Learners with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... Long period of time, to a marked extent Adversely affects education Includes schizophrenia Excludes social maladjustment which some states interpret as conduct disorder-aggressive, disruptive, antisocial behavior An inability to learn cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, heath factors A ...
... Long period of time, to a marked extent Adversely affects education Includes schizophrenia Excludes social maladjustment which some states interpret as conduct disorder-aggressive, disruptive, antisocial behavior An inability to learn cannot be explained by intellectual, sensory, heath factors A ...
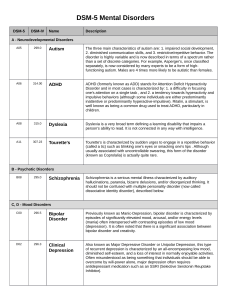
DSM V Mental Disorders
... The three main characteristics of autism are: 1. impaired social development, 2. diminished communication skills, and 3. restrictive/repetitive behavior. The disorder is highly variable and is now described in terms of a spectrum rather than a set of discrete categories. For example, Asperger's, onc ...
... The three main characteristics of autism are: 1. impaired social development, 2. diminished communication skills, and 3. restrictive/repetitive behavior. The disorder is highly variable and is now described in terms of a spectrum rather than a set of discrete categories. For example, Asperger's, onc ...
4053X1 1999 Oct7
... Negative Affectivity • Definition: The tendency to experience aversive emotional states; best predicted by Trait Anxiety and internalizing behavior problems • Evidence: Comorbidity of child anxiety and child Dx of depression Depression Yes ...
... Negative Affectivity • Definition: The tendency to experience aversive emotional states; best predicted by Trait Anxiety and internalizing behavior problems • Evidence: Comorbidity of child anxiety and child Dx of depression Depression Yes ...
BUILDING THE ESSAY DRAFT
... – Controversial diagnosis; given with caution Factors underlying Dissociative Disorders: – Ability to dissociate: trait aspects, some easily able to dissociate, others unable to dissociate – Intense/abusive/traumatic stress as a trigger? ...
... – Controversial diagnosis; given with caution Factors underlying Dissociative Disorders: – Ability to dissociate: trait aspects, some easily able to dissociate, others unable to dissociate – Intense/abusive/traumatic stress as a trigger? ...
Abnormal Psychology - West Essex High School
... • None were exposed as imposters. • They were all discharged within two months after agreeing with the diagnosis. Their discharge papers stated that they have “schizophrenia in remission”. • The conclusion was that it is difficult to accurately determine healthy from unhealthy behavior ...
... • None were exposed as imposters. • They were all discharged within two months after agreeing with the diagnosis. Their discharge papers stated that they have “schizophrenia in remission”. • The conclusion was that it is difficult to accurately determine healthy from unhealthy behavior ...
Somatoform disorders
... Therapy and Prognosis Understand symptoms as emotional message rather than a sing of new disease Avoid more diagnostic tests, laboratory evaluations and operative procedures unless clearly indicated Set a goal to get selected somatization patients referral-ready for mental health care. Group therap ...
... Therapy and Prognosis Understand symptoms as emotional message rather than a sing of new disease Avoid more diagnostic tests, laboratory evaluations and operative procedures unless clearly indicated Set a goal to get selected somatization patients referral-ready for mental health care. Group therap ...
11/4/2013 1 DSM-5 The Bigger Picture
... Social Communication and Interaction Restrictive Repetitive Behaviors ...
... Social Communication and Interaction Restrictive Repetitive Behaviors ...
Co-occurring Disorders: Drug Abuse And Mental Health
... they enter treatment for their alcohol/drug problems. Anxiety disorders. Rates of other anxiety disorders, such as agoraphobia, panic disorder, social phobias, and general anxiety disorder, are high in treatment populations, ranging from 10 to 60 percent. Eating disorders. Most studies find that bet ...
... they enter treatment for their alcohol/drug problems. Anxiety disorders. Rates of other anxiety disorders, such as agoraphobia, panic disorder, social phobias, and general anxiety disorder, are high in treatment populations, ranging from 10 to 60 percent. Eating disorders. Most studies find that bet ...
Mental Health and our Faithful Response
... of social interaction and communication skills and restricted interests and activities. It is relatively rare (0.02-0.05 %) and usually develops before age 3. • Asperger’s Disorder involves less severe impairment of social interaction, repetitive behaviors & interests, and no delays in language. • A ...
... of social interaction and communication skills and restricted interests and activities. It is relatively rare (0.02-0.05 %) and usually develops before age 3. • Asperger’s Disorder involves less severe impairment of social interaction, repetitive behaviors & interests, and no delays in language. • A ...
Chapter 13
... Drugs that increase dopamine levels such as amphetamines and cocaine sometimes intensity them. You can get a psychotic induced experience from amphetamines. Dopamine over activity may underlie patients’ overreacting to irrelevant external and internal stimuli. Brain anatomy: Many people with chronic ...
