Chapter 11 – Potential Vorticity – Lee and Rossby Waves
... The above criteria for instability means that longwave westerly jets in the atmosphere such as Rossby waves are prone to the spontaneous formation of disturbances. From the initial supposition of that the system is baroclinic implies that the intensification of small perturbations is due to extracti ...
... The above criteria for instability means that longwave westerly jets in the atmosphere such as Rossby waves are prone to the spontaneous formation of disturbances. From the initial supposition of that the system is baroclinic implies that the intensification of small perturbations is due to extracti ...
Chapter 11 * Potential Vorticity * Lee and Rossby Waves
... The above criteria for instability means that longwave westerly jets in the atmosphere such as Rossby waves are prone to the spontaneous formation of disturbances. From the initial supposition of that the system is baroclinic implies that the intensification of small perturbations is due to extracti ...
... The above criteria for instability means that longwave westerly jets in the atmosphere such as Rossby waves are prone to the spontaneous formation of disturbances. From the initial supposition of that the system is baroclinic implies that the intensification of small perturbations is due to extracti ...
Abstract
... varying the input parameters, such as [³O₂]₀ and ϕ. Based on our mice study, [³O₂]₀ was varying between 5-60 μM. The blood flow was considered by making g to be time dependent based on the published results [2-3]. Results: Using the obtained results, one can correlate the tissue oxygenation with the ...
... varying the input parameters, such as [³O₂]₀ and ϕ. Based on our mice study, [³O₂]₀ was varying between 5-60 μM. The blood flow was considered by making g to be time dependent based on the published results [2-3]. Results: Using the obtained results, one can correlate the tissue oxygenation with the ...
Computational study of oxygen delivery by red blood cells
... shapes however has only been obtained fairly recently as illustrated in figure 1. It is a fascinating idea to think that nature may have specifically tailored these RBC dynamics in order to optimize their physiological function, i.e. delivery of oxygen to tissue. Currently however, all studies on ox ...
... shapes however has only been obtained fairly recently as illustrated in figure 1. It is a fascinating idea to think that nature may have specifically tailored these RBC dynamics in order to optimize their physiological function, i.e. delivery of oxygen to tissue. Currently however, all studies on ox ...
20 Congrès Français de Mécanique ...
... coupling, implementing a MHD module into Fluidyn-MP platform. This module emphasizes accurate solution of velocity profile and current distribution for MHD fluid flows submitted to high magnetic fields and in 3D complex geometries of industrial configurations. MHD module comprises 2 different method ...
... coupling, implementing a MHD module into Fluidyn-MP platform. This module emphasizes accurate solution of velocity profile and current distribution for MHD fluid flows submitted to high magnetic fields and in 3D complex geometries of industrial configurations. MHD module comprises 2 different method ...
Lecture 4
... XY, YX component – assume uniform flow (flow not rotating in the mean) End up with two components: ...
... XY, YX component – assume uniform flow (flow not rotating in the mean) End up with two components: ...
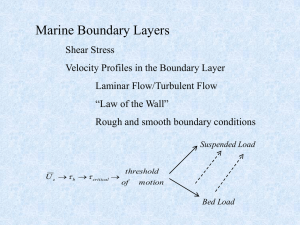
Flume handout
... surroundings. In benthic ecology, water flow is an especially important part of the physical environment. Due to physical properties of fluids in contact with ‘solid’ boundaries (such as the seabed), there is a strong vertical gradient in the velocity of the fluid. Near the seabed, flow speed is ver ...
... surroundings. In benthic ecology, water flow is an especially important part of the physical environment. Due to physical properties of fluids in contact with ‘solid’ boundaries (such as the seabed), there is a strong vertical gradient in the velocity of the fluid. Near the seabed, flow speed is ver ...
ENIAC`s Problem 1 Discussion
... not much interested in duplicating the expensive, fragile, one-of-a-kind computers that were the immediate descendants of the ENIAC. The first commercial computer was the UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer), completed in 1951 by Eckert and Mauchly for the U.S. Bureau of the Census. A total of 46 w ...
... not much interested in duplicating the expensive, fragile, one-of-a-kind computers that were the immediate descendants of the ENIAC. The first commercial computer was the UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer), completed in 1951 by Eckert and Mauchly for the U.S. Bureau of the Census. A total of 46 w ...
numerical methods in computational engineering
... A course in numerical analysis has become accepted as an important ingredient in the undergraduate education of engineers and scientists. Numerical Methods in Engineering and Science reflects experience in teaching such a course for several years. Related work in industry and research has influenced ...
... A course in numerical analysis has become accepted as an important ingredient in the undergraduate education of engineers and scientists. Numerical Methods in Engineering and Science reflects experience in teaching such a course for several years. Related work in industry and research has influenced ...
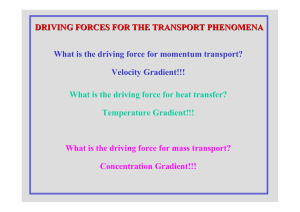
Conservation Equations
... Equation (1.1.4) is an Ordinary differential equation for changes in the average volume density of Φ with time. All information about the spatial variation of Φ within the volume, the fluxes or the sources has been removed but this approach is often good enough for government work or Box Models if o ...
... Equation (1.1.4) is an Ordinary differential equation for changes in the average volume density of Φ with time. All information about the spatial variation of Φ within the volume, the fluxes or the sources has been removed but this approach is often good enough for government work or Box Models if o ...
Computational fluid dynamics

Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial experimental validation of such software is performed using a wind tunnel with the final validation coming in full-scale testing, e.g. flight tests.