SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
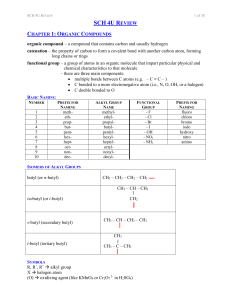
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
... organic compound – a compound that contains carbon and usually hydrogen catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical character ...
Chapter 8: Ionic Compounds
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
Reactions Balancing Chemical Equations uses Law of conservation
... Gas formation is a driving force. • Direct production of a gas CO2, H2S, NO2, SO2 • Production of weak acid which decomposes. ...
... Gas formation is a driving force. • Direct production of a gas CO2, H2S, NO2, SO2 • Production of weak acid which decomposes. ...
Atomic Structure
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
University of Groningen In-situ element analysis from gamma
... having been struck by a neutron, emits a single neutron. Despite the fact that the initial and final neutrons do not need to be the same, the net effect of the reaction is as if the projectile neutron had merely "bounced off" or scattered from the nucleus. In an elastic scattering process shown in f ...
... having been struck by a neutron, emits a single neutron. Despite the fact that the initial and final neutrons do not need to be the same, the net effect of the reaction is as if the projectile neutron had merely "bounced off" or scattered from the nucleus. In an elastic scattering process shown in f ...
Thomson`s Model of the Atom
... Assessment Questions 1. The concept of an atom as a small particle of matter that cannot be divided was proposed by the ...
... Assessment Questions 1. The concept of an atom as a small particle of matter that cannot be divided was proposed by the ...
structure of atom
... In this method, oil droplets in the form of mist, pr oduced by the atomiser, were allowed to enter thr ough a tiny hole in the upper plate of electrical condenser. The downward motion of these dr oplets was viewed through the telescope, equipped with a micrometer eye piece. By measuring the rate of ...
... In this method, oil droplets in the form of mist, pr oduced by the atomiser, were allowed to enter thr ough a tiny hole in the upper plate of electrical condenser. The downward motion of these dr oplets was viewed through the telescope, equipped with a micrometer eye piece. By measuring the rate of ...
The Atomic Theory - Academic Magnet High School
... twice as much oxygen as forming A. In other words, if you could make A with 3 grams of carbon and 4 grams of oxygen, B could be made with the same 3 grams of carbon but with 8 grams of oxygen instead. Dalton asked himself – why does B require twice as much oxygen as A does? Why not 1.21 times as muc ...
... twice as much oxygen as forming A. In other words, if you could make A with 3 grams of carbon and 4 grams of oxygen, B could be made with the same 3 grams of carbon but with 8 grams of oxygen instead. Dalton asked himself – why does B require twice as much oxygen as A does? Why not 1.21 times as muc ...
File
... because they are not corrosive and will not cause a hazard if used in excess. They also have no toxicity if used for indigestion remedies but the CO2 produced can cause wind. Magnesium hydroxide is also suitable for dealing with excess stomach acid as it has low solubility in water and is only weakl ...
... because they are not corrosive and will not cause a hazard if used in excess. They also have no toxicity if used for indigestion remedies but the CO2 produced can cause wind. Magnesium hydroxide is also suitable for dealing with excess stomach acid as it has low solubility in water and is only weakl ...
Monday June 8, 2009
... C. Plant cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane; animal cells have a cell wall but not a cell membrane. D. Plant cells have chloroplasts and mitochondria; animal cells have chloroplasts but do not have mitochondria. ...
... C. Plant cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane; animal cells have a cell wall but not a cell membrane. D. Plant cells have chloroplasts and mitochondria; animal cells have chloroplasts but do not have mitochondria. ...
Molar mass
... Scientists use the mole as a unit of measure • AMU is not practical to use • Can’t measure individual atoms very easily • Measuring in grams is desirable • Ratio of atoms is transferred between amu and grams ...
... Scientists use the mole as a unit of measure • AMU is not practical to use • Can’t measure individual atoms very easily • Measuring in grams is desirable • Ratio of atoms is transferred between amu and grams ...
Chapter 11 - Chemical Elements (Lecture Slides)
... substances that could not be separated into components by any method • In addition Boyle initiated the practice of carefully and completely describing experiments so that anyone might repeat and confirm them – Due to this procedure (carefully documenting experiments) scientists have been able to bui ...
... substances that could not be separated into components by any method • In addition Boyle initiated the practice of carefully and completely describing experiments so that anyone might repeat and confirm them – Due to this procedure (carefully documenting experiments) scientists have been able to bui ...
Chapter 11: Chemical Elements
... • Ionization energy – the amount of energy that it takes to remove an electron from an atom • Ionization energy increases across a period due to additional protons in the nucleus • Ionization energy decreases down a group because of the additional shells situated between the nucleus and the outer el ...
