Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... The theory was found to be extremely successful in describing nature (see rest of the course), but as two of its fathers put it: “To try and stop all attempts to pass beyond the present viewpoint of quantum physics could be very dangerous for the progress of science and would furthermore be contrary ...
... The theory was found to be extremely successful in describing nature (see rest of the course), but as two of its fathers put it: “To try and stop all attempts to pass beyond the present viewpoint of quantum physics could be very dangerous for the progress of science and would furthermore be contrary ...
Fourth lecture, 28.10.03 (dispersion cancellation, time measurement
... Why? No interference between paths leading to different frequencies at the detectors, because in principle one could go back and measure how much energy had been absorbed. Note: it took a long time-integral to enforce this. If the detector had been open only for 1 fs, it would be impossible to tell ...
... Why? No interference between paths leading to different frequencies at the detectors, because in principle one could go back and measure how much energy had been absorbed. Note: it took a long time-integral to enforce this. If the detector had been open only for 1 fs, it would be impossible to tell ...
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
... 1. Even within a particle-like interpretation of the experiment, particles do not have predictable positions and momenta along the paths. The reason for this is that the paths, themselves, are not predictable by any rule as they are in classical mechanics! 2. If we could devise an experiment for mea ...
... 1. Even within a particle-like interpretation of the experiment, particles do not have predictable positions and momenta along the paths. The reason for this is that the paths, themselves, are not predictable by any rule as they are in classical mechanics! 2. If we could devise an experiment for mea ...
Document
... 4. How much work must be done to pull apart the electron and the proton that make up the hydrogen atom if the atom is initially in (a) its ground state and (b) the state with n = 2? ANSWER: (a) 13.6 eV; (b) 3.40 eV 5. What is the probability that in the ground state of the hydrogen atom, the electro ...
... 4. How much work must be done to pull apart the electron and the proton that make up the hydrogen atom if the atom is initially in (a) its ground state and (b) the state with n = 2? ANSWER: (a) 13.6 eV; (b) 3.40 eV 5. What is the probability that in the ground state of the hydrogen atom, the electro ...
Lamb
... A misconception which most physicists acquire in their formative years is that the photoelectric effect requires the quantization of the electromagnetic field for its explanation. ...
... A misconception which most physicists acquire in their formative years is that the photoelectric effect requires the quantization of the electromagnetic field for its explanation. ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
QUANTUM NUMBERS
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
... For an electron in an atom with l=0 is said to be in an s state. For an electron in an atom with l=1 is said to be in an p state. For an electron in an atom with l=2 is said to be in an d state. For an electron in an atom with l=3 is said to be in an e state. ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle
... angular momentum (L), and one for the z component of angular momentum (mL). Thus the normal quantum numbers come out of the theory instead of being put into the theory as Bohr had to do. There is a fourth quantum number (recall your chemistry), but we need a relativistic solution to the problem to g ...
... angular momentum (L), and one for the z component of angular momentum (mL). Thus the normal quantum numbers come out of the theory instead of being put into the theory as Bohr had to do. There is a fourth quantum number (recall your chemistry), but we need a relativistic solution to the problem to g ...
Lec-23_Strachan
... The electronic configuration of the elements explained by quantum numbers and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle explains the configuration ...
... The electronic configuration of the elements explained by quantum numbers and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle explains the configuration ...
Quantum_PPT
... • This is going to be KEmax of an electron since hfo is the minimum energy needed to free an electron (assuming it is freeing a higher energy electron). ...
... • This is going to be KEmax of an electron since hfo is the minimum energy needed to free an electron (assuming it is freeing a higher energy electron). ...
Chapter 1 Quiz
... a) Write the time-independent Schrodinger Equation for each region of this potential, and give the general form of the wavefunctions for an electron traveling through such a potential. Remember, the electron is not bound, so your solutions will take the form of traveling waves (e±ikx), which cannot ...
... a) Write the time-independent Schrodinger Equation for each region of this potential, and give the general form of the wavefunctions for an electron traveling through such a potential. Remember, the electron is not bound, so your solutions will take the form of traveling waves (e±ikx), which cannot ...
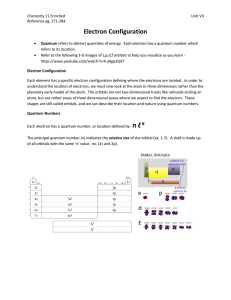
File - Chemistry 11 Enriched
... understand the location of electrons, we must now look at the atom in three dimensions rather than the planetary early model of the atom. The orbitals are not two dimensional tracks like railroads circling an atom, but are rather areas of three dimensional space where we expect to find the electron. ...
... understand the location of electrons, we must now look at the atom in three dimensions rather than the planetary early model of the atom. The orbitals are not two dimensional tracks like railroads circling an atom, but are rather areas of three dimensional space where we expect to find the electron. ...
Student Presentation
... • De Broglie Wavelength – Louis de Broglie suggested that although electrons have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
... • De Broglie Wavelength – Louis de Broglie suggested that although electrons have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
motivation-to-quantum
... even if they never happen! • Each of exponentially many possibilities can be used to perform a part of a computation at the same time. ...
... even if they never happen! • Each of exponentially many possibilities can be used to perform a part of a computation at the same time. ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.