Other Mandibular Osteotomies
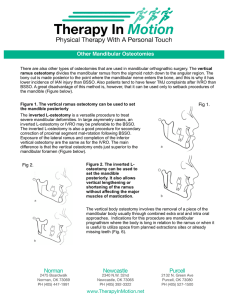
... Other Mandibular Osteotomies There are also other types of osteotomies that are used in mandibular orthognathic surgery. The vertical ramus osteotomy divides the mandibular ramus from the sigmoid notch down to the angular region. The bony cut is made posterior to the point where the mandibular nerve ...
... Other Mandibular Osteotomies There are also other types of osteotomies that are used in mandibular orthognathic surgery. The vertical ramus osteotomy divides the mandibular ramus from the sigmoid notch down to the angular region. The bony cut is made posterior to the point where the mandibular nerve ...
Study Guide Study Guide- Upper Limb
... De Quervain’s disease (Constrictive tenosynovitis), tendonitis of the abductor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis where they pass through the first compartment Distal Radial FractureFracture trying to break fall by putting hand down Dupuytren’s contracture - palmar aponeurosis contracture pu ...
... De Quervain’s disease (Constrictive tenosynovitis), tendonitis of the abductor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis where they pass through the first compartment Distal Radial FractureFracture trying to break fall by putting hand down Dupuytren’s contracture - palmar aponeurosis contracture pu ...
Fall 231 2013 Supplemental package
... want to review what the study focus is for that day’s lab. This is important because you will be liable (tested) for the information listed in your study guide and manual. There are lists of terms that you are required to know, as well as tables and diagrams. These are testable as well. If there are ...
... want to review what the study focus is for that day’s lab. This is important because you will be liable (tested) for the information listed in your study guide and manual. There are lists of terms that you are required to know, as well as tables and diagrams. These are testable as well. If there are ...
33-the walls & joint..
... Laterally : iliac fossae and iliacus muscles. Anteriorly : lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. ...
... Laterally : iliac fossae and iliacus muscles. Anteriorly : lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. ...
Articulations •Bones can only move at their ends. Where one bone
... Articulations •Bones can only move at their ends. Where one bone meets another is known as a joint, or articulation. Each joint motion is dependent on its structure, and •Each all joints are a compromise btn. strength & mobility. ...
... Articulations •Bones can only move at their ends. Where one bone meets another is known as a joint, or articulation. Each joint motion is dependent on its structure, and •Each all joints are a compromise btn. strength & mobility. ...
Foot and Ankle - Doral Academy High School
... • Medial arch is higher than the lateral longitudinal arch. It is made up by ...
... • Medial arch is higher than the lateral longitudinal arch. It is made up by ...
The Vertebral Column
... • C1 the atlas, has no body and no spinous process, it is a ring of bone consisting of anterior and posterior arches and a lateral mass on each side. It carries the skull and the superior articular facets receive the occipital condyles allowing you to nod • C2 the axis, has a body, spine, and other ...
... • C1 the atlas, has no body and no spinous process, it is a ring of bone consisting of anterior and posterior arches and a lateral mass on each side. It carries the skull and the superior articular facets receive the occipital condyles allowing you to nod • C2 the axis, has a body, spine, and other ...
ANATOMY TEAM Lecture (6) Pelvis and Sacrum
... False pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim and enclosed by the Fossae of the iliac bones And it Forms the inferior region of the abdominal cavity. In infants and young children, the urinary bladder is in the abdomen even when empty True pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim and Encloses t ...
... False pelvis lies superior to the pelvic brim and enclosed by the Fossae of the iliac bones And it Forms the inferior region of the abdominal cavity. In infants and young children, the urinary bladder is in the abdomen even when empty True pelvis lies inferior to the pelvic brim and Encloses t ...
chapter 9.powerpoint
... and distal radioulnar joints in which the palm is turned anteriorly or superiorly. • Pronation is a movement of the forearm at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints in which the distal end of the radius crosses over the distal end of the ulna and the palm is turned posteriorly or inferiorly. • O ...
