Slide 1
... category are simply labels rather than meaningful numbers. Ordinal variable: Variables measured with numerical values where the numbers are meaningful (e.g., 2 is larger than 1) but the distance between the numbers is not constant. Interval or Ratio variable: Variables measured with numerical values ...
... category are simply labels rather than meaningful numbers. Ordinal variable: Variables measured with numerical values where the numbers are meaningful (e.g., 2 is larger than 1) but the distance between the numbers is not constant. Interval or Ratio variable: Variables measured with numerical values ...
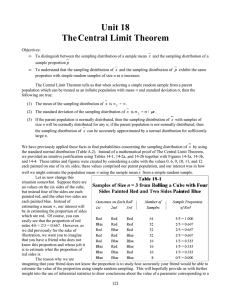
Unit 18 TheCentral Limit Theorem
... (lambda) to represent the proportion in a population, and define p to represent the proportion in a sample. In our present illustration with the cube, λ = 2/3 = 0.667 is the proportion of red sides in the population consisting of the colors painted on each of the six sides of the cube, and p is the ...
... (lambda) to represent the proportion in a population, and define p to represent the proportion in a sample. In our present illustration with the cube, λ = 2/3 = 0.667 is the proportion of red sides in the population consisting of the colors painted on each of the six sides of the cube, and p is the ...
SamplingVariability-and-Sampling-Distribution
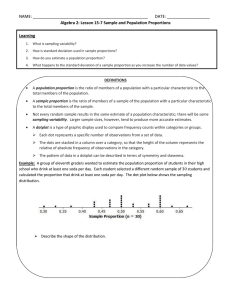
... Recall, if a coin is fair, the probability of getting the head (or tail) is p =______. This means, if, for example, we flip a coin n = 60 times, we would expect to obtain about ______ heads on average. However, due to _____________________________, each sequence of 60 flips can yield different numbe ...
... Recall, if a coin is fair, the probability of getting the head (or tail) is p =______. This means, if, for example, we flip a coin n = 60 times, we would expect to obtain about ______ heads on average. However, due to _____________________________, each sequence of 60 flips can yield different numbe ...
week3
... has the standard normal distribution. • Areas under a normal curve represent proportion of observations from that normal distribution. • There is no formula to calculate areas under a normal curve. Calculations use either software or a table of areas. The table and most software calculate one kind o ...
... has the standard normal distribution. • Areas under a normal curve represent proportion of observations from that normal distribution. • There is no formula to calculate areas under a normal curve. Calculations use either software or a table of areas. The table and most software calculate one kind o ...