atom
... the electrons in energy levels (the “solar system” model). • Bohr was one of the founders of quantum physics – a discipline that states that energy can be given off in small packets or quanta of specific size. • Energy levels closer to the nucleus were lower in energy than those farther away. • When ...
... the electrons in energy levels (the “solar system” model). • Bohr was one of the founders of quantum physics – a discipline that states that energy can be given off in small packets or quanta of specific size. • Energy levels closer to the nucleus were lower in energy than those farther away. • When ...
ppt
... In row 6, a new type of orbital, 4f, appears in between elements 57 and 72. All the elements with 4f electrons have very similar chemical properties. They are known as the Lanthanides (after element Z=57, Lanthanum) or rare earths. A similar pattern repeats in row 7, with the 5f orbitals filling bet ...
... In row 6, a new type of orbital, 4f, appears in between elements 57 and 72. All the elements with 4f electrons have very similar chemical properties. They are known as the Lanthanides (after element Z=57, Lanthanum) or rare earths. A similar pattern repeats in row 7, with the 5f orbitals filling bet ...
Protons Neutrons Electrons
... 10. Which of the atoms on the list must have received electrons from another atom? C, D and F. These atoms have more electrons than protons. Since the atom originally carried no charge, the only way they acquire extra electrons is by a transfer from another atom(s). Notice that each of these atoms a ...
... 10. Which of the atoms on the list must have received electrons from another atom? C, D and F. These atoms have more electrons than protons. Since the atom originally carried no charge, the only way they acquire extra electrons is by a transfer from another atom(s). Notice that each of these atoms a ...
Materials Required
... Gaining Attention: The term Sub-atomic particles will be written on the board as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy ...
... Gaining Attention: The term Sub-atomic particles will be written on the board as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy ...
chemistry important question i
... The thermal decomposition of HCOOH is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 × 10–3 s–1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three-fourths of initial quantity of HCOOH to decompose. (log 0.25 = – 0.6021) 3MARK Copper crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell ...
... The thermal decomposition of HCOOH is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 × 10–3 s–1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three-fourths of initial quantity of HCOOH to decompose. (log 0.25 = – 0.6021) 3MARK Copper crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell ...
Matter -White packet 16-17 (PDF - 1.63 MB)
... made of small molecules called amino acids that connect together like beads on a necklace (Figure below and Figure below). There are only 20 common amino acids needed to build proteins. These amino acids form in thousands of different combinations, making 100,000 or more unique proteins in humans. P ...
... made of small molecules called amino acids that connect together like beads on a necklace (Figure below and Figure below). There are only 20 common amino acids needed to build proteins. These amino acids form in thousands of different combinations, making 100,000 or more unique proteins in humans. P ...
Name ……………………………..………...… …….. Index No
... b) Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements. Element K L M N P ...
... b) Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements. Element K L M N P ...
Chapter2
... With small a, FC gets large, then a ideally be equal to zero? Oppositely charged ions gets closer, leads to increase in FC, but it is counteracted by an opposing repulsive force FR due to - overlapping of the similarly charged electric fields from each ions - the attempt to bring the two positively ...
... With small a, FC gets large, then a ideally be equal to zero? Oppositely charged ions gets closer, leads to increase in FC, but it is counteracted by an opposing repulsive force FR due to - overlapping of the similarly charged electric fields from each ions - the attempt to bring the two positively ...
Chapter1 - WilsonChemWiki
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. In the neutral atom the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Mass number: the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Atomic symbols for is ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. In the neutral atom the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Mass number: the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Atomic symbols for is ...
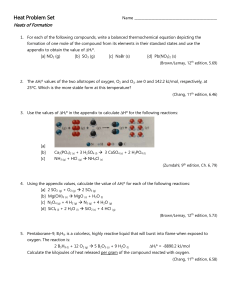
Heats of Formation WS
... Heats of Formation 1. For each of the following compounds, write a balanced thermochemical equation depicting the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states and use the appendix to obtain the value of ∆Hfº. [a] NO2 (g) ...
... Heats of Formation 1. For each of the following compounds, write a balanced thermochemical equation depicting the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states and use the appendix to obtain the value of ∆Hfº. [a] NO2 (g) ...
odd - WWW2
... hydrocarbons have very low boiling points, while the hydrogen-bonding hydrides of nitrogen have much higher boiling points. Following from this, they have different acid-base properties, both hydrides of carbon being neutral while those of nitrogen are basic: NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) N2H4 ...
