Optical Properties of 1P State Electron Bubbles in
... where Eel is the energy of the quantum state of the electron, α is the surface tension of the liquid, A is the surface area of the bubble, P is the pressure, and V is the volume. The energy Eel depends on the quantum numbers of the state and on the shape and size of the bubble. For a given set of qu ...
... where Eel is the energy of the quantum state of the electron, α is the surface tension of the liquid, A is the surface area of the bubble, P is the pressure, and V is the volume. The energy Eel depends on the quantum numbers of the state and on the shape and size of the bubble. For a given set of qu ...
s - Dl4a.org
... • Electrons (and other objects at this scale) do not follow definite paths through space! • They can be represented by a kind of wave, that exhibits interference like water waves • They also behave like particles, in the sense that they are indivisible “lumps” • “Wave-particle duality”: Is it a wave ...
... • Electrons (and other objects at this scale) do not follow definite paths through space! • They can be represented by a kind of wave, that exhibits interference like water waves • They also behave like particles, in the sense that they are indivisible “lumps” • “Wave-particle duality”: Is it a wave ...
Notes on the Electronic Structure of Atoms
... The Spin Quantum Number ms The Spin Quantum Number, m • In the 1920s, it was discovered h i di d that two electrons in the same orbital do not have exactly the y same energy. • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. • Elec ...
... The Spin Quantum Number ms The Spin Quantum Number, m • In the 1920s, it was discovered h i di d that two electrons in the same orbital do not have exactly the y same energy. • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. • Elec ...
Document
... • Electrons (and other objects at this scale) do not follow definite paths through space! • They can be represented by a kind of wave, that exhibits interference like water waves • They also behave like particles, in the sense that they are indivisible “lumps” • “Wave-particle duality”: Is it a wave ...
... • Electrons (and other objects at this scale) do not follow definite paths through space! • They can be represented by a kind of wave, that exhibits interference like water waves • They also behave like particles, in the sense that they are indivisible “lumps” • “Wave-particle duality”: Is it a wave ...
String Theory - Santa Rosa Junior College
... All Superstring theories appear to be correct in certain circumstances M-theory was developed to unify them Proposes that strings are really 1D “slices” of 2D membranes vibrating in 11 rather than 10 spacetime dimensions ...
... All Superstring theories appear to be correct in certain circumstances M-theory was developed to unify them Proposes that strings are really 1D “slices” of 2D membranes vibrating in 11 rather than 10 spacetime dimensions ...
Lecture 2: Quantum Math Basics 1 Complex Numbers
... did when we imagined the two-dimensional complex plane in the previous section. Then, why do we even use complex numbers at all? Well, there are two major reasons: firstly, complex phases are intrinsic to many quantum algorithms, like the Shor’s Algorithm for prime factorization. Complex numbers ca ...
... did when we imagined the two-dimensional complex plane in the previous section. Then, why do we even use complex numbers at all? Well, there are two major reasons: firstly, complex phases are intrinsic to many quantum algorithms, like the Shor’s Algorithm for prime factorization. Complex numbers ca ...
WAVE FUNCTIONS OF DISORDERED TWO
... To calculate velocities and also conductivities from the above formulae one needs the functions |nk+) by definition being eigenfunctions of H. These are scattering, extended or current carrying states we are going to calculate in this work. In impure 2DEG in magnetic and electric fields both extende ...
... To calculate velocities and also conductivities from the above formulae one needs the functions |nk+) by definition being eigenfunctions of H. These are scattering, extended or current carrying states we are going to calculate in this work. In impure 2DEG in magnetic and electric fields both extende ...
here
... double-slit experiment. In which of the interpretations does a single electron go through one and only one slit? (a) Pilot Wave and Collapse (b) Pilot Wave and Many Worlds (c) Collapse and Many Worlds (d) Pilot Wave, Collapse, and Many Worlds 14. An electron microscope can produce clearer images of ...
