Mind from brain: physics & neuroscience
... • Excess of low-level (sensory) processes. • Underfunctioning of high-level neural connections and synchronization, • fMRI and EEG study suggests that adults with ASD have local overconnectivity in the cortex and weak functional connections between the frontal lobe and the rest of the cortex. • Unde ...
... • Excess of low-level (sensory) processes. • Underfunctioning of high-level neural connections and synchronization, • fMRI and EEG study suggests that adults with ASD have local overconnectivity in the cortex and weak functional connections between the frontal lobe and the rest of the cortex. • Unde ...
Mental Illness 101 - Chagrin Falls Schools
... People with this illness have sudden, short periods of psychotic behavior, often in response to a very stressful event, such as a death in the family. Usually lasts less than a month. ...
... People with this illness have sudden, short periods of psychotic behavior, often in response to a very stressful event, such as a death in the family. Usually lasts less than a month. ...
Disorders of Childhood – A General Overview
... Some did well at 1 year follow-up Some do not maintain Tx gains Lowered recidivism rates 6 - 18 months out Number of serious criminal offenses stayed the same These may be more difficult cases May require higher level of treatment ...
... Some did well at 1 year follow-up Some do not maintain Tx gains Lowered recidivism rates 6 - 18 months out Number of serious criminal offenses stayed the same These may be more difficult cases May require higher level of treatment ...
Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder
... Researchers today don’t know what causes obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. There are many theories however some causes may be genetic factors, social factors or psychological factors. ...
... Researchers today don’t know what causes obsessive-compulsive personality disorder. There are many theories however some causes may be genetic factors, social factors or psychological factors. ...
The Oppositional Defiant Child
... individual is age 18 years or older, criteria are not met for Antisocial Personality Disorder. ...
... individual is age 18 years or older, criteria are not met for Antisocial Personality Disorder. ...
Personality disorder
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
... Commonly adults (16 to 65 years old) with severe mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia, manic depressive disorders, severe depressive disorder) with an acute psychiatric crisis of such severity that, without the involvement of a crisis resolution/home treatment team, hospitalisation would be necessary. ...
A mental or emotional condition that makes it difficult for
... -Post Traumatic Stress syndrome – Severe fear and feelings relating to a past negative experience...a condition in which the after-effects of a past event keep a person from living in a normal way _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____ ...
... -Post Traumatic Stress syndrome – Severe fear and feelings relating to a past negative experience...a condition in which the after-effects of a past event keep a person from living in a normal way _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____ ...
Chapter 8 Lesson 4
... Anxiety Disorder • A disorder in which real or imagined fears keep a person from functioning normally – Phobias – Exaggerated fears about something specific (spiders, snakes) – Obsessive-compulsive – Cannot keep certain thoughts out of mind. May develop repetitive behaviors – Stress – affects peopl ...
... Anxiety Disorder • A disorder in which real or imagined fears keep a person from functioning normally – Phobias – Exaggerated fears about something specific (spiders, snakes) – Obsessive-compulsive – Cannot keep certain thoughts out of mind. May develop repetitive behaviors – Stress – affects peopl ...
Causes
... Psychotic Disorders Psychotic disorders are characterized by disturbances in thoughts, perceptions, consciousness, and emotions These disturbances lead to impaired social, personal, and/or occupational functioning ...
... Psychotic Disorders Psychotic disorders are characterized by disturbances in thoughts, perceptions, consciousness, and emotions These disturbances lead to impaired social, personal, and/or occupational functioning ...
The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
... and 4% of adults struggle with ADHD. • These patients are impaired (in at least two settings) from inattention, hyperactivity or impulsivity. • These children and adults underperform, and they place great demands on their families, teachers and coworkers. • ADHD and its treatment are controversial, ...
... and 4% of adults struggle with ADHD. • These patients are impaired (in at least two settings) from inattention, hyperactivity or impulsivity. • These children and adults underperform, and they place great demands on their families, teachers and coworkers. • ADHD and its treatment are controversial, ...
Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Abnormal Behavior: The
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
Hypochondriasis - Cloudfront.net
... later in adulthood. Sympathy or temporary relief from something distressing may reinforce the complaint of these symptoms. ...
... later in adulthood. Sympathy or temporary relief from something distressing may reinforce the complaint of these symptoms. ...
Presentation - National Autism Conference
... randomized trials or >6 controlled single subject trials) for use in children with ASD. FDA approved for select symptoms in ASD. • All other atypicals have only open label studies and case reports (therefore, limited research support) • Haloperidol had Strong Support from studies in the 1970’s (decr ...
... randomized trials or >6 controlled single subject trials) for use in children with ASD. FDA approved for select symptoms in ASD. • All other atypicals have only open label studies and case reports (therefore, limited research support) • Haloperidol had Strong Support from studies in the 1970’s (decr ...
Chapter 9
... Child abuse Any significant family change or stress Intervention Psychotherapy Medication School-Based Intervention Cognitive restructuring, behavioral assignments, problem-solving, self-instructional training, social skills, relaxation exercises, scheduling pleasant activities, anger coping, games ...
... Child abuse Any significant family change or stress Intervention Psychotherapy Medication School-Based Intervention Cognitive restructuring, behavioral assignments, problem-solving, self-instructional training, social skills, relaxation exercises, scheduling pleasant activities, anger coping, games ...
Hypochondriasis - Cloudfront.net
... disorder whether it is sexual or physical. Watching someone die with a serious disease at a young age. ...
... disorder whether it is sexual or physical. Watching someone die with a serious disease at a young age. ...
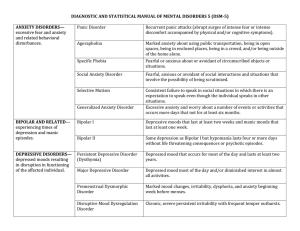
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... period of time, specific aspect of an event or identity and life history; may involve purposeful travel or bewildered wandering (fugue). ...
... period of time, specific aspect of an event or identity and life history; may involve purposeful travel or bewildered wandering (fugue). ...
Challenges in Identifying Mental Health Issues in Individuals with
... Surface manifestations of mental health disorders in severely autistic individuals may not be the same as those presented in our classification schemes, which are based on the manifestations shown by adults with an average IQ. Given that the phenomenology of a psychiatric disorder may be different i ...
... Surface manifestations of mental health disorders in severely autistic individuals may not be the same as those presented in our classification schemes, which are based on the manifestations shown by adults with an average IQ. Given that the phenomenology of a psychiatric disorder may be different i ...
Pediatric Psychiatry
... social - interpersonal, academic, poor social skills learning disorders (in 40% with ADHD), behavioural problems (ODD, CD), substance abuse, depression, anxiety ...
... social - interpersonal, academic, poor social skills learning disorders (in 40% with ADHD), behavioural problems (ODD, CD), substance abuse, depression, anxiety ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.