Periodic Table of Elements II
... multiple electrons, those electrons are added to the next lowest sublevel: 2s, 2p, 3s, and so on. The Aufbau principle states that an electron occupies orbitals in order from lowest energy to highest. The Aufbau (German: “building up, construction”) principle is sometimes referred to as the “buildin ...
... multiple electrons, those electrons are added to the next lowest sublevel: 2s, 2p, 3s, and so on. The Aufbau principle states that an electron occupies orbitals in order from lowest energy to highest. The Aufbau (German: “building up, construction”) principle is sometimes referred to as the “buildin ...
atom
... • An atom is a building block of matter. An element is matter made of only one type of atom. A compound is a substance that contains two or more elements. • A heterogeneous mixture is not a solution because the substances that make up a heterogeneous mixture are not evenly mixed. The substances that ...
... • An atom is a building block of matter. An element is matter made of only one type of atom. A compound is a substance that contains two or more elements. • A heterogeneous mixture is not a solution because the substances that make up a heterogeneous mixture are not evenly mixed. The substances that ...
Chemical Reaction and Matter Review
... Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because this will change the formulas. Classify Chemical Reactions Chemists have identified millions of d ...
... Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. Balance chemical formulas by placing coefficients in front of them. Do not add subscripts, because this will change the formulas. Classify Chemical Reactions Chemists have identified millions of d ...
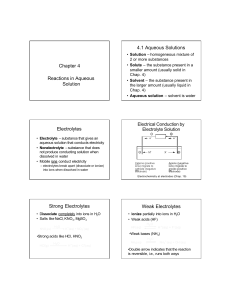
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
AP Thermo I Notes
... First Law of Thermodynamics section 5.2 Energy(E) is neither created nor destroyed. The internal energy of a system is the sum of ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics section 5.2 Energy(E) is neither created nor destroyed. The internal energy of a system is the sum of ...
New AQA C3 revison guide
... c) He was able use the table to successfully predict the properties of some elements which had not yet been discovered. Later when more elements had been discovered and chemists realized that the elements should be in order of atomic number rather than atomic mass, Mendeleev’s Table was shown to be ...
... c) He was able use the table to successfully predict the properties of some elements which had not yet been discovered. Later when more elements had been discovered and chemists realized that the elements should be in order of atomic number rather than atomic mass, Mendeleev’s Table was shown to be ...
Etymology of Atom - New Academic Science
... Rutherford’s model: The results from Rutherford’s experiment (see page 13) were astounding. The vast majority of alpha particles behaved as expected, and hardly scattered at all. But there were alpha particles that scattered through angles greater than 90 degrees, incredible in the light of expectat ...
... Rutherford’s model: The results from Rutherford’s experiment (see page 13) were astounding. The vast majority of alpha particles behaved as expected, and hardly scattered at all. But there were alpha particles that scattered through angles greater than 90 degrees, incredible in the light of expectat ...
Thermodynamics Enthalpy Entropy and Free Energy Student
... § Increases in internal energy may result in a § temperature increase § chemical reaction starting § phase change § Decreases in internal energy may result in a § a decrease in temperature § phase change § Note: even though the change in internal energy can assume several different forms, th ...
... § Increases in internal energy may result in a § temperature increase § chemical reaction starting § phase change § Decreases in internal energy may result in a § a decrease in temperature § phase change § Note: even though the change in internal energy can assume several different forms, th ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... – A common reaction: active metal replaces (displaces) a metal ion from a solution Mg(s) + CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + MgCl2(aq) ...
... – A common reaction: active metal replaces (displaces) a metal ion from a solution Mg(s) + CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + MgCl2(aq) ...
Balanced Chemical Equation
... For ionic compounds, it’s convenient to assign oxidation numbers for the cation and anion separately. According to guideline 2, the oxidation number for sodium is +1. Assuming the usual oxidation number for oxygen (−2 per guideline 3), the oxidation number for sulfur (x) is calculated as directed by ...
... For ionic compounds, it’s convenient to assign oxidation numbers for the cation and anion separately. According to guideline 2, the oxidation number for sodium is +1. Assuming the usual oxidation number for oxygen (−2 per guideline 3), the oxidation number for sulfur (x) is calculated as directed by ...
