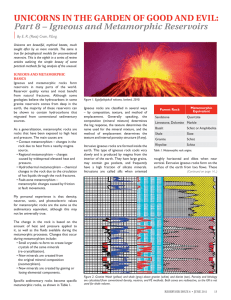
Igneous Rocks
... Melting point of minerals increases with increasing pressure In the hottest regions within the upper mantle and crust, pressure can be low enough for melting to occur ...
... Melting point of minerals increases with increasing pressure In the hottest regions within the upper mantle and crust, pressure can be low enough for melting to occur ...
Eng - UNESDOC
... emigration. The region holds the most complex geology in Mexico. According to the main themes of the site (erosion, culture and geoheritage), many of the selected geosites are related to erosionaldepositional processes and landforms associated with the intensive use of land for farming purposes. A n ...
... emigration. The region holds the most complex geology in Mexico. According to the main themes of the site (erosion, culture and geoheritage), many of the selected geosites are related to erosionaldepositional processes and landforms associated with the intensive use of land for farming purposes. A n ...
The Archean Hemlo gold deposit, Ontario, Canada: Alteration
... mass changes related to the primary gold mineralization event. There are two main mineralized zones in the deposit. These are generally tabular, 2-50 m thick, dip steeply to the north, and extend (discontinuously) for 3.5 km in strike-length and at least 1.5 km in vertical extent. Each typically com ...
... mass changes related to the primary gold mineralization event. There are two main mineralized zones in the deposit. These are generally tabular, 2-50 m thick, dip steeply to the north, and extend (discontinuously) for 3.5 km in strike-length and at least 1.5 km in vertical extent. Each typically com ...
Geological Glossary - The Old Courthouse Museum Batemans Bay
... scoria: Fragments of frothy or very vesicular lava, usually having a basaltic composition. scree: Loose boulder rock material accumulated at the base of a cliff or on a steep mountain slope. sedimentary: Pertaining to or containing fragmental material that originates from the weathering and erosion ...
... scoria: Fragments of frothy or very vesicular lava, usually having a basaltic composition. scree: Loose boulder rock material accumulated at the base of a cliff or on a steep mountain slope. sedimentary: Pertaining to or containing fragmental material that originates from the weathering and erosion ...
Rocks - Faculty Server Contact
... metamorphic rocks can melt to produce magmas, but in most cases regional uplift and erosion results in the metamorphic rocks being once again converted to sediment. The earth is a very dynamic body and rock material is continually recycled. Plate tectonics is the description of this dynamic process ...
... metamorphic rocks can melt to produce magmas, but in most cases regional uplift and erosion results in the metamorphic rocks being once again converted to sediment. The earth is a very dynamic body and rock material is continually recycled. Plate tectonics is the description of this dynamic process ...
GSA-Charlotte 2012
... that would be expected to accompany each phase. The figure is too busty to explore in detail but identifies strong signals as boxes and weak ones as lines, and includes both signals as they were then known as solid symbols and predicts other where they were not as open boxes and dashed lines. 17. Su ...
... that would be expected to accompany each phase. The figure is too busty to explore in detail but identifies strong signals as boxes and weak ones as lines, and includes both signals as they were then known as solid symbols and predicts other where they were not as open boxes and dashed lines. 17. Su ...
Plate tectonics chapter 4 test bank
... 115. List and describe three possible driving forces of tectonic plate motion. 116. How do the three types of convergent boundaries differ from one another? 117. Explain how scientists measure the rate at which tectonic plates move. 118. When convection takes place in the mantle, why does cooler mat ...
... 115. List and describe three possible driving forces of tectonic plate motion. 116. How do the three types of convergent boundaries differ from one another? 117. Explain how scientists measure the rate at which tectonic plates move. 118. When convection takes place in the mantle, why does cooler mat ...
GRANITOID ROCKS
... generate an S-type granite when the melting reactions are intersected. Migmatites The process of granite formation is evident in migmatites. Migmatites are rocks from which granitoid melts were not removed. The light parts of migmatites contain the solidified granitoid melts. The dark parts of migma ...
... generate an S-type granite when the melting reactions are intersected. Migmatites The process of granite formation is evident in migmatites. Migmatites are rocks from which granitoid melts were not removed. The light parts of migmatites contain the solidified granitoid melts. The dark parts of migma ...
