Oppositional Defiant and Conduct Disorder
... • Empirical support for conduct disorder, as a meaningful dimension of psychopathology, has come from many factor analytic studies. • Characteristics like the one’s listed here are often found to occur together in child and adolescent samples. • The clinical significance of this problem is highlight ...
... • Empirical support for conduct disorder, as a meaningful dimension of psychopathology, has come from many factor analytic studies. • Characteristics like the one’s listed here are often found to occur together in child and adolescent samples. • The clinical significance of this problem is highlight ...
Substance-Related Disorders DSM-V
... A. A problematic pattern of alcohol use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by at least two of the following, occurring within a 12-month period: 1. Alcohol is often taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than was intended. 2. There is a persistent desire ...
... A. A problematic pattern of alcohol use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by at least two of the following, occurring within a 12-month period: 1. Alcohol is often taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than was intended. 2. There is a persistent desire ...
Binge-eAting DisorDer - Practice Fusion Tutorials
... Bulimia nervosa. Binge-eating disorder has recurrent binge eating in common with bulimia nervosa but differs from the latter disorder in some fundamental respects. In terms of clinical presentation, the recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior (e.g., purging, driven exercise) seen in bulimia ne ...
... Bulimia nervosa. Binge-eating disorder has recurrent binge eating in common with bulimia nervosa but differs from the latter disorder in some fundamental respects. In terms of clinical presentation, the recurrent inappropriate compensatory behavior (e.g., purging, driven exercise) seen in bulimia ne ...
Click here
... • While the diagnoses in Section II are still categorical, “the revised chapter organization signals how disorders may relate to each other based on underlying vulnerabilities or symptom characteristics. It also breaks out some disorders because of greater understanding of their basic causes. As an ...
... • While the diagnoses in Section II are still categorical, “the revised chapter organization signals how disorders may relate to each other based on underlying vulnerabilities or symptom characteristics. It also breaks out some disorders because of greater understanding of their basic causes. As an ...
Positive affect regulation in anxiety disorders
... designed to screen for 13 of the DSM-IV disorders that have been found to be most prevalent in large epidemiological studies (Kessler et al., 1994). PDSQ items assess current symptoms, but the scale cannot be used to assess clinically significant diagnoses because it does not assess for functional im ...
... designed to screen for 13 of the DSM-IV disorders that have been found to be most prevalent in large epidemiological studies (Kessler et al., 1994). PDSQ items assess current symptoms, but the scale cannot be used to assess clinically significant diagnoses because it does not assess for functional im ...
\ The Medical Model- An Advantage \ Prior to MM, abnormal
... Interpersonal Roots~ poor social skills models Stressful Episodes~ frequently a precipitating factor Slide 19 ...
... Interpersonal Roots~ poor social skills models Stressful Episodes~ frequently a precipitating factor Slide 19 ...
Antipsychotic response in delusional disorder and schizophrenia: a
... previous treatment. The second group included schizophrenia patients who were consecutively selected during the same period of time in our Schizophrenia Unit and initiated an antipsychotic treatment. Schizophrenia patients were ...
... previous treatment. The second group included schizophrenia patients who were consecutively selected during the same period of time in our Schizophrenia Unit and initiated an antipsychotic treatment. Schizophrenia patients were ...
Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder
... hyperactivity-impulsivity that is more frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at a comparable level of development. Some hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment must have been present before age 7 years, although many individuals are diagnosed after ...
... hyperactivity-impulsivity that is more frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at a comparable level of development. Some hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment must have been present before age 7 years, although many individuals are diagnosed after ...
Using DSM-5 in Case Formulation and Treatment Planning
... • Description: Adult version measures 13 domains of symptoms DSM-5 level1 assessment.pdf • Rate each item: ...
... • Description: Adult version measures 13 domains of symptoms DSM-5 level1 assessment.pdf • Rate each item: ...
Psychiatric Comorbidity in Tropical Far North
... symptoms such as depression or hallucinations would disappear within six weeks of stopping drug usage. If after six weeks the psychiatric symptoms were still present a separate psychiatric disorder would need to be considered. For the purposes of this study alcohol will be isolated as the substance ...
... symptoms such as depression or hallucinations would disappear within six weeks of stopping drug usage. If after six weeks the psychiatric symptoms were still present a separate psychiatric disorder would need to be considered. For the purposes of this study alcohol will be isolated as the substance ...
Fulltext: english, pdf
... meet several of the eight criteria proposed by Aubry and colleagues (Aubry et al. 2000) to evaluate a causal relationship between atypical antipsychotic use and initiation of hypomanic/manic symptoms, suggesting that aripiprazole was the proximate cause of hypomanic symptoms. In particular, in both ...
... meet several of the eight criteria proposed by Aubry and colleagues (Aubry et al. 2000) to evaluate a causal relationship between atypical antipsychotic use and initiation of hypomanic/manic symptoms, suggesting that aripiprazole was the proximate cause of hypomanic symptoms. In particular, in both ...
First Responders Guide
... Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: aspects of the person that are „taken away‟, sometimes also associated with other illnesses and not always immediately recognized as indicative of schizophrenia Social withdrawal Lack of motivation and unsustainable interest in an activity Flat or inappropriate af ...
... Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: aspects of the person that are „taken away‟, sometimes also associated with other illnesses and not always immediately recognized as indicative of schizophrenia Social withdrawal Lack of motivation and unsustainable interest in an activity Flat or inappropriate af ...