... • Ionization energy – the amount of energy that it takes to remove an electron from an atom • Ionization energy increases across a period due to additional protons in the nucleus • Ionization energy decreases down a group because of the additional shells situated between the nucleus and the outer el ...
Distinguishing the Atom Reading
... 21. Three chromium isotopes are chromium-50, chromium-52, and chromium-53. How many neutrons are in each isotope, given that chromium has an atomic number of 24? Atomic Structure 115 ...
... 21. Three chromium isotopes are chromium-50, chromium-52, and chromium-53. How many neutrons are in each isotope, given that chromium has an atomic number of 24? Atomic Structure 115 ...
Surviving Chemistry - Bremen High School District 228
... . Electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called orbital Orbital is the most probable location of finding an electron with certain energy in an atom. Below is a list of some historical scientists and their proposed models of atom in order from the earliest model to the current model. Des ...
... . Electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called orbital Orbital is the most probable location of finding an electron with certain energy in an atom. Below is a list of some historical scientists and their proposed models of atom in order from the earliest model to the current model. Des ...
Chemistry Curriculum
... electrons an element has - Identify the special group and element is a member of, the element’s state of matter at room temperature, and the element’s identity as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the periodic table Students will be able to - Determine the number of neutrons a specific isotope o ...
... electrons an element has - Identify the special group and element is a member of, the element’s state of matter at room temperature, and the element’s identity as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid using the periodic table Students will be able to - Determine the number of neutrons a specific isotope o ...
From Atoms to Cells:
... Electron Orbitals and Shells The structure of an atom can be envisioned as a central nucleus surrounded by a “cloud” of electrons that constantly rotate about the nucleus in pathways (see figure 2.1). The pathways, called orbitals, are not actual objects or exact locations, but represent volumes of ...
... Electron Orbitals and Shells The structure of an atom can be envisioned as a central nucleus surrounded by a “cloud” of electrons that constantly rotate about the nucleus in pathways (see figure 2.1). The pathways, called orbitals, are not actual objects or exact locations, but represent volumes of ...
atoms
... – The charge on the cation becomes the subscript on the anion. – The charge on the anion becomes the subscript on the cation. – If these subscripts are not in the lowest wholenumber ratio, divide them by the greatest common Atoms, ...
... – The charge on the cation becomes the subscript on the anion. – The charge on the anion becomes the subscript on the cation. – If these subscripts are not in the lowest wholenumber ratio, divide them by the greatest common Atoms, ...
Document
... (c) Which point of Dalton’s atomic theory is based on the law of constant proportion proposed by Proust in 1799 which states that all pure samples of the same chemical compound contain the same elements combined together in the same proportions by mass? (c) Atoms of different elements combine to for ...
... (c) Which point of Dalton’s atomic theory is based on the law of constant proportion proposed by Proust in 1799 which states that all pure samples of the same chemical compound contain the same elements combined together in the same proportions by mass? (c) Atoms of different elements combine to for ...
physical setting chemistry
... word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 34 The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass units. The only naturally occurring isotopes of element A are ...
... word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions may require the use of the Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 34 The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass units. The only naturally occurring isotopes of element A are ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom
... not only can individual atoms be seen, scientists are now able to move individual atoms around to form shapes, patterns, and even simple machines. This capability has led to the exciting new field of nanotechnology. The promise of nanotechnology is molecular manufacturing—the atom-by-atom building o ...
... not only can individual atoms be seen, scientists are now able to move individual atoms around to form shapes, patterns, and even simple machines. This capability has led to the exciting new field of nanotechnology. The promise of nanotechnology is molecular manufacturing—the atom-by-atom building o ...
chemistry mcmurry fay
... The reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonia has DH = 92.2 kJ. What is the value of DE in kilojoules if the reaction is carried out at a constant pressure of 40.0 atm and the volume change is 1.12 L? N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) ...
... The reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonia has DH = 92.2 kJ. What is the value of DE in kilojoules if the reaction is carried out at a constant pressure of 40.0 atm and the volume change is 1.12 L? N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) ...
Lectures on Chapter 2, Part 1 Powerpoint 97 Document
... Atomic mass Unit (AMU) = 1/12 the mass of a carbon - 12 atom on this scale Hydrogen has a mass of 1.008 AMU. Dalton (D) = The new name for the Atomic Mass Unit, one dalton = one Atomic Mass Unit on this scale, 12C has a mass of 12.00 daltons. Isotopic Mass = The relative mass of an Isotope relative ...
... Atomic mass Unit (AMU) = 1/12 the mass of a carbon - 12 atom on this scale Hydrogen has a mass of 1.008 AMU. Dalton (D) = The new name for the Atomic Mass Unit, one dalton = one Atomic Mass Unit on this scale, 12C has a mass of 12.00 daltons. Isotopic Mass = The relative mass of an Isotope relative ...