Overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder
... comparison of fixation data and light grey for comparison of change-in-fixation data, with F ratio critical value marked by an arrowhead on the y axis. ...
... comparison of fixation data and light grey for comparison of change-in-fixation data, with F ratio critical value marked by an arrowhead on the y axis. ...
Key terms - Ms. Paras
... This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on various orientations in psychology. Learning Objectives • Describe the central characteristics of psychoth ...
... This section of the course provides students with an understanding of empirically based treatments of psychological disorders. The topic emphasizes descriptions of treatment modalities based on various orientations in psychology. Learning Objectives • Describe the central characteristics of psychoth ...
Comorbidity of Asperger`s syndrome and Bipolar disorder
... rather than specific symptoms of AS. In these circumstances, the AS diagnosis is often overlooked. Since these cases appear odd and atypical in comparison with patients commonly observed in the adult psychiatric setting, they often receive several diagnoses in the course of time. The awareness of th ...
... rather than specific symptoms of AS. In these circumstances, the AS diagnosis is often overlooked. Since these cases appear odd and atypical in comparison with patients commonly observed in the adult psychiatric setting, they often receive several diagnoses in the course of time. The awareness of th ...
Understanding Autistic Children in the Classroom
... Until recently, three types of autistic disorders were recognized separately: autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder—not otherwise specified. However, in the 2013 edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V), autism spectrum disor ...
... Until recently, three types of autistic disorders were recognized separately: autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder—not otherwise specified. However, in the 2013 edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V), autism spectrum disor ...
Document
... - feelings of helplessness, sadness, etc. - last for more than a few weeks - interferes with normal every day activities ...
... - feelings of helplessness, sadness, etc. - last for more than a few weeks - interferes with normal every day activities ...
Adjustment and Breakdown
... Cognitive Therapy- an approach in which thoughts are used to control emotions and behaviors Empathy- the capacity for warmth and understanding Prefrontal lobotomy- a operation in which a part of the brain is removed Humanistic therapy- an approach to psychology that focuses on the value, dignity, an ...
... Cognitive Therapy- an approach in which thoughts are used to control emotions and behaviors Empathy- the capacity for warmth and understanding Prefrontal lobotomy- a operation in which a part of the brain is removed Humanistic therapy- an approach to psychology that focuses on the value, dignity, an ...
1 DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria for Communication and Other
... If a child has difficulties with social skills, but does not show restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior, the new diagnosis of social (pragmatic) communication disorder may apply. Distinguishing between autism spectrum disorder and social communication disorder will be critical to ensuring th ...
... If a child has difficulties with social skills, but does not show restricted or repetitive patterns of behavior, the new diagnosis of social (pragmatic) communication disorder may apply. Distinguishing between autism spectrum disorder and social communication disorder will be critical to ensuring th ...
Mental Health Nursing II NURS 2310
... Presence of multiple motor tics along with one or more vocal tics Tics may appear simultaneously or at different periods during the illness Causes marked distress or interferes with various areas of functioning Onset occurs before the age of 18 Characterized by periods of remission Symptom ...
... Presence of multiple motor tics along with one or more vocal tics Tics may appear simultaneously or at different periods during the illness Causes marked distress or interferes with various areas of functioning Onset occurs before the age of 18 Characterized by periods of remission Symptom ...
DIAGNOSTIC AND STATISTICAL MANUAL OF MENTAL DISORDERS
... Axis III: 343.9 Palsy, cerebral Axis IV: Psycho-social stressors, early childhood abuse and neglect, academic difficulties Axis V: 70 ...
... Axis III: 343.9 Palsy, cerebral Axis IV: Psycho-social stressors, early childhood abuse and neglect, academic difficulties Axis V: 70 ...
Social Anxiety Disorder - DSM-5
... lasting six months or longer. In DSM-IV, the timeframe was required only for children; DSM-5 expands this criterion to include adults as well. The minimum symptom period reduces the possibility that an individual is experiencing only transient or temporary fear. To be diagnosed with social anxiety d ...
... lasting six months or longer. In DSM-IV, the timeframe was required only for children; DSM-5 expands this criterion to include adults as well. The minimum symptom period reduces the possibility that an individual is experiencing only transient or temporary fear. To be diagnosed with social anxiety d ...
Somatic, Factitious, and Dissociative Disorders
... Results in medical treatment or significant impairment Must begin before age 30 and for several years Must have multiple complaints in at least four different sites ...
... Results in medical treatment or significant impairment Must begin before age 30 and for several years Must have multiple complaints in at least four different sites ...
H382: The Problems Kids Have
... 8. Diminished ability to think or concentrate 9. Recurrent thoughts of death/SI ...
... 8. Diminished ability to think or concentrate 9. Recurrent thoughts of death/SI ...
The Environmental Science of Mood Disorders
... • Patients with multiple unexplained complaints (somatizers) • Patients excessively worried about serious illness (hypochondriasis) • Patients with psychiatric disorders with somatic symptoms (depression; anxiety) ...