Page 25 - Australian Doctor
... disorder is between 1% and 4% and in any one year about one in 200 Australians can expect to experience an episode of either bipolar depression or mania. More important than the exact percentage of the population that has bipolar disorder is the possibility that almost half remain undetected and und ...
... disorder is between 1% and 4% and in any one year about one in 200 Australians can expect to experience an episode of either bipolar depression or mania. More important than the exact percentage of the population that has bipolar disorder is the possibility that almost half remain undetected and und ...
content validity of the psycj3atric symptom index, ces
... In Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association & National Council of Measurement in Education, 1985) "content-related evidence of validity" is defined as "evidence that shows the extent to which the content of a t ...
... In Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association & National Council of Measurement in Education, 1985) "content-related evidence of validity" is defined as "evidence that shows the extent to which the content of a t ...
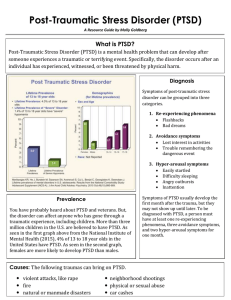
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
... Children's Hospital. Retrieved from http://www.childrenshospital.org/conditionsand-treatments/conditions/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd. Boston Children's Hospital is a leading hospital and research institution on matters of mental and behavioral health. The website provides information about r ...
... Children's Hospital. Retrieved from http://www.childrenshospital.org/conditionsand-treatments/conditions/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd. Boston Children's Hospital is a leading hospital and research institution on matters of mental and behavioral health. The website provides information about r ...
Administrative Assistant Meeting
... criteria were previously met and only some of the symptoms remain currently “In Full Remission” refers to complete absence of any current symptoms No absolute demarcation between In Full Remission and Recovered (when the disorder would no longer be noted) ...
... criteria were previously met and only some of the symptoms remain currently “In Full Remission” refers to complete absence of any current symptoms No absolute demarcation between In Full Remission and Recovered (when the disorder would no longer be noted) ...
Chapter 12 Psychological Disorders
... Somatoform disorder marked by paralysis, weakness, or loss of sensation, but with no discernable physical cause. Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 ...
... Somatoform disorder marked by paralysis, weakness, or loss of sensation, but with no discernable physical cause. Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 ...
Munchausen`s Syndrome by Proxy, Factitious Disorders
... http://www.iom.edu/~/media/Files/Report%20Files/2015/MECFS/MECFScliniciansguide.pdf. ...
... http://www.iom.edu/~/media/Files/Report%20Files/2015/MECFS/MECFScliniciansguide.pdf. ...
About First Person Plural
... Your sense of identity, your perceptions of reality and your sense of continuity of time, experiences and life depend on your thoughts, sensations, feelings, perceptions, sense of body, sense of self, behaviours and memories etc being mostly connected to each other thus, when dissociation is used fr ...
... Your sense of identity, your perceptions of reality and your sense of continuity of time, experiences and life depend on your thoughts, sensations, feelings, perceptions, sense of body, sense of self, behaviours and memories etc being mostly connected to each other thus, when dissociation is used fr ...
Making Sense of Kleptomania: Clinical Considerations Original article
... not in the context of other psychiatric conditions are uncommon. ICD-10 cautions that recurrent shoplifting with premeditated motives for personal gain, organic conditions with memory disturbances and affective conditions such as depression need to be excluded. On the other hand, DSM-IV-TR stated th ...
... not in the context of other psychiatric conditions are uncommon. ICD-10 cautions that recurrent shoplifting with premeditated motives for personal gain, organic conditions with memory disturbances and affective conditions such as depression need to be excluded. On the other hand, DSM-IV-TR stated th ...
b D I S O R D E R An Information Guide
... Other Symptoms of a Bipolar Episode Some patients with bipolar disorder may have problems with movement during their episodes. These disturbances of movement (motor symptoms) occur in up to 25 per cent of depressed patients and up to 28 per cent of patients with mixed or pure manic episodes. These m ...
... Other Symptoms of a Bipolar Episode Some patients with bipolar disorder may have problems with movement during their episodes. These disturbances of movement (motor symptoms) occur in up to 25 per cent of depressed patients and up to 28 per cent of patients with mixed or pure manic episodes. These m ...
Meta-analysis of the SLC6A3/DAT1 VNTR haplotype in
... Subjects were included if a clinical diagnosis of adult ADHD with childhood onset was established. Prior to inclusion, all patients underwent a standard clinical assessment consisting of a psychiatric evaluation by experienced psychiatrists using a semi-structured diagnostic interview for ADHD and c ...
... Subjects were included if a clinical diagnosis of adult ADHD with childhood onset was established. Prior to inclusion, all patients underwent a standard clinical assessment consisting of a psychiatric evaluation by experienced psychiatrists using a semi-structured diagnostic interview for ADHD and c ...
PREMENSTRUAL DYSPHORIC DISORDER AND THE
... information that is gathered, five or more symptoms must have occurred in the majority of the cycles in the past year. These symptoms are broken up into core symptoms and other symptoms (Wysocki, 2008). Core symptoms include a markedly depressed mood, anxiety, affective lability, persistent anger or ...
... information that is gathered, five or more symptoms must have occurred in the majority of the cycles in the past year. These symptoms are broken up into core symptoms and other symptoms (Wysocki, 2008). Core symptoms include a markedly depressed mood, anxiety, affective lability, persistent anger or ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.