... hydrocarbons have very low boiling points, while the hydrogen-bonding hydrides of nitrogen have much higher boiling points. Following from this, they have different acid-base properties, both hydrides of carbon being neutral while those of nitrogen are basic: NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) N2H4 ...
Build an Atom
... Protons have a relative mass of ___________ amu and a charge of ___________. Neutrons have a relative mass of ___________ amu and a charge of ___________. Electrons have a relative mass of nearly___________ amu and a charge of ___________. ...
... Protons have a relative mass of ___________ amu and a charge of ___________. Neutrons have a relative mass of ___________ amu and a charge of ___________. Electrons have a relative mass of nearly___________ amu and a charge of ___________. ...
KEY - Unit 3 Practice Qs
... b. Describe, in terms of subatomic particles found in the nucleus, one difference between the nuclei of carbon-12 atoms and the nuclei of carbon-13 atoms. The response must include both isotopes. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12. 13. The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass unit ...
... b. Describe, in terms of subatomic particles found in the nucleus, one difference between the nuclei of carbon-12 atoms and the nuclei of carbon-13 atoms. The response must include both isotopes. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12. 13. The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass unit ...
Inside the Atom
... 10 000 particles when straight through. However, the ones that did not go straight through were deflected at many different angles. A few even bounced straight back! Rutherford described the result as “firing a 15 inch shell at a piece of tissue paper, expecting it to go straight through, and having ...
... 10 000 particles when straight through. However, the ones that did not go straight through were deflected at many different angles. A few even bounced straight back! Rutherford described the result as “firing a 15 inch shell at a piece of tissue paper, expecting it to go straight through, and having ...
Chemistry exam review
... 1.3.1 Classify the components of a periodic table (period, group, metal, metalloid, nonmetal, transition). 1. The compound formed between element X and oxygen has the chemical formula X2O. Which element would X most likely ...
... 1.3.1 Classify the components of a periodic table (period, group, metal, metalloid, nonmetal, transition). 1. The compound formed between element X and oxygen has the chemical formula X2O. Which element would X most likely ...
3 molecules
... • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
... • Metals - lose # electrons = group number e.g. Ca Ca2+ + 2e- (Ar outer shell) • Nonmetals - gain electrons = 8 - group # e.g. N + 3e N3- (Ne outer shell) ...
chapter42
... The basic ideas about atomic structure must be well understood before we attempt to deal with the complexities of molecular structures and the electronic structure of solids The full mathematical solution of the Schrödinger equation applied to the hydrogen atom gives a complete and beautiful descrip ...
... The basic ideas about atomic structure must be well understood before we attempt to deal with the complexities of molecular structures and the electronic structure of solids The full mathematical solution of the Schrödinger equation applied to the hydrogen atom gives a complete and beautiful descrip ...
Atomic Models and the Development of the Atom
... What Millikan did was to put a charge on a tiny drop of oil, and measure how strong an applied electric field had to be in order to stop the oil drop from falling. Since he was able to work out the mass of the oil drop, and he could calculate the force of gravity on one drop, he could then determine ...
... What Millikan did was to put a charge on a tiny drop of oil, and measure how strong an applied electric field had to be in order to stop the oil drop from falling. Since he was able to work out the mass of the oil drop, and he could calculate the force of gravity on one drop, he could then determine ...
Original
... This is defined as half the distance between two identical nuclei. The metallic radius half the distance between two metal atoms, and the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms in a diatomic molecule. As we move down a group, atomic radius increases. This is because more “levels” are ...
... This is defined as half the distance between two identical nuclei. The metallic radius half the distance between two metal atoms, and the covalent radius is half the distance between two atoms in a diatomic molecule. As we move down a group, atomic radius increases. This is because more “levels” are ...
Chemistry exam review
... 1.3.1 Classify the components of a periodic table (period, group, metal, metalloid, nonmetal, transition). 1. The compound formed between element X and oxygen has the chemical formula X 2O. Which element would X most likely ...
... 1.3.1 Classify the components of a periodic table (period, group, metal, metalloid, nonmetal, transition). 1. The compound formed between element X and oxygen has the chemical formula X 2O. Which element would X most likely ...