... double-slit experiment. In which of the interpretations does a single electron go through one and only one slit? (a) Pilot Wave and Collapse (b) Pilot Wave and Many Worlds (c) Collapse and Many Worlds (d) Pilot Wave, Collapse, and Many Worlds 14. An electron microscope can produce clearer images of ...
Cornell University – Toby Berger
... The mathematical model presented in [4] seeks a middle way between Copenhagen quantum mechanics, where the wave function does not aspire to describe reality but merely represents our knowledge of it, and Everett's many-worlds interpretation which attempts to include the observer as just another phys ...
... The mathematical model presented in [4] seeks a middle way between Copenhagen quantum mechanics, where the wave function does not aspire to describe reality but merely represents our knowledge of it, and Everett's many-worlds interpretation which attempts to include the observer as just another phys ...
Quantum Zeno Effect
... Case 2: Bomb Present in the room. Now suppose that there is a bomb in the room. Then there are two possible outcomes in the first cycle. With probability sin2 Ɵ, the qubit passes the bomb and causes an explosion. With probability cos2Ɵ, the qubit goes through the lower path, does not see the bomb, ...
... Case 2: Bomb Present in the room. Now suppose that there is a bomb in the room. Then there are two possible outcomes in the first cycle. With probability sin2 Ɵ, the qubit passes the bomb and causes an explosion. With probability cos2Ɵ, the qubit goes through the lower path, does not see the bomb, ...
Study of a two-state system : the ammonia molecule
... eigenstates of the system ? (justify your answer). ...
... eigenstates of the system ? (justify your answer). ...
... Dirac’s equation of a free electron. We distinguish our study from many others by focusing on the motion of the electric field ⊂B⊂M[2] that is responsible for revealing the point particle electron in [1] (cf. Demikhovskii et al., 2010) for a similarly motivated study), not the dynamics of an electro ...
ONE HUNDRED YEARS OF LIGHT QUANTA
... So, according to Dirac, the electromagnetic field is made up of field amplitudes that can oscillate harmonically. But these amplitudes, because of the ever-present half quantum of energy ½ hν, can never be permanently at rest. They must always have their fundamental excitations, the so-called “zerop ...
... So, according to Dirac, the electromagnetic field is made up of field amplitudes that can oscillate harmonically. But these amplitudes, because of the ever-present half quantum of energy ½ hν, can never be permanently at rest. They must always have their fundamental excitations, the so-called “zerop ...
Boltzmann factors and partition functions revisited
... Indistinguishable subsystems Indistinguishable means that there is no way in principle to identify individual particles according to their location in space. (Example: identical gas molecules moving around inside a container of volume V .) If the criterion: number of quantum states per particle with ...
... Indistinguishable subsystems Indistinguishable means that there is no way in principle to identify individual particles according to their location in space. (Example: identical gas molecules moving around inside a container of volume V .) If the criterion: number of quantum states per particle with ...
Modern Theory of the Atom: Quantum Mechanical Model
... • Electrons can move between energy levels – higher energy levels farther from nucleus – moving up to higher E level: electron absorbs energy – moving down to lower E level: electron emits light energy ...
... • Electrons can move between energy levels – higher energy levels farther from nucleus – moving up to higher E level: electron absorbs energy – moving down to lower E level: electron emits light energy ...
Unit G495 - Field and particle pictures - Insert
... cross-section of 0.5 mm2 and a p.d. of 1.5 V across it, would have in it a current density of nearly 50 108 A m–2, i.e. a current of almost 50 A. Even this huge current implies a drift velocity of only a few mm s–1. This is at odds with what might be expected, suggesting that the underlying picture ...
... cross-section of 0.5 mm2 and a p.d. of 1.5 V across it, would have in it a current density of nearly 50 108 A m–2, i.e. a current of almost 50 A. Even this huge current implies a drift velocity of only a few mm s–1. This is at odds with what might be expected, suggesting that the underlying picture ...
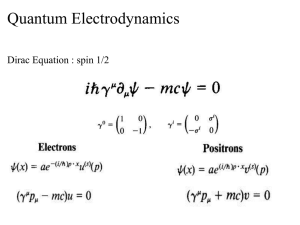
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.