Study Guide - Flagler Schools
... Key Vocabulary: acceleration, activation energy, atomic nucleus, atomic number, atomic mass, barnacles, Bohr model, boiling point, cattails, catalyst, chemical changes, chemical potential energy, circuit, coastal area, combustion, comet, compound, condensation, conductor, conductivity, constant, ...
... Key Vocabulary: acceleration, activation energy, atomic nucleus, atomic number, atomic mass, barnacles, Bohr model, boiling point, cattails, catalyst, chemical changes, chemical potential energy, circuit, coastal area, combustion, comet, compound, condensation, conductor, conductivity, constant, ...
I. Properties of Matter
... when different compounds are formed by a combination of the same elements, different masses of one element combine with the same relative mass of the other element in a ratio of small whole numbers ...
... when different compounds are formed by a combination of the same elements, different masses of one element combine with the same relative mass of the other element in a ratio of small whole numbers ...
3.2 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... (c) CT: Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 or [Ne] 3s2 3p6 or [Ar] (d) S 2 ~: Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 or [Ne] 3s2 3p6 or [Ar] These elements tend to gain or lose electrons to form ions with the electron configurations of the nearest noble gas. 8. The largest jump in ionization energy is between the second and third io ...
... (c) CT: Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 or [Ne] 3s2 3p6 or [Ar] (d) S 2 ~: Is2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 or [Ne] 3s2 3p6 or [Ar] These elements tend to gain or lose electrons to form ions with the electron configurations of the nearest noble gas. 8. The largest jump in ionization energy is between the second and third io ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - Belle Vernon Area School District
... The summer assignment for AP Chemistry has two parts. 1. Complete the practice problems in this packet. You may use the resources listed below as well as any notes/worksheets from Accel. Chem that you may have. 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first w ...
... The summer assignment for AP Chemistry has two parts. 1. Complete the practice problems in this packet. You may use the resources listed below as well as any notes/worksheets from Accel. Chem that you may have. 2. You need to master the formulas, charges, and names of the common ions. On the first w ...
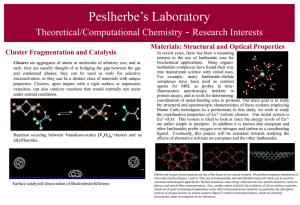
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... In recent years, there has been a mounting interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as ...
... In recent years, there has been a mounting interest in the use of lanthanide ions for biochemical applications. Many organolanthanide complexes have found their way into mainstream science with varied uses. For example, many lanthanide-chelate complexes have been used as contrast agents for MRI, as ...
Chapter 4: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • which AXES the orbitals lie ON OR BETWEEN • Values are whole numbers ranging from –l TO + l ...
... • which AXES the orbitals lie ON OR BETWEEN • Values are whole numbers ranging from –l TO + l ...
Thursday, March 27, 2008
... What is the total number of hydrogen atoms required to form one molecule of C3H5(OH)3? ...
... What is the total number of hydrogen atoms required to form one molecule of C3H5(OH)3? ...
Unit 1: Basic Chemistry Notes (answers)
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
Chapter 11: The Atomic Nature of Matter
... • Uncharged particles in the neutron, with mass ~ that of proton. • The # of neutrons need not match # of protons in atom, eg. H typically has 1 proton and 0 neutrons, but some H atoms may have 1 neutron, but always 1 proton, (called “heavy hydrogen”) • Isotopes = atoms of same element that contain ...
... • Uncharged particles in the neutron, with mass ~ that of proton. • The # of neutrons need not match # of protons in atom, eg. H typically has 1 proton and 0 neutrons, but some H atoms may have 1 neutron, but always 1 proton, (called “heavy hydrogen”) • Isotopes = atoms of same element that contain ...
Chapter 7. Atomic Structure - The University of New Mexico
... nucleus. A theoretical basis for atomic behavior has been worked out in terms of the electronic structure of atoms, based on the laws of physics for subatomic particles, namely quantum mechanics. One of the properties of the elements scientists sought to understand in the Nineteenth Century was atom ...