Paleozoic large igneous provinces of Northern Eurasia: Correlation
... Enormous lava eruptions formed large igneous provinces (LIPs) with millions of cubic kilometers emplaced in relatively short time intervals. Such magmatic events have been most likely initiated by the uplift of hot material from the core–mantle boundary and occurred several times during the Cenozoic ...
... Enormous lava eruptions formed large igneous provinces (LIPs) with millions of cubic kilometers emplaced in relatively short time intervals. Such magmatic events have been most likely initiated by the uplift of hot material from the core–mantle boundary and occurred several times during the Cenozoic ...
CHAPTER 1 - INTRODUCTION TO THE TECTONIC SETTING OF
... Wees et al., 1998] as well as thermal modelling [Fernàndez et al., 1995] shows several rifting stages in eastern Iberia, the major ones being Permian-Early Triassic and Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous of age. (c) The southern Iberian margin. From Triassic until early Liassic (E. Jurassic) the souther ...
... Wees et al., 1998] as well as thermal modelling [Fernàndez et al., 1995] shows several rifting stages in eastern Iberia, the major ones being Permian-Early Triassic and Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous of age. (c) The southern Iberian margin. From Triassic until early Liassic (E. Jurassic) the souther ...
Geology of the Batemans Bay region Geological evolution
... About 444-428Ma two uplift episodes resulted in these sediments being squeezed, folded and brought near the surface during the Benambran Orogeny. ...
... About 444-428Ma two uplift episodes resulted in these sediments being squeezed, folded and brought near the surface during the Benambran Orogeny. ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... The Rock Cycle and Plate Tectonics • Magma is created by melting above a subduction zone • Less dense magma rises and cools to form igneous rock • Igneous rock exposed at surface ...
... The Rock Cycle and Plate Tectonics • Magma is created by melting above a subduction zone • Less dense magma rises and cools to form igneous rock • Igneous rock exposed at surface ...
The Composition of the Continental Crust
... Every rock type known on Earth occurs in continental crust Shuttle view of granite intruding metamorphic ...
... Every rock type known on Earth occurs in continental crust Shuttle view of granite intruding metamorphic ...
ACCESSORY MINERALS IN SON4E GRANITIC ROCKS IN
... eralogy and texture of the intruding rocks led Lee and Bastron (1962) to suggest the possibility of more than one intrusive phase. Study of these rocks is still in progress, but recent results have shown that mineralogical differencesin the intrusive rocks are controlled primarily by variations in t ...
... eralogy and texture of the intruding rocks led Lee and Bastron (1962) to suggest the possibility of more than one intrusive phase. Study of these rocks is still in progress, but recent results have shown that mineralogical differencesin the intrusive rocks are controlled primarily by variations in t ...
Metamorphic Notes
... – Occurs adjacent to magma bodies intruding cooler country rock – Occurs in narrow zone (~1-100 m wide) known as contact aureole – Rocks may be fine- (e.g., hornfels) or coarse-grained (e.g., marble, quartzite) ...
... – Occurs adjacent to magma bodies intruding cooler country rock – Occurs in narrow zone (~1-100 m wide) known as contact aureole – Rocks may be fine- (e.g., hornfels) or coarse-grained (e.g., marble, quartzite) ...
new - i. t creative plus
... However, remember that different rocks melt at different temperatures and pressures • IF SO, WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF METAMORPHISM REGIONAL METAMORPHISM AND CONTACT METAMORPHISM • Contact metamorphism • Contact metamorphism occurs locally, at and near the contacts between intrusions and the surrounding ...
... However, remember that different rocks melt at different temperatures and pressures • IF SO, WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF METAMORPHISM REGIONAL METAMORPHISM AND CONTACT METAMORPHISM • Contact metamorphism • Contact metamorphism occurs locally, at and near the contacts between intrusions and the surrounding ...
Understanding Plate Motions - Maria Montessori Academy Blog
... of these two plates before and after their collision. The reference points (small squares) show the amount of uplift of an imaginary point in the Earth's crust during this mountain-building process. ...
... of these two plates before and after their collision. The reference points (small squares) show the amount of uplift of an imaginary point in the Earth's crust during this mountain-building process. ...
• The earth • Musah Saeed Zango • ETS 101
... However, remember that different rocks melt at different temperatures and pressures • IF SO, WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF METAMORPHISM REGIONAL METAMORPHISM AND CONTACT METAMORPHISM • Contact metamorphism • Contact metamorphism occurs locally, at and near the contacts between intrusions and the surrounding ...
