January 2016 - Stony Brook University
... and a linear multistep method of the form yn+1 = αyn + βyn−1 + hγf (tn−1 , yn−1 ), where h is the time step. a) (6 points) Choose the constants α, β, and γ, so that the order of the method is as high as possible. b) (4 points) Derive the condition under which the resulting method is convergent. ...
... and a linear multistep method of the form yn+1 = αyn + βyn−1 + hγf (tn−1 , yn−1 ), where h is the time step. a) (6 points) Choose the constants α, β, and γ, so that the order of the method is as high as possible. b) (4 points) Derive the condition under which the resulting method is convergent. ...
Distinguished Lecturer Series - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Distinguished Lecturer Series Special Event Sponsored by the Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ...
... Distinguished Lecturer Series Special Event Sponsored by the Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science ...
Title of propsed paper for ASRANet International Colloquium 2002:
... river and prevent the debris from flowing down, have been constructed. On the other hand, the riverbed trends to sink by constructing the check dam, which makes trouble in water supply management in the down stream area. To solve this contradictive problem, the open type check dam structure, which h ...
... river and prevent the debris from flowing down, have been constructed. On the other hand, the riverbed trends to sink by constructing the check dam, which makes trouble in water supply management in the down stream area. To solve this contradictive problem, the open type check dam structure, which h ...
1.1.8 Case study: Bacterial reproduction 1.1.9 Mathematical corner
... This method suggests that, for a given harvesting rate “h”, two outcomes are possible: ...
... This method suggests that, for a given harvesting rate “h”, two outcomes are possible: ...
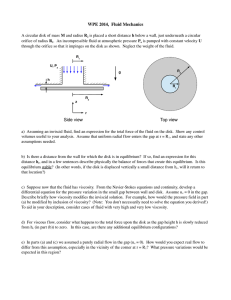
flowing fluids and pressure variation!
... e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane.! For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal a ...
... e.g., pressure is low at the center of a hurricane.! For your culture : The force balance for hurricanes is the pressure force vs. the Coriolis force. That s why hurricanes in the northern hemisphere always spin counter-clockwise. In a tornado, the balance is between pressure force and centrifugal a ...
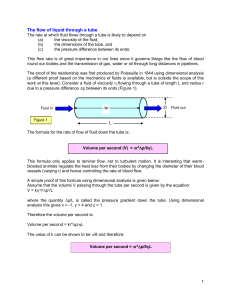
Flow of liquid through a tube
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
Lecture Notes for First Quiz - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
... At the critical value Ra=1708, buoyancy overcomes viscous dissipation and the fluid begins to move. “Benard convection: At first roll-like structures transport heat, then at higher Ra structures become more polygonal in shape, with increasing time variations 5. Other diffusion concepts Prandtl numbe ...
... At the critical value Ra=1708, buoyancy overcomes viscous dissipation and the fluid begins to move. “Benard convection: At first roll-like structures transport heat, then at higher Ra structures become more polygonal in shape, with increasing time variations 5. Other diffusion concepts Prandtl numbe ...
Many Solutions
... any x and y pair that satisfies the first equation will satisfy the second, since taking two numbers that are equal and multiplying them both by 2 will result in two equal numbers. So this system has infinitely many solutions, as the equations both correspond to the same line and lines have infinite ...
... any x and y pair that satisfies the first equation will satisfy the second, since taking two numbers that are equal and multiplying them both by 2 will result in two equal numbers. So this system has infinitely many solutions, as the equations both correspond to the same line and lines have infinite ...
Algebra I - MCPMathReadingFun9
... 6) Generate a system of equations to represent the situation given. Then, solve the system. Two groups of Muchin scholars and teachers went to a science museum. The museum charged the first group of 28 scholars and 5 teachers $284 for the day and charged the second group of 40 scholars and 10 teache ...
... 6) Generate a system of equations to represent the situation given. Then, solve the system. Two groups of Muchin scholars and teachers went to a science museum. The museum charged the first group of 28 scholars and 5 teachers $284 for the day and charged the second group of 40 scholars and 10 teache ...
Solution - Illustrative Mathematics
... any x and y pair that satisfies the first equation will satisfy the second, since taking two numbers that are equal and multiplying them both by 2 will result in two equal numbers. So this system has infinitely many solutions, as the equations both correspond to the same line and lines have infinite ...
... any x and y pair that satisfies the first equation will satisfy the second, since taking two numbers that are equal and multiplying them both by 2 will result in two equal numbers. So this system has infinitely many solutions, as the equations both correspond to the same line and lines have infinite ...
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.