... • Patients with multiple unexplained complaints (somatizers) • Patients excessively worried about serious illness (hypochondriasis) • Patients with psychiatric disorders with somatic symptoms (depression; anxiety) ...
Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder - DSM-5
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
... the hyperactivity and impulsivity criteria, while older adolescents and adults (over age 17 years) must present with five. While the criteria have not changed from DSM-IV, examples have been included to illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. ...
Clinical Assessment, Diagnosis and research Methods
... an episode was due to a medical disorder or use of a substance). ...
... an episode was due to a medical disorder or use of a substance). ...
Psychology Disorders
... – one of a group of serious developmental problems called autism spectrum disorders (ASD) – that appear in early childhood — usually before age 3. – symptoms and severity vary, all autism disorders affect a child's ability to communicate and interact with others. ...
... – one of a group of serious developmental problems called autism spectrum disorders (ASD) – that appear in early childhood — usually before age 3. – symptoms and severity vary, all autism disorders affect a child's ability to communicate and interact with others. ...
The puzzling symptom of paranoia - Sri Lanka Journal of Psychiatry
... her son. It is not possible to say that diagnostic errors are more likely in patients presenting with paranoia. Nevertheless, it is worth exploring the possible reasons for diagnostic errors in the above cases and in general. Current symptom based diagnostic criteria of ICD and DSM can often yield f ...
... her son. It is not possible to say that diagnostic errors are more likely in patients presenting with paranoia. Nevertheless, it is worth exploring the possible reasons for diagnostic errors in the above cases and in general. Current symptom based diagnostic criteria of ICD and DSM can often yield f ...
Other Disorders - Highlands School Behaviour Focus Website
... Asperger’s Disorder • Obsessive interest in stereotyped and restricted areas • Stereotyped & repetitive patterns of behaviour including motor mannerisms; inflexible adherence to nonfunctional specific routines/rituals; preoccupation with parts of objects • Significantly impaired social skills which ...
... Asperger’s Disorder • Obsessive interest in stereotyped and restricted areas • Stereotyped & repetitive patterns of behaviour including motor mannerisms; inflexible adherence to nonfunctional specific routines/rituals; preoccupation with parts of objects • Significantly impaired social skills which ...
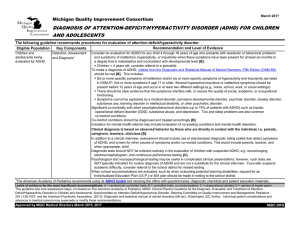
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
histrionic personality disorder
... genes and early childhood events are thought to contribute. It occurs more often in women than in men, although it may be diagnosed more often in women because attentionseeking and sexual forwardness are less socially acceptable for women. Histrionic personality disorder usually begins in early adul ...
... genes and early childhood events are thought to contribute. It occurs more often in women than in men, although it may be diagnosed more often in women because attentionseeking and sexual forwardness are less socially acceptable for women. Histrionic personality disorder usually begins in early adul ...
Vicker, B. (2009) Social communication and language
... Have difficulty staying on topic; may be distracted by associations cued by his or her own words or the dialogue of others. Deliver monologues, lectures, or lessons about a favorite topic rather than allow/participate in reciprocal involvement with a communication partner. Talk aloud to self in publ ...
... Have difficulty staying on topic; may be distracted by associations cued by his or her own words or the dialogue of others. Deliver monologues, lectures, or lessons about a favorite topic rather than allow/participate in reciprocal involvement with a communication partner. Talk aloud to self in publ ...
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASDs)
... trouble maintaining a back-and-forth conversation. They usually obsess over 1 or 2 topics and will talk about these topics whether the listener is interested. Children with Asperger syndrome often interpret language literally and may have particular trouble with humor, teasing, and figures of speech ...
... trouble maintaining a back-and-forth conversation. They usually obsess over 1 or 2 topics and will talk about these topics whether the listener is interested. Children with Asperger syndrome often interpret language literally and may have particular trouble with humor, teasing, and figures of speech ...
The Use Of Medication In Autism
... recognized as being inappropriate • Compulsion - repetitive behavior based on rules and with a stereotypic pattern performed to suppress or diminish dysphoria related to obsession • Occur for more than 1 hour daily and interfere with functioning • Recognized as excessive or unreasonable • Not single ...
... recognized as being inappropriate • Compulsion - repetitive behavior based on rules and with a stereotypic pattern performed to suppress or diminish dysphoria related to obsession • Occur for more than 1 hour daily and interfere with functioning • Recognized as excessive or unreasonable • Not single ...
Obsessive Compulsive Personality Disorder
... of their stubbornness and rigidity make them bad cooperators Acknowledging their disorder make them consider change ...
... of their stubbornness and rigidity make them bad cooperators Acknowledging their disorder make them consider change ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.