Oops !Power Point File of Physics 2D lecture for Today should have
... Apply an External B field on a Hydrogen atom (viewed as a dipole) Consider B || Z axis (could be any other direction too) The dipole moment of the Hydrogen atom (due to electron orbit) experiences a Torque m B which does work to align m || B but this can not be (same Uncertainty principle argu ...
... Apply an External B field on a Hydrogen atom (viewed as a dipole) Consider B || Z axis (could be any other direction too) The dipole moment of the Hydrogen atom (due to electron orbit) experiences a Torque m B which does work to align m || B but this can not be (same Uncertainty principle argu ...
Presentation
... • Consider the order of the states as some kind of social order, or rank, or job position. In a rigid, hierarchical society, positions would be occupied according to certain parameters (e.g. diplomas, family connections, religious or ethnical factors, etc.). In a more intelligent society, people of ...
... • Consider the order of the states as some kind of social order, or rank, or job position. In a rigid, hierarchical society, positions would be occupied according to certain parameters (e.g. diplomas, family connections, religious or ethnical factors, etc.). In a more intelligent society, people of ...
Quantum Grand Canonical Ensemble
... comes from the fact that you get a distinct wavefunction N1 !N2 ! · · · Nl ! times. A subsystem consists of Nj particles, with total energy Ej . It is described by a state vector |Ej , Nj , kj i, where kj are the other quantum numbers necessary to specify the state. The system consists of subsystems ...
... comes from the fact that you get a distinct wavefunction N1 !N2 ! · · · Nl ! times. A subsystem consists of Nj particles, with total energy Ej . It is described by a state vector |Ej , Nj , kj i, where kj are the other quantum numbers necessary to specify the state. The system consists of subsystems ...
Chemistry Ch 4
... Lois de Broglie wondered if electrons (matter), normally thought of as a particle, maybe have some wave properties too. ...
... Lois de Broglie wondered if electrons (matter), normally thought of as a particle, maybe have some wave properties too. ...
4.2_The_Quantum_Model_of_the_Atom1
... photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
... photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
TT 35: Low-Dimensional Systems: 2D - Theory - DPG
... topological origin [1]. All these effects could be described via 2+1 dimensional gauge theories, including topological Chern-Simons (CS) tensor structures of characteristic level [2]. Even if the bare Lagrangian of a theory does not include a CS term, it could be generated at one loop level via cont ...
... topological origin [1]. All these effects could be described via 2+1 dimensional gauge theories, including topological Chern-Simons (CS) tensor structures of characteristic level [2]. Even if the bare Lagrangian of a theory does not include a CS term, it could be generated at one loop level via cont ...
Quantum Theory of the Atom
... B. Orbitals – describes the electron’s location 1. 2 electrons per orbital 2. s sublevel has 1 orbital (2 electrons total) 3. p sublevel has 3 orbital (6 electrons total) 4. d sublevel has 5 orbital (10 electrons total ) 5. f sublevel has 7 orbital (14 electrons total) Looking at the periodic table ...
... B. Orbitals – describes the electron’s location 1. 2 electrons per orbital 2. s sublevel has 1 orbital (2 electrons total) 3. p sublevel has 3 orbital (6 electrons total) 4. d sublevel has 5 orbital (10 electrons total ) 5. f sublevel has 7 orbital (14 electrons total) Looking at the periodic table ...
Worksheet 1 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... Determine the electron configuration for O. Is O a reactive element? Why? Determine the electron configuration for O-. Is O- a stable ion? Why? Determine the electron configuration for O2-. Is O2- a stable ion? Why? O is 1s22s22p4. O is very reactive (the principal quantum numbers 1 and 2 energy lev ...
... Determine the electron configuration for O. Is O a reactive element? Why? Determine the electron configuration for O-. Is O- a stable ion? Why? Determine the electron configuration for O2-. Is O2- a stable ion? Why? O is 1s22s22p4. O is very reactive (the principal quantum numbers 1 and 2 energy lev ...
“Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be
... • Collapse of wavefunction • QM is complete ...
... • Collapse of wavefunction • QM is complete ...
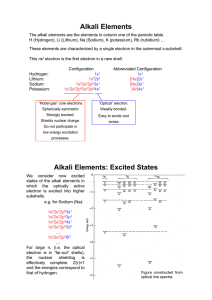
Alkali Elements Alkali Elements: Excited States
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
An attempt to a β rays theory Basic assumptions of the theory (1)
... • b) Electrons (or neutrinos) can be created or destroyed. Such a possibility does not have any analogy with the possibility of creation or annihilation of an electronpositron pair; if, indeed, a positron is interpreted as a Dirac ≪ hole ≫, we can simply view the latter process as a quantum transiti ...
... • b) Electrons (or neutrinos) can be created or destroyed. Such a possibility does not have any analogy with the possibility of creation or annihilation of an electronpositron pair; if, indeed, a positron is interpreted as a Dirac ≪ hole ≫, we can simply view the latter process as a quantum transiti ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.