Physics 43 Ch 42 HW# Key
... to move from the n = 1 state to the n = 2 state? (b) Suppose the electron gains this energy through collisions among hydrogen atoms at a high temperature. At what temperature would the average atomic kinetic energy 3kBT/2, where kB is the Boltzmann constant, be great enough to excite the electron? P ...
... to move from the n = 1 state to the n = 2 state? (b) Suppose the electron gains this energy through collisions among hydrogen atoms at a high temperature. At what temperature would the average atomic kinetic energy 3kBT/2, where kB is the Boltzmann constant, be great enough to excite the electron? P ...
Study Questions and Problems
... The values allowed for the three quantum numbers depend upon each other. The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can ha ...
... The values allowed for the three quantum numbers depend upon each other. The principal quantum n can have any integer value from 1, 2, 3, 4...to infinity. The secondary (or angular momentum) quantum number l can have values from 0, 1, 2, 3, to a maximum of n –1. The magnetic quantum number ml can ha ...
Name
... 13. What happens when an electric current is passed through the gas or vapor of an element? 14. Passing the light emitted by an element through a prism gives the of the element. 15. Is the following sentence true or false? The emission spectrum of an element can be the same as the emission spectrum ...
... 13. What happens when an electric current is passed through the gas or vapor of an element? 14. Passing the light emitted by an element through a prism gives the of the element. 15. Is the following sentence true or false? The emission spectrum of an element can be the same as the emission spectrum ...
Some properties of Thomson`s atom
... sfere of radius a0 . The electron, having charge −e, is considered to be a point particle and is located inside the sphere. a) Find the electric field and the potential generated by the positive charge and the equilibrium position for the electron (assumed to have zero angular momentum). b) Find the ...
... sfere of radius a0 . The electron, having charge −e, is considered to be a point particle and is located inside the sphere. a) Find the electric field and the potential generated by the positive charge and the equilibrium position for the electron (assumed to have zero angular momentum). b) Find the ...
Quiz
... off. The Hamiltonian for this interaction is Hint = λx4 , where x is the position coordinate. (a) Expand out the time evolution operator Uint (t) = e−iHint t to linear order for this impulse interaction. This is a good approximation since ∆t is very small (and the interaction strength λ is also assu ...
... off. The Hamiltonian for this interaction is Hint = λx4 , where x is the position coordinate. (a) Expand out the time evolution operator Uint (t) = e−iHint t to linear order for this impulse interaction. This is a good approximation since ∆t is very small (and the interaction strength λ is also assu ...
Atomic spectra and the Bohr atom
... of same n by giving them different shapes; any integer value from 0 to n-1; orbitals of same n but different l are in different sub-shells: s p d f g ...
... of same n by giving them different shapes; any integer value from 0 to n-1; orbitals of same n but different l are in different sub-shells: s p d f g ...
Modern view of matter and the universe
... are tied with a particular symmetry called Gauge Symmetry in Quantum Physics ...
... are tied with a particular symmetry called Gauge Symmetry in Quantum Physics ...
QUANTUM THEORY OF ATOMS AND MOLECULES
... 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What would you exp ...
... 1. Show that the function = N sin nx/L satisfies the Schrodinger equation for a particle in a 1-D box between x = 0 and x = L and calculate the value of the normalisation factor N. Evaluate the probability of finding the particle between 0.4L and 0.6L when n = 1 and when n = 2. What would you exp ...
Quantum Mechanics I. Introduction Just before 1900, the classical
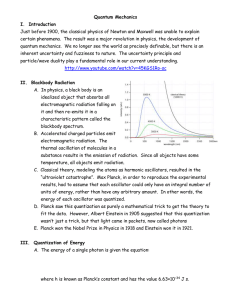
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...
... C. Classical theory, modeling the atoms as harmonic oscillators, resulted in the “ultraviolet catastrophe”. Max Planck, in order to reproduce the experimental results, had to assume that each oscillator could only have an integral number of units of energy, rather than have any arbitrary amount. In ...
Slides - GSI Indico
... • The electromagnetic interaction is one of the four “fundamental” interactions in Nature. It is the interaction among electric charged particles (e.g., electrons and positrons) and it is mediated by the electromagnetic ¯eld (photons, in the “quantum” language) • The relativistic quantum theory desc ...
... • The electromagnetic interaction is one of the four “fundamental” interactions in Nature. It is the interaction among electric charged particles (e.g., electrons and positrons) and it is mediated by the electromagnetic ¯eld (photons, in the “quantum” language) • The relativistic quantum theory desc ...
T3_Static_Potentials_And_Eigenstates
... • Originally postulated by de Broglie in 1924 – NO evidence at this point – He surmised that l=h/p: E=1/2 mv2=p2/2m ...
... • Originally postulated by de Broglie in 1924 – NO evidence at this point – He surmised that l=h/p: E=1/2 mv2=p2/2m ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... different eigen values of a Hermitian operator are orthogonal. 12. The high temperature microwave spectrum of KCl vapor shows an absorption at 7687.94 MHz that can be identified with J=0 to J=1 transition of 39K35Cl molecules in the lowest v=0 vibrational state. Calculate the bond length of KCl and ...
... different eigen values of a Hermitian operator are orthogonal. 12. The high temperature microwave spectrum of KCl vapor shows an absorption at 7687.94 MHz that can be identified with J=0 to J=1 transition of 39K35Cl molecules in the lowest v=0 vibrational state. Calculate the bond length of KCl and ...
Aug 31 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Can stay normalized in time? If satisfies the Schrödinger equation and is normalizable, then indeed ...
... Can stay normalized in time? If satisfies the Schrödinger equation and is normalizable, then indeed ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.