... and distal radioulnar joints in which the palm is turned anteriorly or superiorly. • Pronation is a movement of the forearm at the proximal and distal radioulnar joints in which the distal end of the radius crosses over the distal end of the ulna and the palm is turned posteriorly or inferiorly. • O ...
CHAPTER 9 “Joints and Articulations”
... 10. inversion –- sole of the foot faces or turns medially 11. eversion –- sole of the foot turn laterally 12. protraction –-juttting out of the jaw 13. retraction –- moving the jaw backward 14. elevation –- lifting the limb or body superiorly 15. depression –- moving the body part inferiorly 16. opp ...
... 10. inversion –- sole of the foot faces or turns medially 11. eversion –- sole of the foot turn laterally 12. protraction –-juttting out of the jaw 13. retraction –- moving the jaw backward 14. elevation –- lifting the limb or body superiorly 15. depression –- moving the body part inferiorly 16. opp ...
Development of the Face
... Formation of the palate By the eighth week, the lateral palatine processes fuse with each other as well as with the primary palate and nasal septum. These fusions complete the formation of the ceiling of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavity. The nasal septum separates the right and lef ...
... Formation of the palate By the eighth week, the lateral palatine processes fuse with each other as well as with the primary palate and nasal septum. These fusions complete the formation of the ceiling of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavity. The nasal septum separates the right and lef ...
Neuroanatomy
... http://www.neuroguide.com/neuroimg_1.html#human_neuroanatomy – couldn’t get this one to work at time of writing this – but it looks interesting! ...
... http://www.neuroguide.com/neuroimg_1.html#human_neuroanatomy – couldn’t get this one to work at time of writing this – but it looks interesting! ...
A Case Report - International Journal of Health Sciences and
... Background: Orbital - facial manifestations are relatively rare in neurofibromatosis 1. Encephalocoeles are defined as herniation of meninges with brain matter. Absence of sphenoidal wing leads to Spheno orbital encephalocoele due to protrusion of brain tissue and meninges through superior orbital f ...
... Background: Orbital - facial manifestations are relatively rare in neurofibromatosis 1. Encephalocoeles are defined as herniation of meninges with brain matter. Absence of sphenoidal wing leads to Spheno orbital encephalocoele due to protrusion of brain tissue and meninges through superior orbital f ...
Chapter 9: Articulations
... ♣ An amphiarthrosis is more moveable than a synarthrosis, and stronger than a freely movable joint. ♣ The 2 major types of amphiarthrotic joints are: 1. syndesmosis: bones connected by ligaments 2. symphysis: bones separated by fibrocartilage Diarthroses (Moveable Joints), p. 260 ♣ Diarthroses (syno ...
... ♣ An amphiarthrosis is more moveable than a synarthrosis, and stronger than a freely movable joint. ♣ The 2 major types of amphiarthrotic joints are: 1. syndesmosis: bones connected by ligaments 2. symphysis: bones separated by fibrocartilage Diarthroses (Moveable Joints), p. 260 ♣ Diarthroses (syno ...
YANGCHUANOSAURUS HEPINGENSIS
... quadratojugal. The posterior process is short. The surface of the squamosal is rough, with a small transverse ridge near the base. Quadratojugal. L-shaped, with a smooth surface. The posteromedial edge is fused to the lateral side of the quadrate. The dorsal process is long and slender, with its dor ...
... quadratojugal. The posterior process is short. The surface of the squamosal is rough, with a small transverse ridge near the base. Quadratojugal. L-shaped, with a smooth surface. The posteromedial edge is fused to the lateral side of the quadrate. The dorsal process is long and slender, with its dor ...
Hammer and gouge mastoidectomy for cholesteatoma - Vula
... Surgery may be performed under local or general anaesthesia. General anaesthesia: Avoid muscle paralysis to facilitate detection of facial nerve irritation or injury. Local anaesthesia: With six wheals forming a semicircle, the posterior portion of the auricle and the mastoid region are surrounded b ...
