Thomson scattering: - Ira-Inaf
... The main cause of the acceleration of the particle will be due to the electric field component of the incident wave. The particle will move in the direction of the oscillating electric field, resulting in electromagnetic dipole radiation. The moving particle radiates most strongly in a direction pe ...
... The main cause of the acceleration of the particle will be due to the electric field component of the incident wave. The particle will move in the direction of the oscillating electric field, resulting in electromagnetic dipole radiation. The moving particle radiates most strongly in a direction pe ...
F.S.S. Rosa
... by Dalibard, Dupont-Roc and Cohen-Tannoudji to describe a particle (in our case, an atom) interacting with a reservoir (the radiation field). • This approach provides general expressions for the atomic energy shifts and the exchange rates. ...
... by Dalibard, Dupont-Roc and Cohen-Tannoudji to describe a particle (in our case, an atom) interacting with a reservoir (the radiation field). • This approach provides general expressions for the atomic energy shifts and the exchange rates. ...
<< Previous
... electrons for the first time (again at Tübingen!). However, the results are profoundly different this time because electrons are fermions - and therefore obey the Pauli exclusion principle - whereas photons are bosons and do not. Credit where it's due So why are Jönsson, Tonomura and the other pione ...
... electrons for the first time (again at Tübingen!). However, the results are profoundly different this time because electrons are fermions - and therefore obey the Pauli exclusion principle - whereas photons are bosons and do not. Credit where it's due So why are Jönsson, Tonomura and the other pione ...
Transient induced molecular negative ions formed in cold electron
... potential curve. In this case the electron will spend a considerable time at a radial distance close to rM. The electron can then be said to “orbit” about the centre of force (the polarized molecule). The angular motion speeds up as r decreases in order to conserve angular momentum, and a large numb ...
... potential curve. In this case the electron will spend a considerable time at a radial distance close to rM. The electron can then be said to “orbit” about the centre of force (the polarized molecule). The angular motion speeds up as r decreases in order to conserve angular momentum, and a large numb ...
Solutions for class #5 from Yosumism website Problem 1: Problem 27: YOUR NOTES:
... Yosunism website: http://grephysics.yosunism.com ...
... Yosunism website: http://grephysics.yosunism.com ...
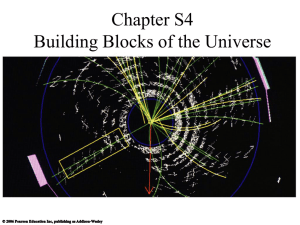
chapterS4BuildingBlo..
... • Much of our knowledge about the quantum realm comes particle accelerators • Smashing together high-energy particles produces showers of new particles ...
... • Much of our knowledge about the quantum realm comes particle accelerators • Smashing together high-energy particles produces showers of new particles ...
Atomic physics: Atomic Spectra: Thomson`s plum
... a dimensionless universal constant. For a given principal quantum number n, k can have n different values leading to different states with slightly different energies. So, we shall have a number of transitions in place of a single one of Bohr’s theory. Thus, the lines generated are the fine structur ...
... a dimensionless universal constant. For a given principal quantum number n, k can have n different values leading to different states with slightly different energies. So, we shall have a number of transitions in place of a single one of Bohr’s theory. Thus, the lines generated are the fine structur ...
Slide - Pacific Institute of Theoretical Physics
... Note the final state of X is not necessarily relevant- it can be changed in an arbitrary way after the 2nd interaction of X. Thus X need not be part of the environment. Note we could also have more than one intermediary- ie., X, Y, etc.- with correlations/entanglement are transmitted along a chain ( ...
... Note the final state of X is not necessarily relevant- it can be changed in an arbitrary way after the 2nd interaction of X. Thus X need not be part of the environment. Note we could also have more than one intermediary- ie., X, Y, etc.- with correlations/entanglement are transmitted along a chain ( ...
view pdf - Sub-Structure of the Electron
... light or models which regard the electron as a solid charged shell rotating with the speed of light2. Diracs approach recently was extended to a more or less complete particle model of the electron3. These models, however, cannot predict the elementary charge or the correct spin nor could the existe ...
... light or models which regard the electron as a solid charged shell rotating with the speed of light2. Diracs approach recently was extended to a more or less complete particle model of the electron3. These models, however, cannot predict the elementary charge or the correct spin nor could the existe ...
Higgs - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... Let’s begin by talking about the thing that physicists call a field. The need often arises to describe something that can have a different value at every point in space… like the air temperature or like the wind velocity or like the strength and direction of some force such as the Earth’s magnetic f ...
... Let’s begin by talking about the thing that physicists call a field. The need often arises to describe something that can have a different value at every point in space… like the air temperature or like the wind velocity or like the strength and direction of some force such as the Earth’s magnetic f ...
Talk, 15 MB - Seth Aubin - College of William and Mary
... Surprise! Reach Tc with only a 30x loss in number. (trap loaded with 2x107 atoms) Experimental cycle = 5 - 15 seconds ...
... Surprise! Reach Tc with only a 30x loss in number. (trap loaded with 2x107 atoms) Experimental cycle = 5 - 15 seconds ...
Why quantum field theory?
... a natural framework in which we can study quantum mechanical systems where different quantum states can have different numbers of particles. In fact, this can be very useful even in non-relativistic physics where we are not forced to use it, or at least there is no basic principle which tells us we ...
... a natural framework in which we can study quantum mechanical systems where different quantum states can have different numbers of particles. In fact, this can be very useful even in non-relativistic physics where we are not forced to use it, or at least there is no basic principle which tells us we ...
Review
... The position x can also be viewed as an operator. It simply multiplies (x,t) by the value of x, similar to the how the potential energy operator simply multiplies (x,t) by the value of the potential energy. Thus, we add position operator ...
... The position x can also be viewed as an operator. It simply multiplies (x,t) by the value of x, similar to the how the potential energy operator simply multiplies (x,t) by the value of the potential energy. Thus, we add position operator ...
Experiment Note - Spectrum Techniques
... The objective of this experiment is to demonstrate the influence of the Compton Effect on gamma-spectrum measurements of gamma-emitting radioisotopes. This demonstration is easily conducted using a Spectrum Techniques UCS-20 Universal Computer Spectrometer (www.spectrumtechniques.com), a small scint ...
... The objective of this experiment is to demonstrate the influence of the Compton Effect on gamma-spectrum measurements of gamma-emitting radioisotopes. This demonstration is easily conducted using a Spectrum Techniques UCS-20 Universal Computer Spectrometer (www.spectrumtechniques.com), a small scint ...
Energy level - Spring-Ford Area School District
... • analogous to the rungs of a ladder The electron cannot exist between energy levels, just like you can’t stand between rungs on a ladder A quantum of energy is the amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to another ...
... • analogous to the rungs of a ladder The electron cannot exist between energy levels, just like you can’t stand between rungs on a ladder A quantum of energy is the amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to another ...
Atomic Structure - Sakshi Education
... iii. The cathode rays travel in straight line in the absence of electric or magnetic field. iv. The cathode rays are deflected towards the positively charged plate in the presence of electric field and South Pole in the magnetic field. This shows that the cathode rays consist of a stream of negative ...
... iii. The cathode rays travel in straight line in the absence of electric or magnetic field. iv. The cathode rays are deflected towards the positively charged plate in the presence of electric field and South Pole in the magnetic field. This shows that the cathode rays consist of a stream of negative ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.