Lecture - 1
... highly energetic compared to chemical reactions. For example, fission of an atom of Uranium-235 releases about 210 MeV of energy, while energy released due to the formation of one molecule of CO2 from the combustion of carbon is about 4.08 eV. The types of nuclear reactions that are of importance in ...
... highly energetic compared to chemical reactions. For example, fission of an atom of Uranium-235 releases about 210 MeV of energy, while energy released due to the formation of one molecule of CO2 from the combustion of carbon is about 4.08 eV. The types of nuclear reactions that are of importance in ...
physics webquest - Walden University ePortfolio for Mike Dillon
... protons, neutrons, and electrons. The following websites might help you in the process. ...
... protons, neutrons, and electrons. The following websites might help you in the process. ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
Pennium (gr. 9-12)
... foundational understanding of chemistry. The number of protons is given in the periodic table (which is the atomic number). The number of electrons can be figured out by subtracting the charge of the given element by the number of protons. An example is P3-: by looking on the periodic table of eleme ...
... foundational understanding of chemistry. The number of protons is given in the periodic table (which is the atomic number). The number of electrons can be figured out by subtracting the charge of the given element by the number of protons. An example is P3-: by looking on the periodic table of eleme ...
Atomic Structure Practice Test
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
... REF: 1 OBJ: 3 STA: SC.B.1.4.2 26. ANS: The atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and also equals the number of electrons in the neutral atom. The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons and can be used, with the atomic number, to find the number of ...
Chapters 1-3 Packet
... malleable, solids at room temperature (except Hg) Nonmetals - elements found on the right side of the staircase, gases, liquid, & solid; usually poor conductors and are brittle Metalloids - elements that lie along staircase which have properties of both metals and nonmetals (except Al, which is usua ...
... malleable, solids at room temperature (except Hg) Nonmetals - elements found on the right side of the staircase, gases, liquid, & solid; usually poor conductors and are brittle Metalloids - elements that lie along staircase which have properties of both metals and nonmetals (except Al, which is usua ...
Chapter 0 - Bakersfield College
... Atomic Notation Atomic number (Z) Number of protons that atom has in nucleus Unique to each type of element Element is substance whose atoms all contain identical number of protons ...
... Atomic Notation Atomic number (Z) Number of protons that atom has in nucleus Unique to each type of element Element is substance whose atoms all contain identical number of protons ...
Entropy and reaction spontaneity Gibbs free energy
... The standard free energy of formation, ∆G0f , of a compound is the standard reaction free energy per mole for its synthesis from elements in their most stable forms. Standard free energies of elements in their most stable forms are equal to zero at 298K. Physical Chemistry EPM/04 ...
... The standard free energy of formation, ∆G0f , of a compound is the standard reaction free energy per mole for its synthesis from elements in their most stable forms. Standard free energies of elements in their most stable forms are equal to zero at 298K. Physical Chemistry EPM/04 ...
Introduction to Chemistry and the Metric System
... The Periodic Table Good things to know: Pre-periodic table patterns: Newland’s Law of Octaves, Dobereiner’s Triads Mendeleev’s Periodic table (based on atomic mass), holes in his table Moseley, atomic number, protons, Modern Periodic Law basic characteristics and names of the major groups ...
... The Periodic Table Good things to know: Pre-periodic table patterns: Newland’s Law of Octaves, Dobereiner’s Triads Mendeleev’s Periodic table (based on atomic mass), holes in his table Moseley, atomic number, protons, Modern Periodic Law basic characteristics and names of the major groups ...
A millennial overview of transition metal chemistry
... of cobalt(), as shown in Fig. 2. (3) A great many transition element compounds have one or more unpaired electrons and therefore have interesting and often useful magnetic properties.2 These magnetic properties range from simple Curie paramagnetism to those associated with high-temperature superco ...
... of cobalt(), as shown in Fig. 2. (3) A great many transition element compounds have one or more unpaired electrons and therefore have interesting and often useful magnetic properties.2 These magnetic properties range from simple Curie paramagnetism to those associated with high-temperature superco ...
Early Ideas About Matter
... servation of mass states that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. Dalton’s atomic theory easily explains that the con servation of mass in chemical reactions is the result of the separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms—atoms that are not created, destroyed or di ...
... servation of mass states that mass is conserved in any process, such as a chemical reaction. Dalton’s atomic theory easily explains that the con servation of mass in chemical reactions is the result of the separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms—atoms that are not created, destroyed or di ...