
Management Techniques for the Health Unit Coordinator
... Risk Factors and Protective Factors • Risk factors—Predisposing characteristics that, if present for a person, make it more likely that he or she will develop a disorder • Protective factors—Coping resources and coping mechanisms that can improve a person’s response to stress, resulting in adaptive ...
... Risk Factors and Protective Factors • Risk factors—Predisposing characteristics that, if present for a person, make it more likely that he or she will develop a disorder • Protective factors—Coping resources and coping mechanisms that can improve a person’s response to stress, resulting in adaptive ...
Neurodevelopmental disorders
... the growth and development of the brain or central nervous system. A narrower use of the term refers to a disorder of brain function that affects emotion, learning ability, self-control and memory and that unfolds as the individual grows. Neurodevelopmental disorders are associated with ...
... the growth and development of the brain or central nervous system. A narrower use of the term refers to a disorder of brain function that affects emotion, learning ability, self-control and memory and that unfolds as the individual grows. Neurodevelopmental disorders are associated with ...
Slide 1
... • Most of DSM 5 will be familiar • Important organizational and criteria set differences exist • Comorbidity within and across diagnoses addressed • Criteria sets parallel the ICD 11 (proposed) ...
... • Most of DSM 5 will be familiar • Important organizational and criteria set differences exist • Comorbidity within and across diagnoses addressed • Criteria sets parallel the ICD 11 (proposed) ...
Mood Disorders
... the following symptoms have persisted (4 or more if the mood is only irritable) 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity 2. Decreased need for sleep 3. More talkative than usual, or pressure to keep talking 4. Racing thoughts (“flight of ideas”) 5. Distractibility 6. Increase in goal-directed activity ...
... the following symptoms have persisted (4 or more if the mood is only irritable) 1. Inflated self-esteem or grandiosity 2. Decreased need for sleep 3. More talkative than usual, or pressure to keep talking 4. Racing thoughts (“flight of ideas”) 5. Distractibility 6. Increase in goal-directed activity ...
Conversion Disorder brochure
... reference to feigning because they claim “there is no evidence that feigning is more common in patients with possible conversion disorder than with other mental disorders. Highlighting it for conversion alone is unnecessarily stigmatizing and may be detrimental to the physician-patient relationship. ...
... reference to feigning because they claim “there is no evidence that feigning is more common in patients with possible conversion disorder than with other mental disorders. Highlighting it for conversion alone is unnecessarily stigmatizing and may be detrimental to the physician-patient relationship. ...
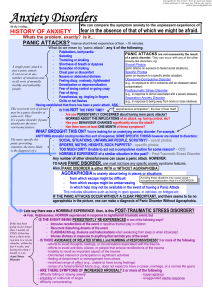
Anxiety Disorders - Deranged Physiology
... Target the distorted threat appraisal process (e.g., through repeated exposure or through techniques focusing on information processing without repeated exposure) in an effort to desensitize the patient to trauma-related triggers. • May speed recovery and prevent PTSD when therapy is given 2 to 3 we ...
... Target the distorted threat appraisal process (e.g., through repeated exposure or through techniques focusing on information processing without repeated exposure) in an effort to desensitize the patient to trauma-related triggers. • May speed recovery and prevent PTSD when therapy is given 2 to 3 we ...
anxiety disorder
... Bipolar Disorder • No difference between the gender of those affected by the disease ...
... Bipolar Disorder • No difference between the gender of those affected by the disease ...
Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD) - Home
... Children with RAD are eligible for the services outlined in Chapter 14 due to speech and language delays, as well as, various other learning delays. Through this law, children are provided with specially designed instruction and other related services after a comprehensive evaluation is completed by ...
... Children with RAD are eligible for the services outlined in Chapter 14 due to speech and language delays, as well as, various other learning delays. Through this law, children are provided with specially designed instruction and other related services after a comprehensive evaluation is completed by ...
STATE SELECTION BOARD SYLLABUS (PSYCHOLOGY ) 2015
... Social Psychology: Attitudes- Nature, Characteristics and Functions of Attitude; Attitude Formation and Change; Attitude Measurement; Prejudices and StereotypesNature and Components of Prejudice; Acquisition of Prejudices; Reduction of Prejudice; Group- Structure and Function; Group processes- Socia ...
... Social Psychology: Attitudes- Nature, Characteristics and Functions of Attitude; Attitude Formation and Change; Attitude Measurement; Prejudices and StereotypesNature and Components of Prejudice; Acquisition of Prejudices; Reduction of Prejudice; Group- Structure and Function; Group processes- Socia ...
Tripken Abnoraml 16 Review geuide and study guid [Type text
... B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) and have been present to a significant degree: 1. inflated self-esteem or grandiosity 2. decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) 3 ...
... B. During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) and have been present to a significant degree: 1. inflated self-esteem or grandiosity 2. decreased need for sleep (e.g., feels rested after only 3 hours of sleep) 3 ...
Draft Module 6 - Structured Assessment and Screenings
... ADDRESSING Guideline to Assess for Client Cultural Influences4 A ge and generational influences D isability status (developmental disability) D isability status (acquired physical/ cognitive/psychological disabilities) R eligion and spiritual orientation E thnicity S ocioeconomic status S exual ori ...
