Bounding in Materials : Atoms:-
... Mathem hussien , University of babylon , College of Engineering - ...
... Mathem hussien , University of babylon , College of Engineering - ...
atom and e
... mechanics into the atomic model. He proposed the idea that electrons were only allowed to orbit the nucleus at certain energy levels. Instead of an infinite number of possible orbits, only certain orbits were allowed. (“quantizing the atom”) Electrons could only jump to a higher energy orbit if they ...
... mechanics into the atomic model. He proposed the idea that electrons were only allowed to orbit the nucleus at certain energy levels. Instead of an infinite number of possible orbits, only certain orbits were allowed. (“quantizing the atom”) Electrons could only jump to a higher energy orbit if they ...
World of Chemistry Chapter 11—Modern Atomic Theory
... A. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus but could not describe the electrons in his model B. Rutherford imagined that the electrons moved around the nucleus in circular orbits like planets around the sun C. Rutherford could NOT explain why the negative electrons did not collapse into the positiv ...
... A. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus but could not describe the electrons in his model B. Rutherford imagined that the electrons moved around the nucleus in circular orbits like planets around the sun C. Rutherford could NOT explain why the negative electrons did not collapse into the positiv ...
Answer key
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
Speed of reactions
... Each different atom has a number . This is called the atomic number. All atoms of the one element have the same atomic number. Atoms of different elements cannot have the same atomic number. An element can be defined as a collection of atoms all with the same atomic number. Elements are arranged in ...
... Each different atom has a number . This is called the atomic number. All atoms of the one element have the same atomic number. Atoms of different elements cannot have the same atomic number. An element can be defined as a collection of atoms all with the same atomic number. Elements are arranged in ...
File
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
... Protons and neutrons are found in the center of the atom, called the nucleus. The electrons move about in the electron cloud that surrounds the nucleus. 46. Which subatomic particle(s) defines the identity of the atom? Protons 47. Which subatomic particle(s) determines chemical properties? electrons ...
Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... Antoine Lavoisier , 1790’s made first list of known elements, 23 total. By 1870, there were 70! John Newlands, 1864—Law of Octaves: When element were placed in order of increasing atomic mass, every 8th ...
... Antoine Lavoisier , 1790’s made first list of known elements, 23 total. By 1870, there were 70! John Newlands, 1864—Law of Octaves: When element were placed in order of increasing atomic mass, every 8th ...
Name
... 1. Describe how particles move and draw a diagram for each state of matter: a. Solid b. Liquid ...
... 1. Describe how particles move and draw a diagram for each state of matter: a. Solid b. Liquid ...
Atomic Spectroscopy and the Bohr Model
... • If we slow down this light using a prism or spectrometer, we can see the constituent colors that make up the color light that we are seeing. This series of lines is called the emission spectrum. This bright line spectrum is used to identify elements. Example on the next page. ...
... • If we slow down this light using a prism or spectrometer, we can see the constituent colors that make up the color light that we are seeing. This series of lines is called the emission spectrum. This bright line spectrum is used to identify elements. Example on the next page. ...
Atoms and Their Parts (Subatomic Particles)
... Atoms and Their Parts (Subatomic Particles) Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All at ...
... Atoms and Their Parts (Subatomic Particles) Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All at ...
Development of Atomic Theory.Part 2.WS
... • What did he learn about electron movement? • Can they change paths? The Modern Theory of the atom states that electrons do not travel in specific paths or orbits. • Describe the region where electrons travel. • Can we predict where an electron may be found? Electron clouds exist at a certain Energ ...
... • What did he learn about electron movement? • Can they change paths? The Modern Theory of the atom states that electrons do not travel in specific paths or orbits. • Describe the region where electrons travel. • Can we predict where an electron may be found? Electron clouds exist at a certain Energ ...
- Palisades School District
... 1. Using your knowledge of metric units, English units, and the information in your text, write down the conversion factors that you would need to convert the following: a. mm to nm b. mg to kg c. km to ft d. in.3 to cm3 2. A sample of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is synthesized in the laboratory. It c ...