... Drugs that increase dopamine levels such as amphetamines and cocaine sometimes intensity them. You can get a psychotic induced experience from amphetamines. Dopamine over activity may underlie patients’ overreacting to irrelevant external and internal stimuli. Brain anatomy: Many people with chronic ...
Ten Questions to be Answered During the Outpatient Neurology Required Elective
... *Describe the difference between “central” hypotonia and hypotonia due to a lower motor neuron disorder. What physical exam findings help to distinguish between “central” and “peripheral” hypotonia? *What are neurological “soft signs”? *What is an “IEP” and what services can it provide for? 8. An 18 ...
... *Describe the difference between “central” hypotonia and hypotonia due to a lower motor neuron disorder. What physical exam findings help to distinguish between “central” and “peripheral” hypotonia? *What are neurological “soft signs”? *What is an “IEP” and what services can it provide for? 8. An 18 ...
rtf format
... communication, behavior, and learning. It is a severe disability which can cause unusual, even disturbing, behavior. ...
... communication, behavior, and learning. It is a severe disability which can cause unusual, even disturbing, behavior. ...
ADHD vs. Mood Disorders - Columbia Associates in Psychiatry
... or friends). At school, the focus is on work, not on feelings which are diffused over many different people, lowering the intensity of interactions. With ADHD, the controlling variables are information overload and excitability. The child with ADHD often does very well in the home under low stimulat ...
... or friends). At school, the focus is on work, not on feelings which are diffused over many different people, lowering the intensity of interactions. With ADHD, the controlling variables are information overload and excitability. The child with ADHD often does very well in the home under low stimulat ...
Abnormal test review -Know which collections of symptoms are
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
... For example: chemical imbalances in the brain are thought to be contributing factors in several disorders such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar, OCD ...
Somatoform and Sleep Disorders
... – Emotions associated with the traumatic event that the client cannot express because of moral or ethical unacceptability are “converted” into physical symptoms. ...
... – Emotions associated with the traumatic event that the client cannot express because of moral or ethical unacceptability are “converted” into physical symptoms. ...
Mental Health Diagnosis in IDD: Bio-psycho
... Mental health and/or behavior problems may be symptoms related to the onset of a medical condition (e.g., ear infection, UTI, diabetes, seizure disorder, thyroid disorder, etc.) or factors related to the environment In most cases, co-occurring complex behavior problems in individuals with ID are cau ...
... Mental health and/or behavior problems may be symptoms related to the onset of a medical condition (e.g., ear infection, UTI, diabetes, seizure disorder, thyroid disorder, etc.) or factors related to the environment In most cases, co-occurring complex behavior problems in individuals with ID are cau ...
WHAT DOES FASD LOOK LIKE?
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
... What is a mental disorder? •A mental disorder is an illness that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors. •Someone with a mental disorder may not feel good about themselves or may have a difficult time developing intimate relationships. •They may have difficulty dealing with everyday ac ...
Abnormal Psychology
... questions in the DSM-IV-TR about a client’s symptoms that lead to a possible diagnosis ...
... questions in the DSM-IV-TR about a client’s symptoms that lead to a possible diagnosis ...
Asperger syndrome

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome, Asperger disorder (AD) or simply Asperger's, is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) that is characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, alongside restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. It differs from other autism spectrum disorders by its relative preservation of linguistic and cognitive development. Although not required for diagnosis, physical clumsiness and atypical (peculiar or odd) use of language are frequently reported. The diagnosis of Asperger's was eliminated in the 2013 fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and replaced by a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder on a severity scale.The syndrome is named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger who, in 1944, studied and described children in his practice who lacked nonverbal communication skills, demonstrated limited empathy with their peers, and were physically clumsy. The modern conception of Asperger syndrome came into existence in 1981 and went through a period of popularization, becoming standardized as a diagnosis in the early 1990s. Many questions and controversies remain about aspects of the disorder. There is doubt about whether it is distinct from high-functioning autism (HFA); partly because of this, its prevalence is not firmly established.The exact cause of Asperger's is unknown. Although research suggests the likelihood of a genetic basis, there is no known genetic cause, and brain imaging techniques have not identified a clear common pathology. There is no single treatment, and the effectiveness of particular interventions is supported by only limited data. Intervention is aimed at improving symptoms and function. The mainstay of management is behavioral therapy, focusing on specific deficits to address poor communication skills, obsessive or repetitive routines, and physical clumsiness. Most children improve as they mature to adulthood, but social and communication difficulties may persist. Some researchers and people with Asperger's have advocated a shift in attitudes toward the view that it is a difference, rather than a disease that must be treated or cured. Globally Asperger's is estimated to affect 31 million people as of 2013.