Guided notes: Part II: History of the atomic theory
... ideas were rejected by ____________, who was very influential, and therefore forgotten for two thousand years. ancient Greek _______________, not scientist ...
... ideas were rejected by ____________, who was very influential, and therefore forgotten for two thousand years. ancient Greek _______________, not scientist ...
Chapter 3
... the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
... the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary
... 2. Atomic Mass – The average mass number of the atoms of an element. 3. Bond Angle – The angle formed between two adjacent bonds. 4. Bond Length – The equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two atoms that are bonded to each other. 5. Bond Strength – An alternative name for bond dissociation ener ...
... 2. Atomic Mass – The average mass number of the atoms of an element. 3. Bond Angle – The angle formed between two adjacent bonds. 4. Bond Length – The equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two atoms that are bonded to each other. 5. Bond Strength – An alternative name for bond dissociation ener ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
... surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
2016 Pre Course CHEMISTRY - Calday Grange Grammar School
... Diamond is able to scratch almost all other substances, whereas graphite may be used as a lubricant. Diamond and graphite both have high melting points. Explain each of these properties of diamond and graphite in terms of structure and bonding. Give one other difference in the properties of diamond ...
... Diamond is able to scratch almost all other substances, whereas graphite may be used as a lubricant. Diamond and graphite both have high melting points. Explain each of these properties of diamond and graphite in terms of structure and bonding. Give one other difference in the properties of diamond ...
chem1chapter3fromheisenberg
... • ground state: e- in lowest possible energy • excited state: egains energy, moving to a state where atom has more energy – in an excited state, e- releases specific quantity of energy as it “falls” back to ground state. ...
... • ground state: e- in lowest possible energy • excited state: egains energy, moving to a state where atom has more energy – in an excited state, e- releases specific quantity of energy as it “falls” back to ground state. ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Smoking at an early age may make it more difficult to quit smoking later. ...
... Smoking at an early age may make it more difficult to quit smoking later. ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Principle Shells and Subshells • Principle electronic shell, n = 1, 2, 3… • Angular momentum quantum number, l = 0, 1, 2…(n-1) l = 0, s l = 1, p l = 2, d l = 3, f ...
... Principle Shells and Subshells • Principle electronic shell, n = 1, 2, 3… • Angular momentum quantum number, l = 0, 1, 2…(n-1) l = 0, s l = 1, p l = 2, d l = 3, f ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
... location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. ...
High School Chemistry
... b. Using the periodic table, predict the charge an atom will acquire when it forms an ion by gaining or losing electrons. c. Compare covalent and ionic bonds with respect to electron behavior and relative bond strengths. d. Diagram a model of a metallic bond and explain how it differs from ionic an ...
... b. Using the periodic table, predict the charge an atom will acquire when it forms an ion by gaining or losing electrons. c. Compare covalent and ionic bonds with respect to electron behavior and relative bond strengths. d. Diagram a model of a metallic bond and explain how it differs from ionic an ...
The 7 Secrets of the Periodic Table
... Valence electrons are the electrons occupying the highest energy levels. It is important to master this concept because the valence electrons are the electrons involved in bonding. You determine the valence electrons by counting the "s" and "p" electrons in that period. You can determine that fluori ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons occupying the highest energy levels. It is important to master this concept because the valence electrons are the electrons involved in bonding. You determine the valence electrons by counting the "s" and "p" electrons in that period. You can determine that fluori ...
Part a
... (a) The slightly positive ends (+) of the water molecules become aligned with the slightly negative ends (–) of other water molecules. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... (a) The slightly positive ends (+) of the water molecules become aligned with the slightly negative ends (–) of other water molecules. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
File
... As you look at the periodic table and focus in on the elements and their characteristics, you can see there are noticeable patterns (trends) that go across a period (horizontal row) on the periodic table. These quantitative (able to measured with numbers and units) characteristics that follow di ...
... As you look at the periodic table and focus in on the elements and their characteristics, you can see there are noticeable patterns (trends) that go across a period (horizontal row) on the periodic table. These quantitative (able to measured with numbers and units) characteristics that follow di ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... indivisible). Democritus theorized that if you took an object and cut it in half again and again you would eventually end up with some particle which could not be further divided. In the early 1800's an English scientist by the name of John Dalton started relating what chemists could see to the conc ...
... indivisible). Democritus theorized that if you took an object and cut it in half again and again you would eventually end up with some particle which could not be further divided. In the early 1800's an English scientist by the name of John Dalton started relating what chemists could see to the conc ...
Chem Midterm Review 2016
... Since these particles were smaller than atoms, but seemed to come from them, they must be subatomic parts. He concluded that electrons must be parts of atoms of all elements So, he discovered the first subatomic particle (electron), the atom is no longer indivisible, and developed the "plum pudding" ...
... Since these particles were smaller than atoms, but seemed to come from them, they must be subatomic parts. He concluded that electrons must be parts of atoms of all elements So, he discovered the first subatomic particle (electron), the atom is no longer indivisible, and developed the "plum pudding" ...
Isotopes - Cloudfront.net
... What was happening to the air particles inside as you tried to add pressure? Why was it so hard to lift the plunger out of the syringe? Why did the marshmallow respond as it did to the changes in pressure? Why can’t you compress water? ...
... What was happening to the air particles inside as you tried to add pressure? Why was it so hard to lift the plunger out of the syringe? Why did the marshmallow respond as it did to the changes in pressure? Why can’t you compress water? ...
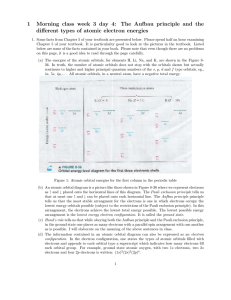
1 Morning class week 3 day 4: The Aufbau principle and the different
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...
Atomic Theory
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1 All matter is made up of invisible particles called atoms • 2 All atoms of one element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of all other element. • 3 Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms • 4 Atoms combine in small whole numbe ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1 All matter is made up of invisible particles called atoms • 2 All atoms of one element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of all other element. • 3 Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms • 4 Atoms combine in small whole numbe ...
Atomic Theory
... 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 mass of a C-12 atom Calculate average atomic mass by using weighted averages which take into account the relative abundance of each isotope. Note that what is on the periodic table is the average atomic mass, not the mass of a single isotope. POGIL – Average Atomic Ma ...
... 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 1/12 mass of a C-12 atom Calculate average atomic mass by using weighted averages which take into account the relative abundance of each isotope. Note that what is on the periodic table is the average atomic mass, not the mass of a single isotope. POGIL – Average Atomic Ma ...
Semester I CP Chemistry Review
... For elements #20 > the ratio of protons to neutrons is 1:1, then stable For elements #21 < the ratio of protons to neutrons is 1:1.5, then stable Or if in band of stability on graph (dots ...
... For elements #20 > the ratio of protons to neutrons is 1:1, then stable For elements #21 < the ratio of protons to neutrons is 1:1.5, then stable Or if in band of stability on graph (dots ...
Ordering the elements in the Periodic Table
... Hence atomic number became more meaningful and the three pairs of elements that seemed to be in the wrong order could be explained. Moseley used what was then brand-new technology in his experiments. A device now called an electron gun had just been developed. He used this to fire a stream of electr ...
... Hence atomic number became more meaningful and the three pairs of elements that seemed to be in the wrong order could be explained. Moseley used what was then brand-new technology in his experiments. A device now called an electron gun had just been developed. He used this to fire a stream of electr ...