Early risk factors for adult bipolar disorder in
... investigated whether the early signs of psychopathology predict BPD later in life. Numerous studies have demonstrated high rates of developing mania among children or adolescents with depression [23-28]. Therefore, earlyonset depressive symptoms or MDD might predict later BPD. Disruptive behavioral ...
... investigated whether the early signs of psychopathology predict BPD later in life. Numerous studies have demonstrated high rates of developing mania among children or adolescents with depression [23-28]. Therefore, earlyonset depressive symptoms or MDD might predict later BPD. Disruptive behavioral ...
Early risk factors for adult bipolar disorder in
... investigated whether the early signs of psychopathology predict BPD later in life. Numerous studies have demonstrated high rates of developing mania among children or adolescents with depression [23-28]. Therefore, earlyonset depressive symptoms or MDD might predict later BPD. Disruptive behavioral ...
... investigated whether the early signs of psychopathology predict BPD later in life. Numerous studies have demonstrated high rates of developing mania among children or adolescents with depression [23-28]. Therefore, earlyonset depressive symptoms or MDD might predict later BPD. Disruptive behavioral ...
backbasics2013 ADHD learning disabilities and autism spectrum
... -useful to support clinical evaluation and monitor progress, ...
... -useful to support clinical evaluation and monitor progress, ...
Principles of managing patients with personality disorder
... borderline cluster, have higher rates of suicide and accidental deaths than the general population (Dowson & Grounds, 1995). Some of the traits associated with the antisocial cluster (cluster B) personality disorders such as impulsivity and recklessness may contribute to high rates of physical morbi ...
... borderline cluster, have higher rates of suicide and accidental deaths than the general population (Dowson & Grounds, 1995). Some of the traits associated with the antisocial cluster (cluster B) personality disorders such as impulsivity and recklessness may contribute to high rates of physical morbi ...
0-3 Diagnostic Classification System
... The reason for the lack of reliability, validity, and accuracy data can be found in the administration manual. In the introductory chapter to the manual it is noted that: In any scientific enterprise, but particularly in a new field, a healthy tension exists between the desire to analyze findings fr ...
... The reason for the lack of reliability, validity, and accuracy data can be found in the administration manual. In the introductory chapter to the manual it is noted that: In any scientific enterprise, but particularly in a new field, a healthy tension exists between the desire to analyze findings fr ...
PowerPoint * Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2
... • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self, cognition, behavior, affect, perceptions, and/or memories. This disruption may be observed by others or reported by the pati ...
... • A. Disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states (alters) or an experience of possession, as evidenced by discontinuities in sense of self, cognition, behavior, affect, perceptions, and/or memories. This disruption may be observed by others or reported by the pati ...
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... •60%) of the respondents with undiagnosed medical conditions said that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (41%) to severe (19%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. These physical symptoms or aches and pains include backaches (13%), headaches (14%), dig ...
... •60%) of the respondents with undiagnosed medical conditions said that on days when they feel anxious or depressed, there is a moderate (41%) to severe (19%) change in their physical symptoms or aches and pains. These physical symptoms or aches and pains include backaches (13%), headaches (14%), dig ...
Epidemiology of ADHD
... in children and adolescents in the US. Merikangas et al. (7) found a 12-month prevalence of ADHD around 8.6% (±0.7) in a nationally representative probability sample of non–institutionalised children and adolescents (8–15 years of age) from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Inter ...
... in children and adolescents in the US. Merikangas et al. (7) found a 12-month prevalence of ADHD around 8.6% (±0.7) in a nationally representative probability sample of non–institutionalised children and adolescents (8–15 years of age) from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Inter ...
word document
... (1) Eating, in a discrete period of time (for example, within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat during a similar period of time under similar circumstances. (2) A sense of lack of control over eating during the episode (for example, a feeling ...
... (1) Eating, in a discrete period of time (for example, within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is definitely larger than most people would eat during a similar period of time under similar circumstances. (2) A sense of lack of control over eating during the episode (for example, a feeling ...
dsm-iv-tr classification - Pearson Higher Education
... An ellipsis (. . .) is used in the names of certain disorders to indicate that the name of a specific mental disorder or general medical condition should be inserted when recording the name (e.g., 293.0 Delirium Due to Hypothyroidism). ...
... An ellipsis (. . .) is used in the names of certain disorders to indicate that the name of a specific mental disorder or general medical condition should be inserted when recording the name (e.g., 293.0 Delirium Due to Hypothyroidism). ...
Psychiatric Disorders Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Their Nature
... Objectives: To retrospectively establish the nature and frequency of Axis I psychiatric disorders pre- and post-TBI. Participants: One hundred participants who were 0.5 to 5.5 years post mild to severe TBI and 87 informants, each evaluated at a single time point. Main Measure: The Structured Clinica ...
... Objectives: To retrospectively establish the nature and frequency of Axis I psychiatric disorders pre- and post-TBI. Participants: One hundred participants who were 0.5 to 5.5 years post mild to severe TBI and 87 informants, each evaluated at a single time point. Main Measure: The Structured Clinica ...
Specificity of autonomic arousal to DSM
... 0005-7967/$ – see front matter Ó 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. ...
... 0005-7967/$ – see front matter Ó 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. ...
Anxiety Disorders - University of Delaware
... E.g. contamination risks (if no guarantee, then I’m not touching it) The ‘normal’ level of acceptance of risk is too high ...
... E.g. contamination risks (if no guarantee, then I’m not touching it) The ‘normal’ level of acceptance of risk is too high ...
Document
... instability and inappropriate anger, but their frantic efforts to avoid abandonment and repetitive self-injury disappear. ...
