sampling distribution
... possible samples of the same size from the same population. * Parameter – number that describes a characteristic of a population (like a mean or proportion) – use Greek letters to denote. * Statistic – number that describes a characteristic of a sample, often used to estimate to a parameter. * Sampl ...
... possible samples of the same size from the same population. * Parameter – number that describes a characteristic of a population (like a mean or proportion) – use Greek letters to denote. * Statistic – number that describes a characteristic of a sample, often used to estimate to a parameter. * Sampl ...
Key Terms - The Joy of Stats
... Nominal and ordinal (categoric) level of measurement, interval-ratio level of measurement, continuous and categoric variables, binary/dichotomous variables ...
... Nominal and ordinal (categoric) level of measurement, interval-ratio level of measurement, continuous and categoric variables, binary/dichotomous variables ...
Sampling Distribution with CLT Worksheet
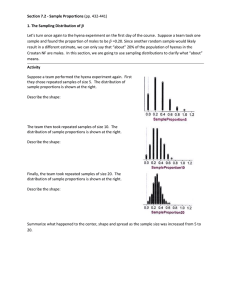
... d) If conditions have been met (which they should have), sketch and label a normal distribution with mean and standard deviation based on the sample of 80 cars. ...
... d) If conditions have been met (which they should have), sketch and label a normal distribution with mean and standard deviation based on the sample of 80 cars. ...
Sample mean: M. Population mean: μ. μ is pronounced `mew,` like
... The Central Limit Theorem Part One: The mean of all possible sample means will equal the population mean. (‘All possible’ is roughly the same as ‘a very large number’.) The standard deviation of those sample means will equal the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample ...
... The Central Limit Theorem Part One: The mean of all possible sample means will equal the population mean. (‘All possible’ is roughly the same as ‘a very large number’.) The standard deviation of those sample means will equal the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample ...
90 – 100 = A- to A 80 – 90 = B
... Instructor: For All Practical Purposes, 7th Edition (Minimal) A calculator that has at least a square root key. You may use your calculator on all exams and quizzes. ...
... Instructor: For All Practical Purposes, 7th Edition (Minimal) A calculator that has at least a square root key. You may use your calculator on all exams and quizzes. ...