... However, remember that different rocks melt at different temperatures and pressures • IF SO, WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF METAMORPHISM REGIONAL METAMORPHISM AND CONTACT METAMORPHISM • Contact metamorphism • Contact metamorphism occurs locally, at and near the contacts between intrusions and the surrounding ...
Some Geology Basics
... Sedimentary rocks make up only a small percentage of the crust, but sediments and sedimentary rocks cover most of the planet’s surfaces and sea floor. Sedimentary rocks may contain some of the igneous rock-forming minerals (especially quartz), but the process of weathering tends to break the mineral ...
... Sedimentary rocks make up only a small percentage of the crust, but sediments and sedimentary rocks cover most of the planet’s surfaces and sea floor. Sedimentary rocks may contain some of the igneous rock-forming minerals (especially quartz), but the process of weathering tends to break the mineral ...
Dec 2 Continental Drift (LT 1-2)
... Yes, since the Mesosaurus could not travel the ocean between these continents, it had to have lived in these areas when the continents were still joined. While more than one piece of evidence is needed to "prove a theory", the Mesosaurus does seem to support Continental Drift. The Mesosaurus c ...
... Yes, since the Mesosaurus could not travel the ocean between these continents, it had to have lived in these areas when the continents were still joined. While more than one piece of evidence is needed to "prove a theory", the Mesosaurus does seem to support Continental Drift. The Mesosaurus c ...
Topic 11
... - formed from particles of weathered rock - sediments can usually be seen (the rock looks and feels “dirty”) - clastic sediments can be lithified (turned into rock) in two ways: 1. compaction -- sediments accumulate, causing pressure that squeezes sediments together EX/ silt siltstone; clay shal ...
... - formed from particles of weathered rock - sediments can usually be seen (the rock looks and feels “dirty”) - clastic sediments can be lithified (turned into rock) in two ways: 1. compaction -- sediments accumulate, causing pressure that squeezes sediments together EX/ silt siltstone; clay shal ...
The GeOLOGY OF ALMOPIA SPeLeOPARK
... SW-NE and SE-NW directions. An extensional tectonic regime has being active in this area since the Neogene. The AVRs form several distinct centers, consisting of lava domes and subordinate lava flows and dikes. The eruptive centers are surrounded by large amounts of volcanoclastic materials. A chara ...
... SW-NE and SE-NW directions. An extensional tectonic regime has being active in this area since the Neogene. The AVRs form several distinct centers, consisting of lava domes and subordinate lava flows and dikes. The eruptive centers are surrounded by large amounts of volcanoclastic materials. A chara ...
Great Lakes tectonic zone
The Great Lakes tectonic zone is bounded by South Dakota at its tip and heads northeast to south of Duluth, Minnesota, then heads east through northern Wisconsin, Marquette, Michigan, and then trends more northeasterly to skim the northern-most shores of lakes Michigan and Huron before ending in the Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, area.During the Late Archean Era the Algoman orogeny added landmass to the Superior province by volcanic activity and continental collision along a boundary that stretches from present-day South Dakota, U.S., into the Lake Huron region near Sudbury, Ontario, Canada.This crustal boundary is the Great Lakes tectonic zone. It is 1,400 km (870 mi) long, and separates the older Archean gneissic terrane to the south from younger Late Archean greenstone-granite terrane to the north.The zone is characterized by active compression during the Algoman orogeny (about 2,700 million years ago), a pulling-apart (extensional) tectonics (2,450 to 2,100 million years ago), a second compression during the Penokean orogeny (1,900 to 1,850 million years ago), a second extension during Middle Proterozoic time (1,600 million years ago) and minor reactivation during Phanerozoic time (the past 500 million years).Collision began along the Great Lakes tectonic zone (GLTZ) with the Algoman mountain-building event and continued for tens of millions of years. During the formation of the GLTZ, the gneissic Minnesota River Valley subprovince was thrust up onto the Superior province's edge as it consumed the Superior province's oceanic crust. Fragmentation of the Kenorland supercontinent began 2,450 million years ago and was completed by 2,100 million years ago. The Wyoming province is the continental landmass that is hypothesized to have rifted away from the southern Superior province portion of Kenorland, before moving rapidly west and docking with the Laurentia supercontinent 1,850 to 1,715 million years ago. Sedimentation from the GLTZ-rifting environment continued into the Penokean orogeny, which is the next major tectonic event in the Great Lakes region. Several earthquakes have been documented in Minnesota, Michigan's Upper Peninsula and Sudbury in the last 120 years along the GLTZ.