... nucleus. A theoretical basis for atomic behavior has been worked out in terms of the electronic structure of atoms, based on the laws of physics for subatomic particles, namely quantum mechanics. One of the properties of the elements scientists sought to understand in the Nineteenth Century was atom ...
atomic number
... shell filled. You need to find another element that will take that electron away from you. When you lose that electron, you will you’ll have full shells. • Whenever an atom has full shells, we say it is "happy." Let's look at chlorine (Cl). Chlorine has seventeen electrons and only needs one more to ...
... shell filled. You need to find another element that will take that electron away from you. When you lose that electron, you will you’ll have full shells. • Whenever an atom has full shells, we say it is "happy." Let's look at chlorine (Cl). Chlorine has seventeen electrons and only needs one more to ...
Chemistry in Biology
... 2. Ionic Bond—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of atoms called ions. • Most ionic compounds are crystalline at room temperature and have higher melting points than molecu ...
... 2. Ionic Bond—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of atoms called ions. • Most ionic compounds are crystalline at room temperature and have higher melting points than molecu ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... Representation of Bohr’s proposal of orbitals. Lower numbered levels are closer to nucleus and of lower energy. ...
... Representation of Bohr’s proposal of orbitals. Lower numbered levels are closer to nucleus and of lower energy. ...
Electronegativity
... How well an atom can attract a pair of bonding electrons to itself. It is a calculated value and can not actually be measured. How do you think it changes across a period? Down a group? Electronegativity: • Increases across a period • Decreases down a group ...
... How well an atom can attract a pair of bonding electrons to itself. It is a calculated value and can not actually be measured. How do you think it changes across a period? Down a group? Electronegativity: • Increases across a period • Decreases down a group ...
atomic number
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
this PDF file - Sydney Open Journals online
... lighter elements, including lithium, boron, and beryllium, those from beryllium being both more intense and more penetrating than from any other element tested. Repeating these experiments, Professor J oliot of the Radium Institute in Paris, and his wife-a daughter of Madame Curiefound that these se ...
... lighter elements, including lithium, boron, and beryllium, those from beryllium being both more intense and more penetrating than from any other element tested. Repeating these experiments, Professor J oliot of the Radium Institute in Paris, and his wife-a daughter of Madame Curiefound that these se ...
Atomic Structure
... an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses one or more electrons. • + Ions: have lost one or more electrons • - Ions: have gained one or more electrons ...
... an atom (or group of atoms) gains or loses one or more electrons. • + Ions: have lost one or more electrons • - Ions: have gained one or more electrons ...
ite and - Smithycroft Secondary School
... outer electrons are grouped together. I can state that compounds are held together by bonds I can state that there are two different types of bonding (ionic and covalent) when elements join together, which affect the properties of their compounds I can show covalent bonding as a sharing of electrons ...
... outer electrons are grouped together. I can state that compounds are held together by bonds I can state that there are two different types of bonding (ionic and covalent) when elements join together, which affect the properties of their compounds I can show covalent bonding as a sharing of electrons ...
2.1 Early Ideas in Atomic Theory
... forensics to art. The language of chemistry includes its own vocabulary as well as its own form of shorthand. Chemical symbols are used to represent atoms and elements. Chemical formulas depict molecules as well as the composition of compounds. Chemical equations provide information about the qualit ...
... forensics to art. The language of chemistry includes its own vocabulary as well as its own form of shorthand. Chemical symbols are used to represent atoms and elements. Chemical formulas depict molecules as well as the composition of compounds. Chemical equations provide information about the qualit ...
Atomic Theory - Wappingers Central School District
... - hydrogen had to come from nitrogen - suggested hydrogen nucleus was a particle & named it the proton ...
... - hydrogen had to come from nitrogen - suggested hydrogen nucleus was a particle & named it the proton ...
File
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
... atomic emission spectra; Bohr model of the hydrogen atom including explanation of H line spectrum and orbits, electron cloud and the probability model, wave/particle duality of electrons revisited, relate electron configurations of atoms to the Bohr and electron cloud models, describe the concepts o ...
Essential Question: What type of model did Thompson ,Rutherford
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
ionic bond. - cloudfront.net
... • Metals- conduct heat, have low ionization energy • Low EN; give up electrons easily. • Metals have luster (shine), are malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...
... • Metals- conduct heat, have low ionization energy • Low EN; give up electrons easily. • Metals have luster (shine), are malleable (can be hammered into sheets) and are ductile (drawn into wires). ...