... Surgery may be performed under local or general anaesthesia. General anaesthesia: Avoid muscle paralysis to facilitate detection of facial nerve irritation or injury. Local anaesthesia: With six wheals forming a semicircle, the posterior portion of the auricle and the mastoid region are surrounded b ...
Vol
... quadratojugal. The posterior process is short. The surface of the squamosal is rough, with a small transverse ridge near the base. Quadratojugal. L-shaped, with a smooth surface. The posteromedial edge is fused to the lateral side of the quadrate. The dorsal process is long and slender, with its dor ...
... quadratojugal. The posterior process is short. The surface of the squamosal is rough, with a small transverse ridge near the base. Quadratojugal. L-shaped, with a smooth surface. The posteromedial edge is fused to the lateral side of the quadrate. The dorsal process is long and slender, with its dor ...
Cranio-orbitozygomatic Approach and Its Orbitopterional Modification
... the temporal bone, just anterior to the articular tubercle of the zygoma (Figure 2B). The process is divided obliquely, in an attempt for providing a more stable base for fixation. The fourth and final cut is the most difficult cut of the two-piece COZ approach, since it is often not possible to see ...
... the temporal bone, just anterior to the articular tubercle of the zygoma (Figure 2B). The process is divided obliquely, in an attempt for providing a more stable base for fixation. The fourth and final cut is the most difficult cut of the two-piece COZ approach, since it is often not possible to see ...
- Ameghiniana
... 100. Position of the boundary between the mastoid and paraoccipital processes: at the same level or above the external auditory meatus (0); beneath the external auditory meatus (1). (Ubilla et al,. 1999: character 15) 101. Shape of the squamosal process: straight (0); curved (1). (Ubilla et al., 199 ...
... 100. Position of the boundary between the mastoid and paraoccipital processes: at the same level or above the external auditory meatus (0); beneath the external auditory meatus (1). (Ubilla et al,. 1999: character 15) 101. Shape of the squamosal process: straight (0); curved (1). (Ubilla et al., 199 ...
Temporal Lobe
... left-handed individuals, the left hemisphere contains the language centers. These are left hemisphere dominant. Cerebral dominance becomes established during the first few years after birth. ...
... left-handed individuals, the left hemisphere contains the language centers. These are left hemisphere dominant. Cerebral dominance becomes established during the first few years after birth. ...
pharyngitis: to treat or not to treat
... 1- Tonsillar artery (from Facial Artery) 2- Ascending palatine artery (from Facial Artery) 3- Ascending pharyngeal Artery (from external carotid) 4- Descending palatine artery ( from Maxillary artery) 5- Dorsalis lingulae artery (from Lingual artery) ...
... 1- Tonsillar artery (from Facial Artery) 2- Ascending palatine artery (from Facial Artery) 3- Ascending pharyngeal Artery (from external carotid) 4- Descending palatine artery ( from Maxillary artery) 5- Dorsalis lingulae artery (from Lingual artery) ...
The Nervous System Introduction The Meninges The Meninges The
... 2 CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3 CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4 CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. Figure 12.26a ...
... 2 CSF flows through the ventricles and into the subarachnoid space via the median and lateral apertures. Some CSF flows through the central canal of the spinal cord. 3 CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4 CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the arachnoid villi. Figure 12.26a ...
Skull

This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)The skull is a bony structure in the head of most vertebrates (in particular, craniates) that supports the structures of the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of encephalization, housing the brain, many sensory structures (eyes, ears, nasal cavity), and the feeding system. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to help the brain use auditory cues to judge direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, the skull also has a defensive function (e.g. horned ungulates); the frontal bone is where horns are mounted. The English word ""skull"" is probably derived from Old Norse ""skalli"" meaning bald, while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion).The skull is made of a number of fused flat bones.