... ADDRESSING Guideline to Assess for Client Cultural Influences4 A ge and generational influences D isability status (developmental disability) D isability status (acquired physical/ cognitive/psychological disabilities) R eligion and spiritual orientation E thnicity S ocioeconomic status S exual ori ...
Myers AP - Unit 12
... Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, updated as of 2000 “text revision”; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders. ...
... Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, updated as of 2000 “text revision”; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... weight above the minimum normal weight for one’s age and height, intense fear of becoming obese, body image distortion, absence of at least three menstrual cycles otherwise expected to occur. – B. Bulimia Nervosa- Recurrent episodes of binge eating, loses control of eating behavior when binging, use ...
... weight above the minimum normal weight for one’s age and height, intense fear of becoming obese, body image distortion, absence of at least three menstrual cycles otherwise expected to occur. – B. Bulimia Nervosa- Recurrent episodes of binge eating, loses control of eating behavior when binging, use ...
PSYCHOSIS
... to medical conditions, substance intox or w/d, or focal brain lesions • Functional/Primary= psychoses originating from psychiatric illness (Schizophrenia, Major Depression, Bipolar Dis or Schizoaffective Disorder) ...
... to medical conditions, substance intox or w/d, or focal brain lesions • Functional/Primary= psychoses originating from psychiatric illness (Schizophrenia, Major Depression, Bipolar Dis or Schizoaffective Disorder) ...
Vanessa Gallegos - Bipolar I: The Causes and the Unknown
... Researchers agree that there is no single cause for bipolar I disorder, but rather a combination of different factors (2). Diagnosis begins in ruling out other mood altering ailments, such as brain tumors and strokes. If the symptoms cannot be explained by a physical ailment, the next step is a ment ...
... Researchers agree that there is no single cause for bipolar I disorder, but rather a combination of different factors (2). Diagnosis begins in ruling out other mood altering ailments, such as brain tumors and strokes. If the symptoms cannot be explained by a physical ailment, the next step is a ment ...
Becoming familiar with the DSM 5
... hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, interested and involved in a wide range of activities, socially effective, generally satisfied with life, n ...
... hand, is sought out by others because of his or her many positive qualities. No symptoms. • 81-90 Absent or minimal symptoms (e.g., mild anxiety before an exam), good functioning in all areas, interested and involved in a wide range of activities, socially effective, generally satisfied with life, n ...
PSYCHOSIS IN CHILDHOOD AND ADOLESCENCE
... Appropriate body language if paranoid Gather information slowly initially Confidentiality (and its limitations) Family involvement ...
... Appropriate body language if paranoid Gather information slowly initially Confidentiality (and its limitations) Family involvement ...
Mental Health Nursing: Anxiety Disorders
... Anxiety and depression symptoms can overlap: Sleep disturbance, appetite changes, cardiac and GI problems, poor concentration, irritability, or change in energy level ...
... Anxiety and depression symptoms can overlap: Sleep disturbance, appetite changes, cardiac and GI problems, poor concentration, irritability, or change in energy level ...
Slide 1
... 1. Realize that co-morbidity is the rule, not the exception, in bipolar disorder (BP) 2. Assess affective and co-morbid symptoms concurrently 3. Focus pharmacotherapy on achieving mood stabilization. Use psychological treatments–eg., patient education or illness management–to address comorbidity iss ...
... 1. Realize that co-morbidity is the rule, not the exception, in bipolar disorder (BP) 2. Assess affective and co-morbid symptoms concurrently 3. Focus pharmacotherapy on achieving mood stabilization. Use psychological treatments–eg., patient education or illness management–to address comorbidity iss ...
Preview the test
... 4) The DAST is highly reliable and corresponds well with the DSM diagnosis of substance use, however it does not a) address the impact substance use is having on a person’s life. b) obtain information regarding specific substances used. c) it does not attempt to discern if multiple substances are us ...
... 4) The DAST is highly reliable and corresponds well with the DSM diagnosis of substance use, however it does not a) address the impact substance use is having on a person’s life. b) obtain information regarding specific substances used. c) it does not attempt to discern if multiple substances are us ...
Chapter 6 - Forensic Consultation
... of complaints about pain, for which medical attention has been sought but that appears to have no ...
... of complaints about pain, for which medical attention has been sought but that appears to have no ...
updated April 17, 2011 [Review Sheet 210 Final exam]
... 1. Describe the essential features of personality disorders according to the DSM-IV and why they are listed on Axis II A personality disorder is enduring, it cannot go away and it is a patter of inner experience and behavior that is not normal for one’s cultural expectations. They are pervasive, inf ...
... 1. Describe the essential features of personality disorders according to the DSM-IV and why they are listed on Axis II A personality disorder is enduring, it cannot go away and it is a patter of inner experience and behavior that is not normal for one’s cultural expectations. They are pervasive, inf ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY OF CHILDREN AND FAMILY
... - Nausea or abdominal distress - Feeling of unreality - Numbness or tingling in hands and feet - Hot and cold - Chest pain or discomfort - Fears of going crazy or losing control - Fear of dying ...
... - Nausea or abdominal distress - Feeling of unreality - Numbness or tingling in hands and feet - Hot and cold - Chest pain or discomfort - Fears of going crazy or losing control - Fear of dying ...





















![updated April 17, 2011 [Review Sheet 210 Final exam]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010384833_1-7e99b174dc3d15561e317c3ce61c7199-300x300.png)