... instability and inappropriate anger, but their frantic efforts to avoid abandonment and repetitive self-injury disappear. ...
instructional package - Horry Georgetown Technical College
... 1. Explain the terms “tolerance” and “withdrawal symptoms” and give examples. 2. Describe the typical effects of cocaine and contrast these with the effects of the other major stimulant, amphetamines, and caffeine. 3. Describe the general effect of the hallucinogen LSD. 4. Describe the current shor ...
... 1. Explain the terms “tolerance” and “withdrawal symptoms” and give examples. 2. Describe the typical effects of cocaine and contrast these with the effects of the other major stimulant, amphetamines, and caffeine. 3. Describe the general effect of the hallucinogen LSD. 4. Describe the current shor ...
Helping A Friend Or Family Member
... even if they don’t understand exactly what is happening. It’s important to spend time with children, explain the situation and encourage them to share their feelings and questions. Talk to children at a level they can understand. Younger children might be satisfied with “Mommy (or other relative) do ...
... even if they don’t understand exactly what is happening. It’s important to spend time with children, explain the situation and encourage them to share their feelings and questions. Talk to children at a level they can understand. Younger children might be satisfied with “Mommy (or other relative) do ...
The Physician`s Role in Managing Acute Stress Disorder
... behaviors. Persons with this disorder are at increased risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder. Other risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder include current or family history of anxiety or mood disorders, a history of sexual or physical abuse, lower cognitive ability, engaging in ex ...
... behaviors. Persons with this disorder are at increased risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder. Other risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder include current or family history of anxiety or mood disorders, a history of sexual or physical abuse, lower cognitive ability, engaging in ex ...
Child Anxiety Disorders
... there has been a marked increase in attention given to child anxiety disorders. • Indeed, the decade of the 1980's was characterized by a mushrooming of investigations and knowledge of anxiety disorders in children and adolescents. • This increased focus on child anxiety ...
... there has been a marked increase in attention given to child anxiety disorders. • Indeed, the decade of the 1980's was characterized by a mushrooming of investigations and knowledge of anxiety disorders in children and adolescents. • This increased focus on child anxiety ...
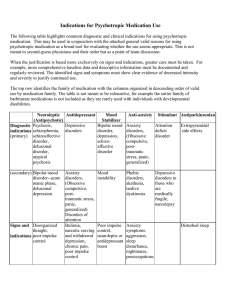
Indications for Psychotropic Medication Use
... without sedation, a psychotropic may be used for its sedating effect. For some individuals these medical procedures may include dental work, diagnostic evaluations such as EEGs, EKGs, C-T scans or physical exams. If used for this purpose, an adequate dose to accomplish the desired sedation must be s ...
... without sedation, a psychotropic may be used for its sedating effect. For some individuals these medical procedures may include dental work, diagnostic evaluations such as EEGs, EKGs, C-T scans or physical exams. If used for this purpose, an adequate dose to accomplish the desired sedation must be s ...
Borderline Personality Disorder
... • Malfunction of the emotional centres (the limbic system, especially the amygdala); in combination with the malfunction of the narrative centre; reflect respectively, the high emotional loading of the content of the traumatic material, and the difficulty in accurate recall and the ability to constr ...
... • Malfunction of the emotional centres (the limbic system, especially the amygdala); in combination with the malfunction of the narrative centre; reflect respectively, the high emotional loading of the content of the traumatic material, and the difficulty in accurate recall and the ability to constr ...
When you just can`t forget
... Distressing experiences can cause great fear, as well as a sense of helplessness and powerlessness. Such experiences are described as traumatic. Traumatic events can over a long period of time influence the feelings, thought and moods of those affected. A traumatic event can cause emotional and phy ...
... Distressing experiences can cause great fear, as well as a sense of helplessness and powerlessness. Such experiences are described as traumatic. Traumatic events can over a long period of time influence the feelings, thought and moods of those affected. A traumatic event can cause emotional and phy ...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5)
... called Persistent Depressive Disorder which includes chronic major depression and dysthymic disorder ...
... called Persistent Depressive Disorder which includes chronic major depression and dysthymic disorder ...
PERSONALITY DISORDER
... The precise causes of borderline personality disorder are unknown, but several theories are being investigated. Because it’s five time more common in firstdegree relatives of people who have it, researchers suspect genetic may play a role. Biological factors may involve: Dysfunction in the brain’s l ...
... The precise causes of borderline personality disorder are unknown, but several theories are being investigated. Because it’s five time more common in firstdegree relatives of people who have it, researchers suspect genetic may play a role. Biological factors may involve: Dysfunction in the brain’s l ...
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS--diagnosing mania correctly
... employment. The way to tell the difference is that ADHD Sx are chronic rather than episodic and have an onset before age 7 and lack the expansive and elevated mood found in mania. 30-50% of those who had ADHD as children will continue to have ADHD Sx as adults. SUBSTANCE ABUSE can also cause mood sw ...
... employment. The way to tell the difference is that ADHD Sx are chronic rather than episodic and have an onset before age 7 and lack the expansive and elevated mood found in mania. 30-50% of those who had ADHD as children will continue to have ADHD Sx as adults. SUBSTANCE ABUSE can also cause mood sw ...
Mental Illness in William Shakespeare`s King Lear
... the diagnostic criteria of NPD in the DSM-IV, Lear fits this description well. It goes on to say that if someone with NPD is criticized or are undermined “They may react with disdain, rage, or defiant counterattacks.” (Goldman et al. 659). By examining Lear’s reaction to Cordelia, it is reasonable t ...
... the diagnostic criteria of NPD in the DSM-IV, Lear fits this description well. It goes on to say that if someone with NPD is criticized or are undermined “They may react with disdain, rage, or defiant counterattacks.” (Goldman et al. 659). By examining Lear’s reaction to Cordelia, it is reasonable t ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.