... 1. Using your knowledge of metric units, English units, and the information in your text, write down the conversion factors that you would need to convert the following: a. mm to nm b. mg to kg c. km to ft d. in.3 to cm3 2. A sample of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is synthesized in the laboratory. It c ...
Chemistry 101 Topic 4
... anions arranged so that the + and – charges are balanced. Any stable sample of ma:er is electrically neutral. This principle helps determine how ionic compounds are organized. • Many ionic compounds con ...
... anions arranged so that the + and – charges are balanced. Any stable sample of ma:er is electrically neutral. This principle helps determine how ionic compounds are organized. • Many ionic compounds con ...
Chemistry EOC Review
... 11) The protons are ____________ charged particles found in the _____________ along with __________, which have no charge. The total number of these nucleons in an atom is the __________________ of the atom. The electrons are the _____________ charged particles found _________________________ . Elec ...
... 11) The protons are ____________ charged particles found in the _____________ along with __________, which have no charge. The total number of these nucleons in an atom is the __________________ of the atom. The electrons are the _____________ charged particles found _________________________ . Elec ...
History of Modern Atomic Theory-2012
... Aristotle’s theory of earth, wind, fire, and water was believed until the early 1800’s. ...
... Aristotle’s theory of earth, wind, fire, and water was believed until the early 1800’s. ...
Review Questions
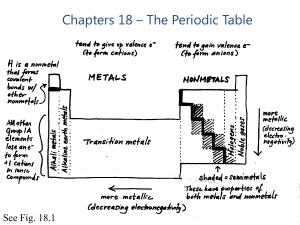
... electricity, high density, high melting temperature. Nonmetals tend to be gases or brittle solids at room temperature, poor conductors of heat and electricity (insulators), low density, low melting temperature Metalloids (Semi-metals) dull, brittle, semi-conductors (used in computer chips), properti ...
... electricity, high density, high melting temperature. Nonmetals tend to be gases or brittle solids at room temperature, poor conductors of heat and electricity (insulators), low density, low melting temperature Metalloids (Semi-metals) dull, brittle, semi-conductors (used in computer chips), properti ...
Ch_3___History_of_Modern_Atomic_Theory_2012
... Aristotle’s theory of earth, wind, fire, and water was believed until the early 1800’s. ...
... Aristotle’s theory of earth, wind, fire, and water was believed until the early 1800’s. ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... Life requires ~25 chemical elements Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
... Life requires ~25 chemical elements Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
... the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
September 22 Bellwork
... Protons with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom Neutrons with a neutral charge also found in the nucleus of an atom Electrons with a negative charge found outside of the nucleus in the electron cloud ...
... Protons with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom Neutrons with a neutral charge also found in the nucleus of an atom Electrons with a negative charge found outside of the nucleus in the electron cloud ...
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... • Other elements in Group 5A do not form p bonds, but exist as aggregates with single bonds (e.g. P4, As4, etc.) ...
... • Other elements in Group 5A do not form p bonds, but exist as aggregates with single bonds (e.g. P4, As4, etc.) ...
Lesson 3.1
... by grams and kilograms, so scientists use “atomic mass units” or “amu.” A proton OR a neutron is equal to one amu. Atomic Number – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. Isotopes – All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but sometimes the number of neu ...
... by grams and kilograms, so scientists use “atomic mass units” or “amu.” A proton OR a neutron is equal to one amu. Atomic Number – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic number. Isotopes – All atoms of an element have the same number of protons, but sometimes the number of neu ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... Electrons with the same quantum number n are about the same distance from the nucleus, move in about the same electric field, and have similar energies. Such electrons occupy the same atomic shell. The energy of an electron depends also on the quantum number l. ...
... Electrons with the same quantum number n are about the same distance from the nucleus, move in about the same electric field, and have similar energies. Such electrons occupy the same atomic shell. The energy of an electron depends also on the quantum number l. ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... be more dense and found in the center of the Earth with the less dense metal-less compounds and elements making up the crust and surface. ...
... be more dense and found in the center of the Earth with the less dense metal-less compounds and elements making up the crust and surface. ...