. broad leaf (maple and oak) 2. Needle leaf (pine and cactus) 48. Stems- support the leaves and carry the water and ...
... 45. Root hairs-Take in the nutrients for the plant. 46. Roots-take in nutrients and water, hold the plant in the soil, and some store food made by the leaves. 47. Two types of leaves- 1. broad leaf (maple and oak) 2. Needle leaf (pine and cactus) 48. Stems- support the leaves and carry the water and ...
Angiosperms: flowering plants
... • Seed production is advantageous to longevity of the genetic material and dispersal • Closed carpels that develop to make fruit aid in dispersal also via animals that eat the fruit • Pollen is well-adapted to cross-fertilization via bees, bats, birds, etc • Flowers attract pollinators • Angiosperms ...
... • Seed production is advantageous to longevity of the genetic material and dispersal • Closed carpels that develop to make fruit aid in dispersal also via animals that eat the fruit • Pollen is well-adapted to cross-fertilization via bees, bats, birds, etc • Flowers attract pollinators • Angiosperms ...
plant_Kingdom
... All plants: *eukaryotes and autotrophic. *Most live on land and have a way to obtain water. * Many have a waterproof layer covering their leaves called the cuticle - prevents water loss. ...
... All plants: *eukaryotes and autotrophic. *Most live on land and have a way to obtain water. * Many have a waterproof layer covering their leaves called the cuticle - prevents water loss. ...
GRADE – 6 CBSE
... Discuss the special features of aquatic plants that help them survive in their habitat. a) In aquatic plants, the roots are much reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place. In some of these plants, the roots are fixed in the soil below the water. b) The stems of these plan ...
... Discuss the special features of aquatic plants that help them survive in their habitat. a) In aquatic plants, the roots are much reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place. In some of these plants, the roots are fixed in the soil below the water. b) The stems of these plan ...
Orange Hawkweed
... leaves, broader at the tip but still three to four times longer than wide. The entire plant has a milky sap which is bitter to taste. Prior to flowering, the central stems will elongate to 20 to 70 cm (8 to 20 inches) and produce 5 to 30 flowers. The Orange Hawkweed is also called Devil’s Paint Brus ...
... leaves, broader at the tip but still three to four times longer than wide. The entire plant has a milky sap which is bitter to taste. Prior to flowering, the central stems will elongate to 20 to 70 cm (8 to 20 inches) and produce 5 to 30 flowers. The Orange Hawkweed is also called Devil’s Paint Brus ...
Section 16.3 - CPO Science
... • Each kernel of corn on a cob is actually an individual fruit! • In peaches, the fruits are soft and fleshy and contain a single, stony seed. • Legumes like beans and peas produce a fruit called a pod that contains many seeds. ...
... • Each kernel of corn on a cob is actually an individual fruit! • In peaches, the fruits are soft and fleshy and contain a single, stony seed. • Legumes like beans and peas produce a fruit called a pod that contains many seeds. ...
Printable
... Yucca filamentosa Introduction Adam’s Needle is a slow growing native plant found scattered through the woods in the southeastern United States. Leaves appear as though they have been shaved because leaf margins bear curved, filamentous threads of leaf tissue. The leaf terminates in a sharp spine. P ...
... Yucca filamentosa Introduction Adam’s Needle is a slow growing native plant found scattered through the woods in the southeastern United States. Leaves appear as though they have been shaved because leaf margins bear curved, filamentous threads of leaf tissue. The leaf terminates in a sharp spine. P ...
Container Evaluation of New Ornamentals
... Rhaphiolepis x delcourii ‘Georgia Petite’ - A good Indian hawthorn with excellent resistance to Entomosporium leaf spot. As of 8/14/03 the foliage was clean under nursery conditions and plenty of rainfall. Plants averaged 14" in height by 20" width. Viburnum obovatum - a selection made from central ...
... Rhaphiolepis x delcourii ‘Georgia Petite’ - A good Indian hawthorn with excellent resistance to Entomosporium leaf spot. As of 8/14/03 the foliage was clean under nursery conditions and plenty of rainfall. Plants averaged 14" in height by 20" width. Viburnum obovatum - a selection made from central ...
Plant Adaptation
... The bark is like cork and is fire resistant. The fruit is called “monkey bread” and has lots of Vitamin C. • This tree is native to Madagascar and can survive the constant droughts there. ...
... The bark is like cork and is fire resistant. The fruit is called “monkey bread” and has lots of Vitamin C. • This tree is native to Madagascar and can survive the constant droughts there. ...
Plant evolutionary developmental biology

Evolutionary developmental biology (evo-devo) refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early sign of this occurred in 1999.Most of the synthesis in evo-devo has been in the field of animal evolution, one reason being the presence of elegant model systems like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However, in the past couple of decades, a wealth of information on plant morphology, coupled with modern molecular techniques has helped shed light on the conserved and unique developmental patterns in the plant kingdom also.























